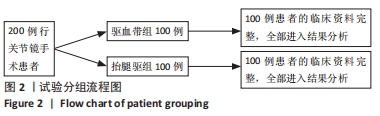
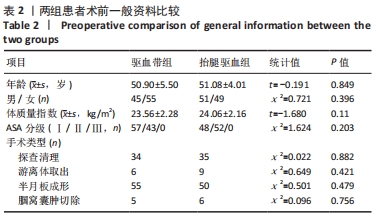
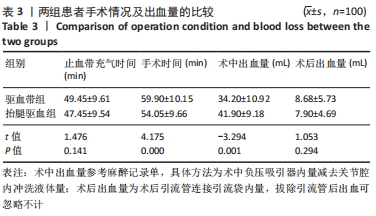
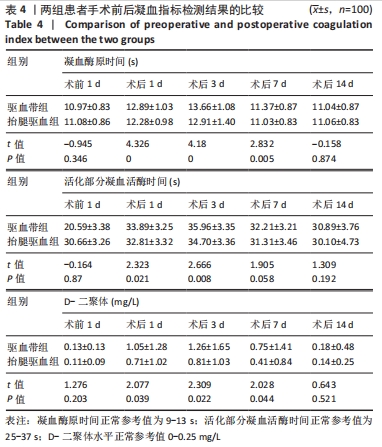
[1] 陈成帷,潘哲尔,周也立,等.常规止血带下膝关节镜手术后早期深静脉血栓的发生率及危险因素分析[J].中国骨伤,2018,31(9): 829-834.
[2] SHIRVANIAN S, TAPSON VF. Venous thromboembolism: identifying patients at risk and establishing prophylaxis. Curr Med Res Opin. 2015; 31(12):2297-2311.
[3] MINAKAWA M, FUKUDA I, MIYATA H, et al. Outcomes of Pulmonary Embolectomy for Acute Pulmonary Embolism. Circ J. 2018;82(8):2184-2190.
[4] DAVISON S P, HAYES KD. Commentary on: Analysis of the American Society of Anesthesiologists Physical Status Classification System and Caprini Risk Assessment Model in Predicting Venous Thromboembolic Outcomes in Plastic Surgery Patients. Aesthet Surg J. 2016;36(4):506-507.
[5] KRYCH AJ, SOUSA PL, MORGAN JA, et al. Incidence and Risk Factor Analysis of Symptomatic Venous Thromboembolism After Knee Arthroscopy. Arthroscopy. 2015;31(11):2112-2118.
[6] SUN Y, CHEN D, XU Z, et al. Incidence of Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Venous Thromboembolism After Elective Knee Arthroscopic Surgery: A Retrospective Study With Routinely Applied Venography. Arthroscopy. 2014;30(7):818-822.
[7] SARFANI S, CANTWELL S, SHIN A, et al. Challenging the Dogma of Tourniquet Pressure Requirements for Upper Extremity Surgery. J Wrist Surg. 2016;5(2):120-123.
[8] SCHNETTLER T, PAPILLON N, REES H. Use of a Tourniquet in Total Knee Arthroplasty Causes a Paradoxical Increase in Total Blood Loss. J Bone Joint Surg. 2017;99(16):1331-1336.
[9] RODRIGUEZ-COLLAZO ER, URSO ML. Combined use of the Ilizarov method, concentrated bone marrow aspirate (cBMA), and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) to expedite healing of bimalleolar fractures. Str Trauma Limb Rec. 2015;10(3):161-166.
[10] MAEDA MPH, IWASE PH, KANDA MPA, et al. A study of the blood flow restriction pressure of a tourniquet system to facilitate development of a system that can prevent musculoskeletal complications. Am J Disaster Med. 2017;12(3):139-145.
[11] 李嫚,李东红,徐宗慧.3种驱血方法在骨科上肢手术应用的对比研究[J].护理研究,2014,28(1):67-68.
[12] 彭丽贞.不同驱血方法在骨科下肢手术中的应用研究[J].临床医学工程,2016,23(8):1123-1124.
[13] ZHANG M, LIU G, ZHAO Z, et al. Comparison of lower limb lifting and squeeze exsanguination before tourniquet inflation during total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019;20(1):35.
[14] SKOWRON M, KOCIUGA J, DOMZALSKI M. Electrostimulation has a positive effect on the knee function after knee arthroscopic surgery: A randomized trial. J Back Musculoskelet Reh. 2020;33(5):777.
[15] BOGUNOVIC L, HAAS AK, BROPHY RH, et al. The Perioperative Continuation of Aspirin in Patients Undergoing Arthroscopic Surgery of the Knee. Am J Sports Med. 2019;47(9):2138-2142.
[16] JUNG KH, YOUM YS, CHO SD, et al. Iatrogenic Medial Collateral Ligament Injury by Valgus Stress During Arthroscopic Surgery of the Knee. Arthroscopy. 2019;35(5):1520-1524.
[17] MANNION AF, BIANCHI G, MARIAUX F, et al. Can the Charlson Comorbidity Index be used to predict the ASA grade in patients undergoing spine surgery? Eur Spine J. 2020;29(12):2941-2952.
[18] SING DC, LUAN TF, FEELEY BT, et al. Is Obesity a Risk Factor for Adverse Events After Knee Arthroscopy? Arthroscopy. 2016;32(7):1346-1353.
[19] LIU PL, LI DQ, ZHANG YK, et al. Effects of Unilateral Tourniquet Used in Patients Undergoing Simultaneous Bilateral Total Knee Arthroplasty. Orthop Surg. 2017;9(2):180-185.
[20] HUANG G, TANG Y, WANG H, et al. Lower limb vein thrombosis-induced pulmonary embolism and paradoxical multiple arterial embolisms: A case report with a 10-year follow-up. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019; 98(30):e16522.
[21] JOHNSON AP, KOGANTI D, WALLACE A, et al. Asymptomatic Trauma Patients Screened for Venous Thromboembolism Have a Higher Risk Profile with Lower Rate of Pulmonary Embolism: A Five-Year Single-Institution Experience. Am Surg. 2020;86(2):104-109.
[22] CHOPARD R, ALBERTSEN IE, PIAZZA G. Diagnosis and Treatment of Lower Extremity Venous Thromboembolism: A Review. JAMA. 2020; 324(17):1765-1776.
[23] ZHAO Z, MA J, MA X. Comparative efficacy and safety of different hemostatic methods in total hip arthroplasty: a network meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):1-10.
[24] LALONE EA, GREWAL R, KING GJW, et al. A Structured Review Addressing the Use of Radiographic Measures of Alignment and the Definition of Acceptability in Patients with Distal Radius Fractures. Hand (N Y). 2015;10(4):621-638.
[25] COLLEONI JL, RIBEIRO FN, MOS P, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis after total knee arthroplasty (TKA): aspirin vs. rivaroxaban. Rev Bras Ortop. 2018;53(1):22-27.
[26] ZHAO X, ALI SJ, SANG X. Clinical Study on the Screening of Lower Extremity Deep Venous Thrombosis by D-Dimer Combined with RAPT Score Among Orthopedic Trauma Patients. Indian J Orthop. 2020; 54(S2):316-321.
[27] CHENG J, FU Z, ZHU J, et al. The predictive value of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, fibrinogen, and D-dimer for deep venous thrombosis following surgery for traumatic lower limb fracture. Ann Palliat Med. 2020;9(5):3385-3392.
[28] ABDULKARIM A, KRAUSE KE, SHEEHAN E. Pain and functional outcomes with tourniquet use in total knee arthroplasty. Irish J Med Sci. 2015; 184:S201.
[29] 曹青刚,包倪荣,赵建宁.止血带导致全膝关节置换术后肢体肿痛机制的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2019,32(4):428-431.
[30] GOCER H, YAZICI AK, POLAT AV. Should venous doppler ultrasonography be routinely applied before lower extremity major orthopedic surgery? Niger Med J. 2017;58(1):32-36.
[31] ZAN P, MOL MO, YAO JJ, et al. Release of the tourniquet immediately after the implantation of the components reduces the incidence of deep vein thrombosis after primary total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint Res. 2017;6(9):535-541.
[32] MORI N, KIMURA S, ONODERA T, et al. Use of a pneumatic tourniquet in total knee arthroplasty increases the risk of distal deep vein thrombosis: A prospective, randomized study. knee. 2016;23(5):887-889.
[33] ISHII Y, NOGUCHI H, SATO J, et al. Impact of anesthesia modality and mechanical venous thromboembolism prophylaxis on the incidence of symptomatic deep venous thrombosis after TKA. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018;9(2):142-145.
[34] 尹健东,王鑫灵,左彪,等.全膝关节置换过程中挤压驱血和抬腿驱血与置换后并发症的关系[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(9):1331-1336.
[35] WRIGHT AA, TAYLOR JB, FORD KR, et al. Risk factors associated with lower extremity stress fractures in runners: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 2015;49(23):1517-1523.
[36] ARSOY D, GIORI NJ, WOOLSON ST. Mobile Compression Reduces Bleeding-related Readmissions and Wound Complications After THA and TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2018;476(2):381-387.
[37] ISSA K, PIERCE T P, HARWIN SF, et al. No Decrease in Knee Survivorship or Outcomes Scores for Patients With HIV Infection Who Undergo TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(2):465-471.
[38] LIU Y, SI H, ZENG Y, et al. More pain and slower functional recovery when a tourniquet is used during total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2020;28(6):1842-1860.
[39] ALONSO-ALGARABEL M, ESTEBAN-SEBASTIÀ X, SANTILLÁN-GARCÍA A, et al. Tourniquet use in out-of-hospital emergency care: a systematic review. Emergencias. 2019;31(1):47-54.
|