| [1]van de Graaf VA, Noorduyn JCA, Willigenburg NW, et al. Effect of early surgery vs physical therapy on knee function among patients with nonobstructive meniscal tears the escape randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;320(13): 1328-1337.[2]Lin Z, Huang W, Ma L, et al. Kinematic features in patients with lateral discoid meniscus injury during walking. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1):5053.[3]Blake MH, Johnson DL. Knee meniscus injuries: common problems and solutions. Clin Sports Med. 2018;37(2): 293-306.[4]Järvinen TLN, Guyatt GH.Arthroscopic surgery for knee pain. Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(20):1502.[5]Sadlik B,Jaroslawski G,Puszkarz M,et al. Cartilage repair in the knee using umbilical cord Wharton' s Jelly-derived mesenchymal stem cells embedded onto collagen scaffolding and implanted under dry arthroscopy. Arthrosc Tech. 2017; 7(1):e57-e63.[6]McLean M, McCall K, Smith IDM, et al. Tranexamic acid toxicity in human periarticular tissues. Bone Joint Res. 2019; 8(1): 11–18.[7]Bai J, Zhang P, Liang X, et al. Association between dementia and mortality in the elderly patients undergoing hip fracture surgery: a meta-analysis. Orthop Surg Res. 2018; 13(1):298.[8]Georgiev GP, Tanchev PP, Zheleva Z, et al. Comparison of topical and intravenous administration of tranexamic acid for blood loss control during total joint replacement: Review of literature. J Orthop Trans. 2018;13:7-12.[9]Clavé A, Gérard R, Lacroix J,et al.A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on the efficacy of tranexamic acid combined with rivaroxaban thromboprophylaxis in reducing blood loss after primary cementless total hip arthroplasty.Bone Joint J. 2019;101-B:207-212.[10]Li ZJ, Zhao MW, Zeng L. Additional dose of intravenous tranexamic acid after primary total knee arthroplasty further reduces hidden blood loss. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018;131(6): 638-642.[11]Kim EJ, Yong OK, Shim KW, et al. Effects of Tranexamic Acid Based on its Population Pharmacokinetics in Pediatric Patients Undergoing Distraction Osteogenesis for Craniosynostosis: Rotational Thromboelastometry (ROTEMTM) Analysis. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(8):788-795.[12]Gulabi D, Yuce Y, Erkal KH, et al. The combined administration of systemic and topical tranexamic acid for total hip arthroplasty: Is it better than systemic?. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2019. DOI:10.1016/j.aott.2019.03.001.[13]Fillingham YA, Ramkumar DB, Jevsevar DS, et al. The efficacy of tranexamic acid in total hip arthroplasty: a network meta-analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(10):3083-3089.[14]Sun Q, Li J, Chen J,et al.Comparison of intravenous, topical or combined routes of tranexamic acid administration in patients undergoing total knee and hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open. 2019; 9(1):e024350.[15]Kuo FC, Lin PY, Wang JW,et al.Intravenous tranexamic acid use in revision total joint arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:3163-3170.[16]Han YH, Huang HT, Pan JK,et al.Is the combined application of both drain-clamping and tranexamic acid superior to the single use of either application in patients with total-knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018;97(36): e11573.[17]李明晋,陈小华,唐小莉,等.膝关节腔注射氨甲环酸对单纯半月板损伤患者关节肿胀?疼痛?关节功能恢复的影响[J].中国药房, 2018, 29(8):1098-1101.[18]李奎生.膝关节半月板损伤的影像学诊断研究[J].中国CT和MRI杂志, 2016,14(9):117-119.[19]Yaghmour KM, Al-Khateeb H.Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction without the use of a tourniquet. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2019;101(2):123-125.[20]Hasanain S, Apostu D, Alrefaee A, et al. Comparing the effect of tourniquet vs. tourniquet-less in simultaneous bilateral total knee replacements. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(7): S0883540318301426.[21]Meng Y, Li Z, Gong K, et al. Tranexamic acid reduces intraoperative occult blood loss and tourniquet time in obese knee osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a prospective cohort study. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14: 675-683.[22]Salzler MJ, Lin A, Miller CD, et al. Complications after arthroscopic knee surgery. Am J Sports Med. 2014;42(2): 292-296.[23]Uribe AA, Arbona FL, Flanigan DC, et al. Comparing the efficacy of iv ibuprofen and ketorolac in the management of postoperative pain following arthroscopic knee surgery. a randomized double-blind active comparator pilot study. Front Surg. 2018;5(59):00059-1-00059-10.[24]Valkering KP, Van Bergen CJ, Buijze GA, et al. Painexperience andfunctional outcome ofinpatient versus outpatient anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, an equivalence randomized controlled trial with 12 months follow-up. Knee. 2015;22:111-116.[25]Koizumi M, Ishimaru M, Matsui H, et al. Tranexamic acid and post-tonsillectomy hemorrhage: propensity score and instrumental variable analyses. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;276(1):249-254. [26]Junejo F, Akhtar MI, Hamid M, et al. Comparison between intravenous boluses versus infusion of tranexamic acid (txa) to reduce bleeding in paediatric cyanotic congenital heart disease (chd) surgeries. J Coll Phys Surg. 2018;28(3):180.[27]Xu S, Chen JY, Zheng Q,et al.The safest and most efficacious route of tranexamic acid administration in total joint arthroplasty: A systemic review and network meta-analysis. Thromb Res. 2019;11(176):61-66.[28]Wang D, Zhu H, Meng WK, et al. Comparison of oral versus intra-articular tranexamic acid in enhanced-recovery primary total knee arthroplasty without tourniquet application: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):85.[29]White TC, Eichinger JK, Friedman RJ. Minimizing blood loss and transfusions in total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2018;31(7):594-599.[30]Wu Q,Zhang HA,Liu SL,et al.Is TXA clinically effective and safe to prevent blood loss in total knee arthroplasty? A meta-analysis of 34 randomized controlled trials. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(3):525-541.[31]Adravanti P, Salvo ED, Calafiore G, et al. A prospective, randomized, comparative study of intravenous alone and combined intravenous and intraarticular administration of tranexamic acid in primary total knee replacement. Arthroplasty Today. 2018;4(1):85-88.[32]赵洪顺,阿尖措,高顺红,等.全髋关节置换局部应用氨甲环酸术中术后失血及白细胞介素6和C-反应蛋白的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(4):493-498.[33]李锐博,尹诗九,钟航,等.静脉联合关节腔内注射氨甲环酸后引流管夹闭时间对人工全膝关节置换术后失血量的影响及安全性评价[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2017, 31(4):417-421.[34]Karaaslan F, Karao?lu S, Yurdakul E. Reducing intra-articular hemarthrosis after arthroscopic anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction by the administration of intravenous tranexamic acid:a prospective, randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(11):2720-2726.[35]Laoruengthana A, Rattanaprichavej P, Rasamimongkol S, et al. Intra-articular tranexamic acid mitigates blood loss and morphine use after total knee arthroplasty. a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2019.DOI:10.1016/j.arth. 2019.01.030.[36]宝音,王嘎日迪,李晓东.氨甲环酸不同给药途径对膝关节置换失血量的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(12):1096-1101.[37]朱诗白,翟洁,蒋超,等.膝关节置换围手术期的快速康复措施[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(3):456-463.[38]Nishihara S, Hamada M. Does tranexamic acid alter the risk of thromboembolism after total hip arthroplasty in the absence of routine chemical thromboprophylaxis. Bone Joint J. 2015; 97(4):458-462.[39]Stasiowska MK, Ng SC, Gubbay AN,et al. Postoperative pain management.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2015;76(10):570-575. |
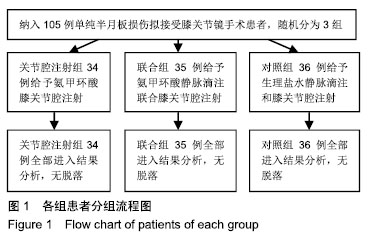
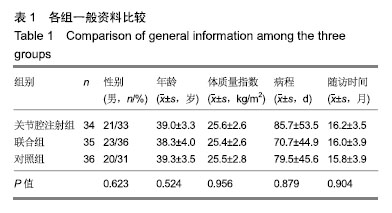
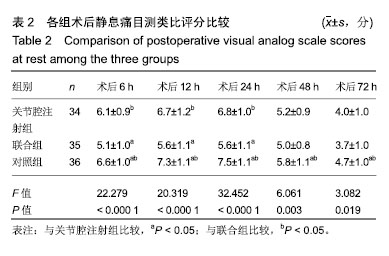
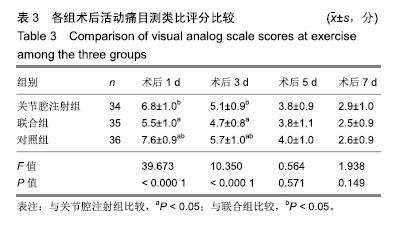
.jpg)
.jpg)
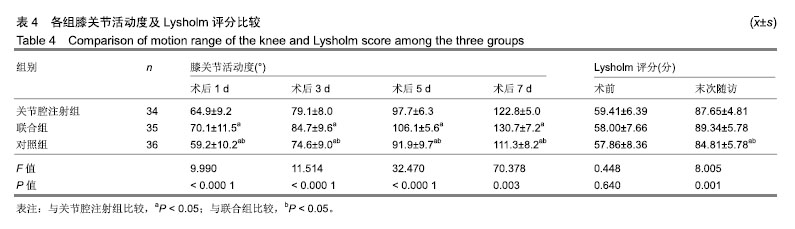
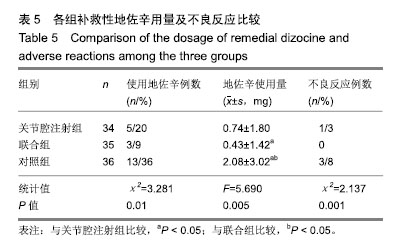
.jpg)