中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (33): 5324-5328.doi: 10.12307/2021.321
• 人工假体 artificial prosthesis • 上一篇 下一篇
D-二聚体、红细胞沉降率和C-反应蛋白在髋、膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成中的诊断价值
范鑫超1,鲍文娟2,张 凯2,孙喜龙2,黄 腾2,高 博2,翟金帅2,周逸彬3,邱长茂2,李文毅2,李西成2
- 1河北北方学院骨科,河北省张家口市 075000;2河北省人民医院骨科,河北省石家庄市 050000;3河北大学附属医院骨科,河北省保定市 071000
Diagnostic value of D-dimer, erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein in deep vein thrombosis of lower extremity after hip and knee arthroplasty
Fan Xinchao1, Bao Wenjuan2, Zhang Kai2, Sun Xilong2, Huang Teng2, Gao Bo2, Zhai Jinshuai2, Zhou Yibin3, Qiu Changmao2, Li Wenyi2, Li Xicheng2
- 1Department of Orthopedics, Hebei North University, Zhangjiakou 075000, Hebei Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Hebei Provincial People’s Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050000, Hebei Province, China; 3Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding 071000, Hebei Province, China
摘要:

文题释义:
单髁置换:指仅对膝关节病变一侧关节间室进行表面置换,用人工假体代替膝关节破损的软骨表面,一般多为内侧间室。
下肢深静脉血栓:是由于下肢深静脉的血液凝固形成血栓,阻塞血液回流,从而引起的一系列临床症状。
背景:下肢深静脉血栓形成是髋膝关节置换的后常见并发症,关于其影响因素介绍较多,但有关影响因素的阈值介绍较少。
目的:探讨D-二聚体、红细胞沉降率、C-反应蛋白对髋、膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的诊断价值。
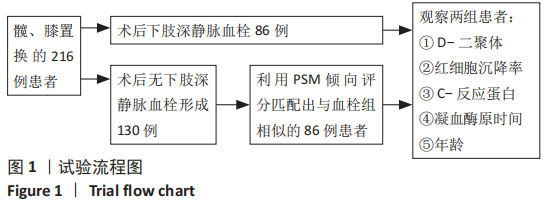
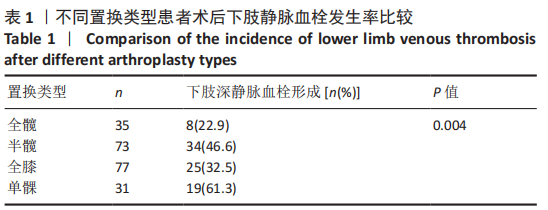
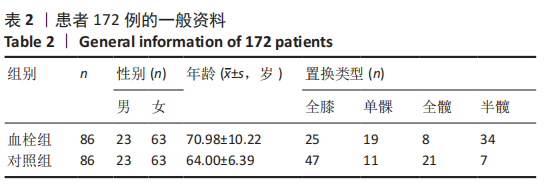
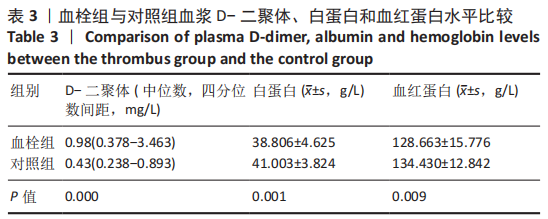
方法:回顾性分析2018年1月至2020年11月在河北省人民医院行髋、膝关节置换的216例患者的临床资料,包括全膝关节置换77例,单髁置换31例,全髋关节置换35例,半髋关节置换73例。术后第1天行双下肢深静脉彩超,并由2名以上主治医师确诊为下肢深静脉血栓形成。其中术后下肢深静脉血栓形成患者86例,术后无下肢深静脉血栓者130例,比较不同置换下肢深静脉血栓形成率差异。以年龄、性别及置换类型为标准利用PSM倾向评分配对方法从130例术后无下肢深静脉血栓患者中选取86例患者作为对照组,比较172例患者(血栓形成组和对照组各86例)血浆D-二聚体、白蛋白及血红蛋白水平,利用ROC曲线分析各指标诊断髋、膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的诊断效力。
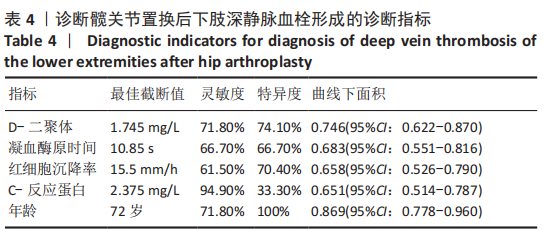
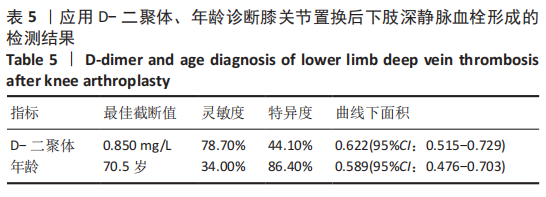
结果与结论:①患者172例中,与对照组相比,血栓组患者D-二聚体水平升高(P < 0.05);②诊断髋关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的D-二聚体灵敏度为71.8%、特异度为74.1%;凝血酶原时间灵敏度为66.7%、特异度为66.7%;红细胞沉降率灵敏度为61.5%、特异度为70.4%;C-反应蛋白水平灵敏度为94.9%、特异度为33.3%;年龄灵敏度为71.8%、特异度为100%;③诊断膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的D-二聚体灵敏度为78.7%、特异度为44.1%;④上述数据证实,对髋、膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成患者而言,D-二聚体水平均具有较好的诊断敏感度,相比之下D-二聚体水在诊断膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成时敏感度更高;而凝血酶原时间、红细胞沉降率、C-反应蛋白水平及年龄仅在诊断髋关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成时具有一定的灵敏度和特异度。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8795-1444 (范鑫超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: