[1] TANI I, NAKANO N, TAKAYAMA K, et al. Navigated total knee arthroplasty for owteoarthritis with extra-articular deformity. Acta Ortop Bras. 2018;26(3):170-174.
[2] MANNING WA, BLAIN A, LONCSTAFF L, et al. A load measuring device can achieve fine-tuning of mediolateral load at knee arthroplasty but May lead to a more lax knee state. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(7):2238-2250.
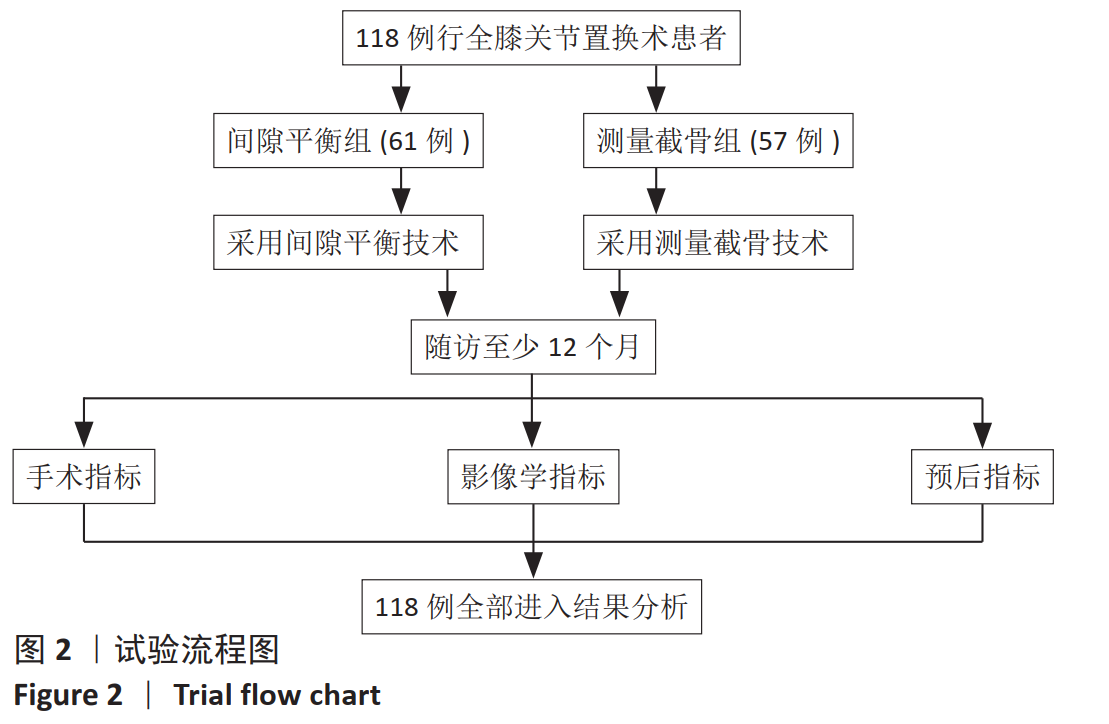
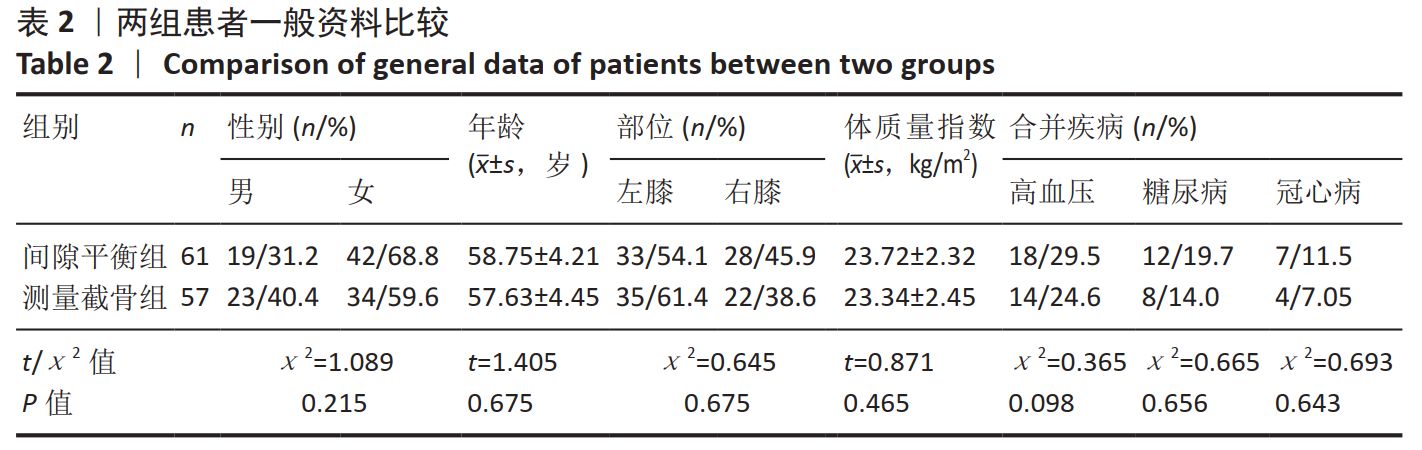
[3] 谢川江,邱洪九,李帅峰,等.计算机导航辅助下间隙平衡技术在全膝关节置换术中的应用价值[J].第三军医大学学报,2019,41(21):2120-2126.
[4] BROWN MJC, DEAKIN AH, PICARD F, et al. Lower lomb alignment becomes more varus and hypereztended form supine to bipedal stance in asymptomatic, osteoarthritic and prosthetic neutral ro varus knees. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019;27(5):1635-1641.
[5] AHN JH, LEE SH, KANG HW. Quantification of the Effect of Vertical Bone Resection of the Medial Proximal Tibia for Achieving Soft Tussue Balancing in Total Knee Arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Surg. 2016;8(1):49-56.
[6] 周天健,姜未,罗奇,等.间隙平衡、测量截骨用于全膝关节置换术中股骨外翻截骨的对照研究[J].中国医师杂志,2018,20(7):1065-1066.
[7] SPRINGER BD, PARRATTE S, ABDEL MP. Measured resection versur gap balancing for total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2014;472(7):2016-2022.
[8] 符得红,戴祝.全膝关节置换术中间隙平衡技术的应用进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2018,33(4):446-448.
[9] 徐亚伟,郭晓琳,孙聪,等.术前影像学测量对全膝关节置换术后HSS评分的影响[J].外科,2018,7(2):37-43.
[10] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组.骨关节炎诊疗指南(2018年版)[J].中华骨科杂志,2018,38(12):705-715.
[11] AICHER B, PEIL H, PEIL B, et al. Pain measurement: Visual Analogue Scale (VAS) and Verbal Rating Scale (VRS) in clinical trials with OTC analgesics in headache. Cephalgia. 2013;32(3):185-197.
[12] Noble PC, Suderi CR, Brekke AC, et al. Development of a New Knee Society Scoring System. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470(470):20-32.
[13] SSCHOENMAKERS DAL, FECZKO PZ, BOONEN B, et al. Measurement of lower limb alignment: there are within-person difference between weight-hearing and non-weight-bearing measurement modalities. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(11):3569-3575.
[14] 柴瑞宝,刘瑞,张子安.间隙平衡与测量截骨技术在全膝关节置换的比较[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2020,28(9):804-808.
[15] SHALHOUB S, MOSCHETTI WE, DABUZHSKY L, et al. Laxity Profiles in the Native and Replaced Knee-Application to Robotic-Assisted Gap-Balancing Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(9):3043-3048.
[16] 洪伟祥,冯建民,王毅,等.测量截骨与间隙平衡技术在全膝关节置换术中应用的中期随访比较[J].国际骨科杂志,2016,37(4):255-259.
[17] SHETH NP, HUSAIN A, NELSON CL. Surgical Techniques fot Total Knee Arthroplasty: Measured Resection, Gap Balancing, and Hybrid. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017; 25(7):499-508.
[18] TSUBOSAKA M, MURATSU H, TAKAYAMA K, et al. Comparison of Intraoperative Soft Tissue Balance Between Cruciate-Retaining and Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Arthroplasty Performed by a Newly Developed Medial Preserving Gap Technique. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(3):729-734.
[19] CHO KJ, SEON JK, JANG WY, et al. Objective quantification of ligament balancing using VERASENSE in measured resection and modified gap balance total knee arthroplasty. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):266.
[20] 范霖,杨东,刘凯缘,等.全膝关节置换术中间隙平衡截骨与测量截骨技术的对照研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2019,39(15):935-943.
[21] LEE JK, LEE S, CHUN SH, et al. Rotational allgnment of femoral compoonent with different methods in total knee arthroplasty: a ran-domized, controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Discord. 2017;18(1):217.
[22] CLEMENT ND, MAKARAM N, BELL J, et al. ColumbusR computer navigated total knee arthroplasty: Gap balancing versus measured resection. Knee. 2017;24(6): 1442-1447.
[23] 齐志远,陈秀民,王在斌,等.全膝关节置换术应用间隙平衡截骨的疗效评价[J].中华关节科杂志(电子版),2019,13(6):672-678.
[24] PANJWANI TR, MULIAJI A, DOSHI I, et al. Comparison of functional outcomes of computer-assisted vs conventional total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review and meta-analysis of high-quality, prospective studies. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(3): 586-593.
[25] HEESTERBEEK PJC, HAFFNER N, WYMENGA AB, et al. Patient-related factors influence stiffness of the soft tissuc complex during intraoperative gap balancing in cruciate-retaining total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arhtrosc. 2017;25(9):2760-2768.
[26] 李红,孙朝军,胡志富,等.全膝关节置换术行股骨远端髓外与髓内定位截骨的影像学评估[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2017,11(5):541-545.
[27] DYRHOVEEN GS, FENSTAD AM, FURNES O, et al. Survivorship and relative revision in computer-navigated versus conventional total knee replacement at 8-year follow-up. Acta Orthop. 2016;87(6):592-599.
[28] 贺强,卿忠,姚舒馨,等.全膝关节节置换术后下肢位置变化的影像学研究[J].实用骨科杂志,2016,22(3):212-215.
[29] 李红,孙朝军,胡志富,等.全膝关节置换术行股骨远端髓外与髓内定位截骨的影像学评估[J].中华关节外科杂志(电子版),2017,11(5):541-545.
[30] 陆斌,杨卧龙,高胜山,等.测量截骨联合间隙平衡技术在全膝关节置换股骨外旋截骨中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(15):2323-2328.
[31] BABAZADEH S, DOWSEY MM, VASIMALLA MG, et al. Gap balancing sacrifices joint-line maintenance to improve gap symmetry: 5-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(1):75-78.
[32] NAGAI K, MURATSU H, TAKEOKA Y, et al. The Influence of Joint Distraction Force on the Soft-Tissue Balance Using Modified Gap-Balancing Technique in Posterior-Stabilized Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(10):2995-2999.
[33] MOOD YW, KIM HJ, AHN HS, et al. Comparison of soft tissue balancing, femornal component rotatoin, and joint line change between the gap balancing and measured rescetoin techniquses in primary total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Balitmore). 2016;95(39):e5006. |