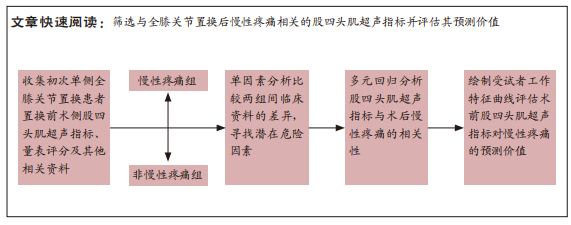
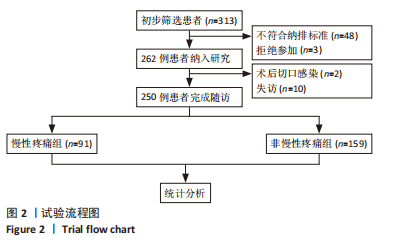
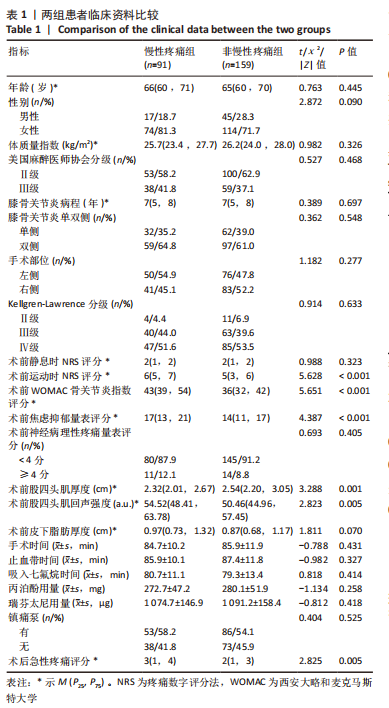
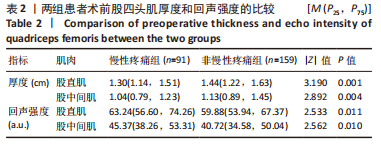
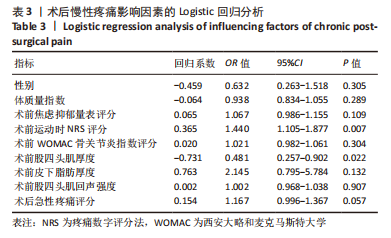
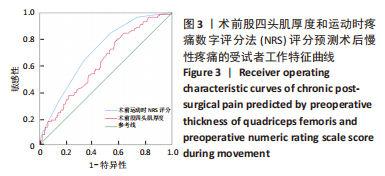
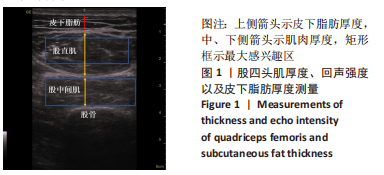
[1] SHARMA L. Osteoarthritis of the Knee. N Engl J Med. 2021;384(1):51-59.
[2] KATZ JN, ARANT KR, LOESER RF. Diagnosis and Treatment of Hip and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Review. JAMA. 2021;325(6):568-578.
[3] PRICE AJ, ALVAND A, TROELSEN A, et al. Knee replacement. Lancet. 2018;392(10158):1672-1682.
[4] GLARE P, AUBREY KR, MYLES PS. Transition from acute to chronic pain after surgery. Lancet. 2019;393(10180):1537-1546.
[5] LEWIS GN, RICE DA, MCNAIR PJ, et al. Predictors of persistent pain after total knee arthroplasty: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. 2015;114(4):551-561.
[6] THOMAZEAU J, ROUQUETTE A, MARTINEZ V, et al. Predictive Factors of Chronic Post-Surgical Pain at 6 Months Following Knee Replacement: Influence of Postoperative Pain Trajectory and Genetics. Pain Physician. 2016;19(5):E729-E741.
[7] KIM DH, PEARSON-CHAUHAN KM, MCCARTHY RJ, et al. Predictive Factors for Developing Chronic Pain After Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(11):3372-3378.
[8] GELLHORN AC, STUMPH JM, ZIKRY HE, et al. Ultrasound measures of muscle thickness may be superior to strength testing in adults with knee osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1):350.
[9] PERKISAS S, BAUDRY S, BAUER J, et al. Application of ultrasound for muscle assessment in sarcopenia: towards standardized measurements. Eur Geriatr Med. 2018;9(6):739-757.
[10] COPSEY B, THOMPSON JY, VADHER K, et al. Problems persist in reporting of methods and results for the WOMAC measure in hip and knee osteoarthritis trials. Qual Life Res. 2019;28(2):335-343.
[11] TANIGUCHI M, FUKUMOTO Y, YAGI M, et al. Enhanced echo intensity and a higher extracellular water-to-intracellular water ratio are helpful clinical signs for detecting muscle degeneration in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2021;40(10):4207-4215.
[12] VASILOPOULOS T, WARDHAN R, RASHIDI P, et al. Patient and Procedural Determinants of Postoperative Pain Trajectories. Anesthesiology. 2021;134(3):421-434.
[13] BUGADA D, ALLEGRI M, GEMMA M, et al. Effects of anaesthesia and analgesia on long-term outcome after total knee replacement: A prospective, observational, multicentre study. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2017;34(10):665-672.
[14] MAEDA H, IMADA K, ISHIDA K, et al. Quadriceps Thickness and Echo Intensity Predict Gait Independence in Individuals with Severe and Mild Hemiparetic Stroke. Eur Neurol. 2020;83(2):167-173.
[15] YOSHIKO A, BEPPU M, IZUMIDA R, et al. Long-term assessment of morphological, functional, and quantitative parameters of skeletal muscle in older patients after unilateral total hip arthroplasty. Exp Gerontol. 2020;137:110971.
[16] STOCK MS, THOMPSON BJ. Echo intensity as an indicator of skeletal muscle quality: applications, methodology, and future directions. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2021;121(2):369-380.
[17] NAGAE M, UMEGAKI H, YOSHIKO A, et al. Echo intensity is more useful in predicting hospital-associated complications than conventional sarcopenia-related parameters in acute hospitalized older patients. Exp Gerontol. 2021;150:111397.
[18] AKAZAWA N, KISHI M, HINO T, et al. Intramuscular adipose tissue in the quadriceps is more strongly related to recovery of activities of daily living than muscle mass in older inpatients. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2021;12(4):891-899.
[19] YOUNG HJ, JENKINS NT, ZHAO Q, et al. Measurement of intramuscular fat by muscle echo intensity. Muscle Nerve. 2015;52(6):963-971.
[20] LEWEK MD, RUDOLPH KS, SNYDER-MACKLER L. Quadriceps femoris muscle weakness and activation failure in patients with symptomatic knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2004;22(1):110-115.
[21] RICE DA, MCNAIR PJ. Quadriceps arthrogenic muscle inhibition: neural mechanisms and treatment perspectives. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2010;40(3):250-266.
[22] THOMAS AC, SOWERS M, KARVONEN-GUTIERREZ C, et al. Lack of quadriceps dysfunction in women with early knee osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(5):595-599.
[23] CALATAYUD J, CASAÑA J, EZZATVAR Y, et al. High-intensity preoperative training improves physical and functional recovery in the early post-operative periods after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017;25(9): 2864-2872.
[24] CHOPP-HURLEY JN, WIEBENGA EG, BULBROOK BD, et al. Evaluating the relationship between quadriceps muscle quality captured using ultrasound with clinical severity in women with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2020;80:105165.
[25] SABATINO A, REGOLISTI G, DI MARIO F, et al. Validation by CT scan of quadriceps muscle thickness measurement by ultrasound in acute kidney injury. J Nephrol. 2020;33(1):109-117.
[26] TANIGUCHI M, FUKUMOTO Y, YAGI M, et al. Enhanced echo intensity in vastus medialis is associated with worsening of functional disabilities and symptoms in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a 3 years longitudinal study. Rheumatol Int. 2022:1-8. doi: 10.1007/s00296-022-05246-6.
[27] ZHANG X, PAN X, DENG L, et al. Relationship between Knee Muscle Strength and Fat/Muscle Mass in Elderly Women with Knee Osteoarthritis Based on Dual-Energy X-Ray Absorptiometry. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(2):573.
[28] 杨帆, 弋石泉, 尹乾兵. 术前活动能力与TKA患者术后膝前痛的相关性[J]. 中国医药导刊,2021,23(6):419-423.
[29] 沈松坡, 翁习生, 冯宾. 全膝关节置换术后疼痛原因分析及疼痛预测模型的研究进展[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2018,38(17):1082-1088.
[30] KITSUDA Y, TANIMURA C, INOUE K, et al. Effectiveness of ultrasonographic skeletal muscle assessment in patients after total knee arthroplasty. Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 2019;5(3):94-101.
[31] PINTO RS, CORREA CS, RADAELLI R, et al. Short-term strength training improves muscle quality and functional capacity of elderly women. Age (Dordr). 2014;36(1):365-372.
[32] PARDO E, EL BH, BOIZEAU P, et al. Reliability of ultrasound measurements of quadriceps muscle thickness in critically ill patients. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018;18(1):205.
[33] DRESEN E, WEIßBRICH C, FIMMERS R, et al. Medical high-protein nutrition therapy and loss of muscle mass in adult ICU patients: A randomized controlled trial. Clin Nutr. 2021;40(4):1562-1570.
[34] MAYER KP, THOMPSON BM, MONTGOMERY-YATES AA, et al. Acute skeletal muscle wasting and dysfunction predict physical disability at hospital discharge in patients with critical illness. Crit Care. 2020; 24(1):637.
[35] 马威, 庞坚, 张洁帆, 等. 膝骨关节炎患者跌倒恐惧影响因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2023,27(29):4690-4695.
[36] NOISEUX NO, CALLAGHAN JJ, CLARK CR, et al. Preoperative predictors of pain following total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2014;29(7): 1383-1387.
[37] 李志昌, 姜龙, 张舒, 等. 终末期骨关节炎患者全膝关节置换术前的躯体功能客观测定[J]. 北京大学学报(医学版),2016,48(2):257-262.
[38] 陈帆, 王迪, 杨歆璐, 等. 术前血浆血管紧张素Ⅱ2型受体浓度与全膝关节置换术后慢性疼痛的相关性[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2021, 37(5):475-479.
[39] 陈洁茹, 胡继成, 陈家琪, 等. 术前疼痛灾难化和全膝关节置换术后慢性疼痛的相关性[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志,2022,38(7):721-725.
[40] CHEN F, GAO W, HU J, et al. Preoperative angiotensin II type 2 receptor is a predictor for developing chronic post-surgical pain after total knee arthroplasty surgery. Life Sci. 2021;278:119654.
[41] WYLDE V, TRELA-LARSEN L, WHITEHOUSE MR, et al. Preoperative psychosocial risk factors for poor outcomes at 1 and 5 years after total knee replacement. Acta Orthop. 2017;88(5):530-536.
[42] WEINRIB AZ, AZAM MA, BIRNIE KA, et al. The psychology of chronic post-surgical pain: new frontiers in risk factor identification, prevention and management. Br J Pain. 2017;11(4):169-177.
|