[1] MANDL LA. Osteoarthritis year in review 2018: clinical. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2019;27(3):359-364.
[2] PAN P, SONG K, YAO Y, et al. The Impact of Intraoperative Hypothermia on Blood Loss and Allogenic Blood Transfusion in Total Knee and Hip Arthroplasty: A Retrospective Study. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020: 1096743.
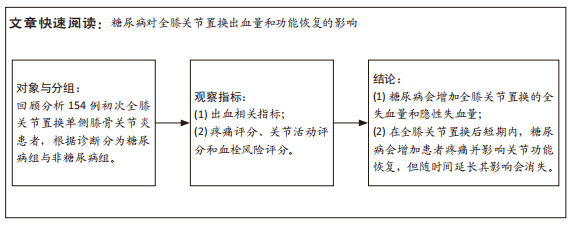
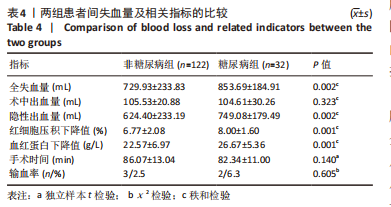
[3] 王云龙,甄平.单侧全膝关节置换围置换期的隐性失血:问题与特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(11):1786-1791.
[4] TEDESCO D, GORI D, DESAI KR, et al. Drug-Free Interventions to Reduce Pain or Opioid Consumption After Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(10):e172872.
[5] 徐欣,李向华,丁立荣,等.应用综合评估量表对糖尿病慢性伤口感染患者伤口愈合和生活质量的影响[J].中国病案,2021,22(5): 107-109.
[6] GU A, WEI C, ROBINSON HN, et al. Postoperative Complications and Impact of Diabetes Mellitus Severity on Revision Total Knee Arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2020;33(3):228-234.
[7] VERONESE N, COOPER C, REGINSTER JY, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus and osteoarthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019;49(1):9-19.
[8] RIOS-ARCE ND, HUM NR, LOOTS GG. Interactions Between Diabetes Mellitus and Osteoarthritis: From Animal Studies to Clinical Data. JBMR Plus. 2022;6(5):e10626.
[9] BERRÍOS-TORRES SI, UMSCHEID CA, BRATZLER DW, et al. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(8):784-791.
[10] MARADIT KREMERS H, SCHLECK CD, LEWALLEN EA, et al. Diabetes Mellitus and Hyperglycemia and the Risk of Aseptic Loosening in Total Joint Arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(9S):S251-S253.
[11] MA RCW. Epidemiology of diabetes and diabetic complications in China. Diabetologia. 2018;61(6):1249-1260.
[12] CITAK M, TOUSSAINT B, ABDELAZIZ H, et al. Elevated HbA1c is not a risk factor for wound complications following total joint arthroplasty: a prospective study. Hip Int. 2020;30(1_suppl):19-25.
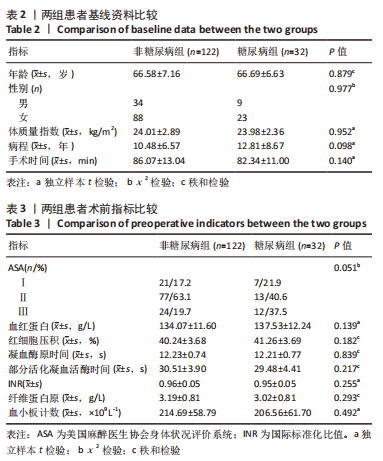
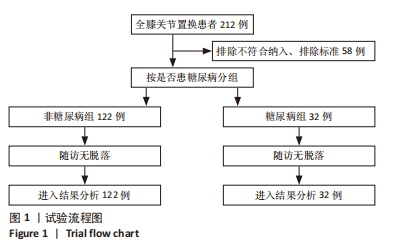
[13] 陈莉明,陈伟,陈燕燕,等.成人围手术期血糖监测专家共识[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2021,29(2):81-85.
[14] NADLER SB, HIDALGO JH, BLOCH T. Prediction of blood volume in normal human adults. Surgery. 1962;51(2):224-232.
[15] GROSS JB. Estimating allowable blood loss: corrected for dilution. Anesthesiology. 1983;58(3):277-280.
[16] HAWKER GA, MIAN S, KENDZERSKA T, et al. Measures of adult pain: Visual Analog Scale for Pain (VAS Pain), Numeric Rating Scale for Pain (NRS Pain), McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ), Short-Form McGill Pain Questionnaire (SF-MPQ), Chronic Pain Grade Scale (CPGS), Short Form-36 Bodily Pain Scale (SF-36 BPS), and Measure of Intermittent and Constant Osteoarthritis Pain (ICOAP). Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63 Suppl 11:S240-252.
[17] YING C, GUO C, WANG Z, et al. A Prediction Modeling Based on the Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) Knee Score for Poor Postoperative Functional Prognosis of Elderly Patients with Patellar Fractures. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:6620504.
[18] ZHOU H, HU Y, LI X, et al. Assessment of the Risk of Venous Thromboembolism in Medical Inpatients using the Padua Prediction Score and Caprini Risk Assessment Model. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2018; 25(11):1091-1104.
[19] CHARLIER E, DEROYER C, CIREGIA F, et al. Chondrocyte dedifferentiation and osteoarthritis (OA). Biochem Pharmacol. 2019;165:49-65.
[20] 廖德发.我国骨性关节炎流行病学调查现状[J].微创医学,2017, 12(4):521-524.
[21] MORA JP, SCUDERI GR. Minimally Invasive Total Knee Arthroplasty: Does Surgical Technique Actually Impact the Outcome? Orthop Clin North Am. 2020;51(3):303-315.
[22] GUNARATNE R, PRATT DN, BANDA J, et al. Patient Dissatisfaction Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(12):3854-3860.
[23] WEBB ML, GOLINVAUX NS, IBE IK, et al. Comparison of Perioperative Adverse Event Rates After Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Diabetes: Insulin Dependence Makes a Difference. J Arthroplasty. 2017; 32(10):2947-2951.
[24] SAIKI Y, OJIMA T, KABATA T, et al. Gradual exacerbation of knee flexion angle after total knee arthroplasty in patients with diabetes mellitus. Mod Rheumatol. 2021;31(6):1215-1220.
[25] 丁罗宾,赵佳,关健,等.糖尿病对膝关节置换术失血及早期疗效的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2019,27(11):961-965.
[26] ZHENG Y, LEY SH, HU FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018;14(2): 88-98.
[27] KISCHER CW, SPEER DP. Microvascular changes in Dupuytren’s contracture. J Hand Surg Am. 1984;9A(1):58-62.
[28] QIAO L, LI Y, SUN S. Insulin Exacerbates Inflammation in Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes. Inflammation. 2020;43(3):916-936.
[29] HAMADA D, MAYNARD R, SCHOTT E, et al. Suppressive Effects of Insulin on Tumor Necrosis Factor-Dependent Early Osteoarthritic Changes Associated With Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(6):1392-1402.
[30] LAIGUILLON MC, COURTIES A, HOUARD X, et al. Characterization of diabetic osteoarthritic cartilage and role of high glucose environment on chondrocyte activation: toward pathophysiological delineation of diabetes mellitus-related osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(9):1513-1522.
[31] ROSA SC, RUFINO AT, JUDAS FM, et al. Role of glucose as a modulator of anabolic and catabolic gene expression in normal and osteoarthritic human chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(10):2813-2824.
[32] NA A, OPPERMANN LM, JUPITER DC, et al. Diabetes Mellitus Blunts the Symptoms, Physical Function, and Health-Related Quality of Life Benefits of Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review With Meta-analysis of Data From More Than 17 000 Patients. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2021;51(6):269-280.
[33] QIN W, HUANG X, YANG H, et al. The Influence of Diabetes Mellitus on Patients Undergoing Primary Total Lower Extremity Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020: 6661691. |