中国组织工程研究 ›› 2025, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (6): 1285-1295.doi: 10.12307/2025.316
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
内质网应激与常见退行性骨骼疾病的发生与发展
钱 琨1,2,李子卿1,2,孙 水1,2
- 1山东第一医科大学附属省立医院骨关节科,山东省济南市 250021;2医学科技创新中心骨科实验室,山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院),山东省济南市 250117
-
收稿日期:2024-01-27接受日期:2024-04-19出版日期:2025-02-28发布日期:2024-06-22 -
通讯作者:孙水,主任医师,博士生导师,山东第一医科大学附属省立医院骨关节科,山东省济南市 250021;医学科技创新中心骨科实验室,山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院),山东省济南市 250117 -
作者简介:钱琨,男,1997年生,山东省菏泽市人,山东第一医科大学在读硕士,主要从事骨关节疾病的防治研究。
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases
Qian Kun1, 2, Li Ziqing1, 2, Sun Shui1, 2
- 1Department of Joint Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250021, Shandong Province, China; 2Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Medical Science and Technology Innovation Center, Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan 250117, Shandong Province, China
-
Received:2024-01-27Accepted:2024-04-19Online:2025-02-28Published:2024-06-22 -
Contact:Sun Shui, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Department of Joint Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250021, Shandong Province, China; Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Medical Science and Technology Innovation Center, Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan 250117, Shandong Province, China -
About author:Qian Kun, Master candidate, Department of Joint Surgery, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong First Medical University, Jinan 250021, Shandong Province, China; Orthopaedic Research Laboratory, Medical Science and Technology Innovation Center, Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences, Jinan 250117, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
内质网应激:内质网是真核细胞中最大的膜结合细胞器,参与蛋白质和脂质的合成、解毒以及细胞内Ca2+储存等。当细胞受到营养不足、促炎细胞因子、衰老、低pH值、缺氧等刺激时,可能导致内质网稳态紊乱,使管腔中的蛋白质发生错误折叠或未折叠,即内质网应激。
骨关节炎:是常见的关节退行性疾病,主要症状包括疼痛和关节活动受限,涉及软骨退化、滑膜炎、半月板病变和软骨下骨重塑等病理表现。关节软骨的受损和破坏是骨关节炎最显著的病理特征。
骨质疏松症:是一种全身性骨代谢疾病,分为原发性骨质疏松症(衰老、雌激素缺乏)和继发性骨质疏松症(药物、疾病引起的骨量丢失),主要特征包括骨量减少、骨微结构损坏和骨脆性增加,易导致骨折。
椎间盘退变:是常见的肌肉骨骼系统退行性疾病,也是导致慢性下腰痛的主要因素。主要病理特征包括髓核细胞凋亡、细胞外基质的破坏以及炎性细胞的浸润等,进而引起椎间盘含水量下降、弹性降低等变化,最终导致椎间盘结构紊乱、负荷能力降低。
背景:常见的退行性骨骼疾病,如骨关节炎、骨质疏松症和椎间盘退变,其具体的发病分子机制目前尚未明确,可能涉及内质网应激。目前,关于内质网应激在这些常见骨骼疾病发病机制中的系统作用和相关治疗进展的研究较为有限。
目的:综述内质网应激在常见的退行性骨骼疾病中的作用,深入探讨这些疾病的分子机制并提供新的防治思路和视角。
方法:检索2000-2024年相关文献,以“内质网应激,骨骼疾病,未折叠蛋白反应,骨关节炎,骨质疏松症,椎间盘退变,自噬,凋亡,铁死亡,焦亡”为中文检索词检索中国知网、万方、维普数据库;以“endoplasmic reticulum stress,bone disease,unfolded protein response,osteoarthritis,osteoporosis,intervertebral disc degeneration,autophagy,apoptosis,ferroptosis,pyroptosis”为英文检索词检索PubMed、Web of science 数据库。排除重复和较陈旧的文献,共115篇文献符合纳入标准。
结果与结论:①内质网应激在细胞生理调节中具有双重效应。轻度的内质网应激有助于促进成骨分化和细胞外基质合成,然而持续过度的内质网应激则会导致细胞死亡。②内质网应激诱导的细胞自噬、凋亡等与骨关节炎、骨质疏松症、椎间盘退变密切相关。③衰老、药物不良反应、代谢紊乱、钙平衡失调、不良生活习惯等多种原因可导致内质网应激的长期激活,从而引起骨重塑紊乱、软骨损伤、髓核细胞死亡等病理表现,最终导致骨关节炎、骨质疏松和椎间盘退变的发生。④对引发内质网应激的相关机制进行干预,有望在预防和治疗骨关节炎、骨质疏松症和椎间盘退变等常见退行性骨病方面发挥作用。
https://orcid.org/0009-0001-6350-8368(钱琨)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
钱 琨, 李子卿, 孙 水. 内质网应激与常见退行性骨骼疾病的发生与发展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295.
Qian Kun, Li Ziqing, Sun Shui . Endoplasmic reticulum stress in the occurrence and development of common degenerative bone diseases[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2025, 29(6): 1285-1295.

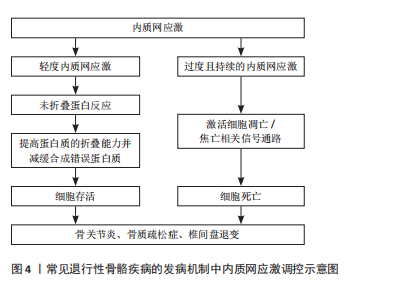
内质网是真核细胞中最大的膜结合细胞器,在蛋白质和脂质的生物合成、解毒代谢以及细胞内Ca2+储存等过程中发挥着重要作用[9]。在真核细胞中,有超过1/3的蛋白质需要在内质网中进行折叠,以促使其结构成熟[10]。当细胞受到营养不足、促炎细胞因子、衰老、低pH值、缺氧等刺激时,可引起内质网稳态紊乱,导致管腔中的蛋白质发生错误折叠或未折叠,即内质网应激[9,11]。在内质网应激状态下,细胞通过未折叠蛋白反应对转录和翻译进行调节,提高蛋白质的折叠能力并减缓合成错误蛋白质,从而减轻内质网负担[12-13]。然而,过度且持续的内质网应激状态将激活细胞内的凋亡信号,导致细胞死亡[12]。多项研究表明,内质网应激与骨关节炎、骨质疏松症、椎间盘退变等多种退行性骨骼疾病的发生和发展密切相关[9,12],见图4。因此,探讨内质网应激在相关骨骼疾病发病机制中的作用具有重要临床意义。
2.2 内质网应激 内质网应激的感受蛋白包括活化转录因子 6(activating transcription factor 6,ATF6)、肌醇必需酶1α(inositol-requiring enzyme 1α,IRE1α)和蛋白激酶样内质网激酶(PRK-like ER kinase,PERK)。在生理状态下,它们与免疫球蛋白重链结合蛋白(binding protein for immunoglobulins,BIP)/葡萄糖调节蛋白 78(glucose regulated protein 78,GRP78)结合,保持非激活状态[9]。在内质网应激时,这3种感受蛋白与BIP解离后被激活,进而启动未折叠蛋白反应[11]。持续强烈的内质网应激将导致细胞凋亡,主要通过凋亡信号激酶 1(apoptosissignal-regulating kinase 1,ASK1)/c-Jun氨基酸末端激酶(c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase,JNK)、增强子结合蛋白同源蛋白(C/EBP homologous protein,CHOP)、Bcl-2家族和半胱氨酸天冬氨酸特异性蛋白酶12(Caspase-12)等信号通路进行介导[14-16],见图5。
2.2.1 IRE1α通路 在内质网应激时,内质网膜Ⅰ型跨膜蛋白IRE1α会与BIP解离,并通过自身磷酸化来激活核酸内切酶的活性[11,17]。激活后的IRE1α剪切X-box结合蛋白1(X boxbinding protein 1,XBP1)的mRNA,生成活性的转录蛋白XBP1s。XBP1s是具有碱性亮氨酸拉链(basic leucine zipper,bZIP)结构的转录因子,通过与内质网应激反应元件(ER stress responseelement,ERSE)基因的启动子结合,激活内质网相关降解(ER-associated degradation,ERAD)机制,清除未折叠或折叠错误的蛋白质[18-19]。此外,IRE1α的活化可导致Caspase-12、Caspase-4和JNK 活性增强,从而诱导细胞发生凋亡[9,20]。
2.2.2 ATF6通路 ATF6是内质网膜Ⅱ型跨膜蛋白[11]。当细胞发生内质网应激时,ATF6与GRP78解离并通过转运进入高尔基体,被位点1蛋白酶(site 1 protease,S1P)和位点2蛋白酶(site 2 protease,S2P)剪切活化。然后,活化的ATF6进入细胞核,促进XBP1和内质网分子伴侣蛋白基因的转录,从而帮助蛋白质在内质网腔内的正确折叠
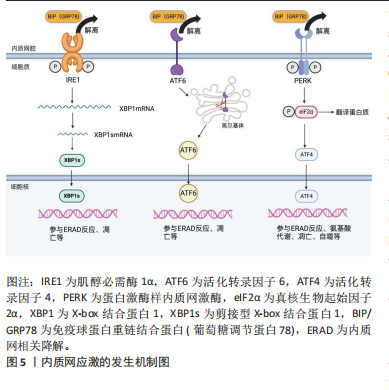
和转运,减缓内质网应激[9,13]。严重的内质网应激将导致CHOP被激活,使细胞发生凋亡[13]。
2.2.3 PERK通路 内质网应激发生时,内质网Ⅰ型跨膜蛋白PERK会与BIP解离,随后形成同型二聚体并进行自我磷酸化。活化后的PERK直接磷酸化真核生物起始因子2α (eukaryotic translation-initiation factor 2α,eIF2α)的α亚基,从而干扰5’帽端的组装,抑制错误蛋白的进一步合成[13,17]。此外,磷酸化的eIF2α可以促进活化转录因子 4(activating transcription factor 4,ATF4)的翻译。ATF4参与氨基酸代谢、谷胱甘肽生物合成、抗氧化应激、凋亡、自噬等相关基因的表达,在缓解内质网应激和调节细胞适应性方面发挥重要作用[21-23]。
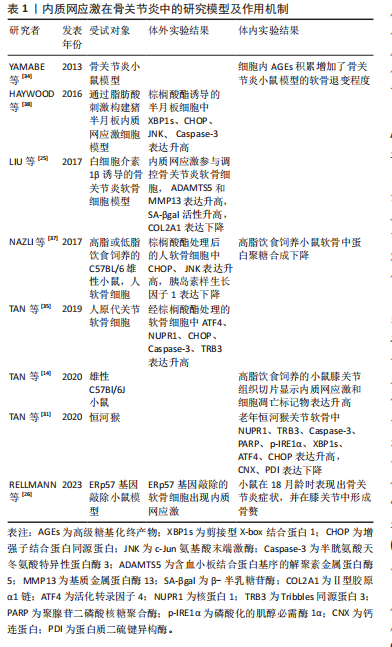
2.3 内质网应激与骨关节炎 骨关节炎是一种常见的关节退行性疾病,其主要症状包括疼痛和关节活动受限,涉及软骨退化、滑膜炎、半月板病变和软骨下骨重塑等病理表现[9,24]。目前,全球约有2.5亿骨关节炎患者,尤其在65岁以上的人群中更为普遍,给个体健康和社会经济都带来了巨大负担[25-26]。骨关节炎最明显的病理特征是关节软骨的受损和破坏。软骨细胞是关节软骨中唯一的细胞成分,其主要功能是支持软骨并调节软骨内细胞外基质的合成和降解,在软骨代谢中发挥重要作用。软骨细胞位于缺乏神经和血管的微环境中,对各种理化因素的刺激表现出极高的敏感性,更容易引发内质网应激[27-28]。近期的研究发现,在内质网应激患者的软骨组织中,内质网应激反应生物标志物如GRP78、CHOP、ATF6、PERK和IRE1的表达呈上升趋势,并与软骨的退变呈正相关,为骨关节炎发病机制提供了新的线索[9,29]。
衰老是骨关节炎的致病因素,同时也是软骨细胞内质网中蛋白质聚集的危险因素[26]。随着年龄增长,分子伴侣受到氧化损伤的影响,制约了它们在蛋白质稳态中的功能。同时,未折叠蛋白反应机制对软骨细胞的保护减弱,软骨细胞凋亡增加,从而促使骨关节炎的发生[26,30]。在骨关节炎软骨细胞中,LIU等[25]发现衰老标志物β-半乳糖苷酶明显增加,并在抑制内质网应激后减少。动物实验表明,老年关节软骨中分子伴侣如钙连蛋白(calnexin,CNX)和蛋白质二硫键异构酶(protein disulfide isomerase,PDI)的表达减少,而内质网应激标志物XBP1s、p-IRE1α、ATF4以及凋亡标志物CHOP、Caspase-3、聚腺苷二磷酸核糖聚合酶[poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase,PARP]等表达增加[31]。
高血糖、血脂异常等代谢因素与骨关节炎的发病密切相关[32]。除衰老外,吸烟、糖尿病或摄入高温处理的食物也会导致体内高级糖基化终产物(advanced glycation end products,AGEs)水平上升,从而引发一系列病理生理变化[33]。在软骨细胞内,AGEs与BIP等分子伴侣结合形成大分子复合物,通过内质网应激引起细胞功能障碍,最终诱发细胞凋亡[34]。血脂异常引起的内质网应激在骨关节炎发生中也发挥重要作用。游离脂肪酸在非脂肪组织中积累可导致脂毒性,是肥胖引发骨关节炎的重要因素[9,35]。
研究表明,游离脂肪酸在关节液和关节软骨组织的异位沉积量与骨关节炎软骨损伤的严重程度相关[36]。在这一过程中,内质网应激和未折叠蛋白反应途径的激活是脂毒性的关键机制[37]。游离脂肪酸能够引发内质网应激并激活未折叠蛋白反应信号通路,从而导致半月板损伤和关节软骨细胞的凋亡[37-38]。核蛋白1(nuclear protein 1,NUPR1)和Tribbles同源蛋白3(tribbles-related proteins,TRB3)是具有凋亡前活性的应激诱导蛋白。TAN等[35]发现游离脂肪酸可通过提高CHOP、NUPR1和TRB3的表达来激活软骨细胞的凋亡途径。此外,高脂饮食诱发的内质网应激还能够激活RE1/XBP1s/JNK和ATF4/CHOP信号通路,使小鼠膝关节软骨细胞发生凋亡[14]。
在骨关节炎病变中,软骨组织中细胞凋亡异常增加,同时伴随着细胞外基质的过度丧失[39]。内质网应激不仅增加软骨细胞的凋亡,还与炎症反应相互作用,加速细胞外基质的水解,从而加剧骨关节炎的发展。胰岛素样生长因子1在软骨中可促进基质合成和细胞存活。NAZLI等[37]发现游离脂肪酸诱导的内质网应激通过激活MAPK/JNK信号通路抑制胰岛素样生长因子1的功能。在高糖刺激条件下,LI等[40]观察到缺氧诱导因子1α和葡萄糖转运蛋白1的表达增加,导致大鼠纤维样滑膜细胞中AGEs的积累,从而促进内质网应激和炎症递质的释放,引发软骨细胞退变。此外,Rasheed等[41]指出AGEs诱导人软骨细胞发生内质网应激,通过eIF2α、p38-MAPK和NF-κB通路引起炎症因子环氧合酶2和前列腺素E2的表达升高,最终导致软骨细胞损伤。
内质网应激在骨关节炎中的研究模型及作用机制,见表1。
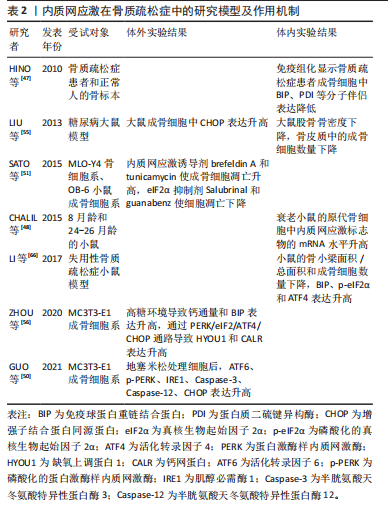
2.4 内质网应激与骨质疏松症 骨质疏松症是一种全身性骨代谢疾病,分为原发性骨质疏松症(衰老、雌激素缺乏)和继发性骨质疏松症(药物、疾病引起的骨量丢失)[9],其主要特征包括骨量减少、骨微结构损坏和骨脆性增加,易导致骨折[42]。该病常见于中老年人群,全球约有2亿人受骨质疏松症的影响[9,43]。骨重塑是一个动态过程,
它由破骨细胞主导的骨吸收和成骨细胞主导的骨形成相互偶联,这一过程对于维持骨骼的稳定性和完整性至关重 要[44-45]。内质网应激对骨重塑的平衡具有双重作用[21,43]。轻度的内质网应激有助于成骨分化和细胞外基质合成,但衰老、药物不良反应、代谢紊乱、Ca2+平衡失调、不良生活习惯等多种原因会导致内质网应激的长期激活,从而引起骨重塑紊乱,导致骨质疏松症的发生[9,42-43]。
衰老是骨质疏松症的重要潜在机制,成骨细胞中因衰老而积累的AGEs可通过内质网应激诱导细胞凋亡[46]。HINO等[47]发现,骨质疏松症患者的成骨细胞中内质网分子伴侣和KDEL表达减少,这表明衰老成骨细胞在分泌蛋白合成或蛋白折叠能力方面存在缺陷。此外,相较于成年小鼠,CHALIL等[48]在老年小鼠(24-26月龄)的骨细胞中观察到ATF4、XBP1和CHOP的mRNA水平升高,这导致了对机械负荷的合成代谢反应降低。
糖皮质激素被广泛用于治疗炎症和免疫性疾病,但长期大量使用可诱发骨质疏松症[49]。高剂量的地塞米松(一种糖皮质激素类药物)通过促进Ca2+流入引发内质网应激,导致ATF6、p-PERK、p-IRE1和CHOP的表达升高,从而诱导成骨细胞凋亡[50]。此外,SATO等[51]发现糖皮质激素可通过内质网应激加速成骨细胞和骨细胞的凋亡,使用eIF2α去磷酸化抑制剂(如Salubrinal或guanabenz)可防止其对骨骼的有害效应。
随着糖尿病患者数量的不断增多,慢性高血糖、AGEs和氧化应激引起的糖尿病性骨质疏松症患病率也在逐渐增加[52]。长期高血糖可通过诱发内质网应激导致胰岛β细胞凋亡,从而以葡萄糖浓度依赖的方式抑制成骨分化[53-54]。通过建立糖尿病大鼠模型,LIU等[55]发现高血糖通过激活内质网应激提升了CHOP的表达,破坏了骨重塑的平衡,诱导骨质疏松症的发生。此外,ZHOU等[56]观察到高浓度葡萄糖可通过激活PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP信号通路诱导成骨细胞发生凋亡。
不同于凋亡,铁死亡是一种铁依赖性的细胞程序性死亡方式。先前研究表明,铁死亡激活剂erastin通过干扰谷氨酸传递来激活内质网应激,从而诱导多种促凋亡蛋白的表达,说明内质网应激与铁死亡之间存在关联[57]。 在内质网应激时,erastin启动PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP信号传导通路,CHOP的激活导致p53上调凋亡调节因子(p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis,PUMA)的表达,从而参与铁死亡和细胞凋亡的协同作用[58]。ZHAO等[59]研究表明,在高糖环境下,内质网应激相关蛋白活化转录因子3(activating transcription factor 3,ATF3)在成骨细胞和2型糖尿病性骨质疏松症大鼠模型中表达升高,这个过程通过抑制异二聚体-胱氨酸/谷氨酸反向转运体 (cystine/glutamate antiporter,system Xc-)的活性来诱导成骨细胞的铁死亡。
多项研究表明,脂蛋白代谢紊乱与骨质疏松症的发展密切相关。YANG等[60]研究显示,棕榈酸酯对人成骨细胞的活性抑制呈现出剂量依赖性,并引起了人成骨细胞中GRP78、Caspase-3和CHOP的表达水平增加。GILLET等[61]也得出类似结论,认为棕榈酸酯可通过引发内质网应激产生细胞毒性作用,诱导骨髓间充质干细胞和成骨细胞凋亡。此外,SATO等[62]研究发现胆固醇氧化物(7-酮基胆固醇)可引发内质网应激,提高成骨细胞中Caspase-3和Caspase-7的表达。体内Ca2+对于维持骨重塑的稳态至关重要,持续的Ca2+紊乱和内质网应激会增加患骨质疏松症的风险[63-64]。CHENG等[65]发现质子泵抑制剂兰索拉唑可引起成骨细胞内Ca2+增加并诱发内质网应激,这一过程通过激活GRP78/ATF4/CHOP通路引起小鼠成骨细胞凋亡,导致骨质疏松症的发生。此外,GUO等[50]研究表明,使用Ca2+抑制剂2-APB可以保护成骨细胞免受内质网应激介导的细胞凋亡。
除此之外,失用性骨质疏松症也与内质网应激的激活存在关联。在失用性骨质疏松症大鼠模型中,LI等[66]发现GRP78、p-eIF2α和ATF4等内质网应激标志物的表达显著增加。
内质网应激在骨质疏松症中的研究模型及作用机制,见表2。
2.5 内质网应激与椎间盘退变 椎间盘退变是导致慢性下腰痛的重要因素,大约40%的慢性下腰痛与椎间盘退变有关[67]。随着社会人口老龄化的加剧,其发病率呈上升趋势,给社会和经济都带来沉重的负担[68-69]。椎间盘是连接椎骨的重要组织,主要由髓核、纤维环和软骨终板构成。椎间盘长期处于低氧环境下,营养供应主要依靠软骨终板和纤维环的被动扩散,因此更容易受到周围微环境的影响[70]。
椎间盘退变的病理特征主要包括髓核细胞凋亡、细胞外基质的破坏以及炎性细胞的浸润等[71-73]。越来越多的研究表明,内质网应激在椎间盘退变的致病过程中发挥重要作用,如应对外界刺激、介导细胞死亡等[74-75]。
衰老与椎间盘退变密切相关。衰老细胞破坏了细胞外基质的分解代谢和合成代谢之间的平衡,加速了分解代谢的过程,导致椎间盘细胞外基质的成分产生显著改变[76-77]。退变髓核组织中的内质网应激相关基因如GRP78、ATF6、PERK、CHOP等表达水平显著增加,并且与退变程度呈正相关[2,78-79]。随着年龄增加,AGEs的积累改变了椎间盘基质的理化性质和生物力学性能,引起椎间盘基质刚度增加并干扰细胞正常代谢,促进椎间盘退变的发生[80-81]。LIAO等[7]发现AGEs参与了椎间盘退变的发病机制,内质网应激和细胞凋亡标志物水平明显增加,并且内质网应激水平与AGEs的积累量呈显著相关。此外,内质网是主要的Ca2+储存器,细胞内Ca2+稳态紊乱可引发内质网应激,从而诱导细胞凋亡[63]。LUO等[82]研究发现AGEs通过激活Ca2+释放通道1,4,5-三磷酸肌醇1型受体(inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 1,IP3R1)和兰尼碱受体(ryanodine receptor,RyR)增加了细胞内Ca2+的释放,并通过抑制肌质网Ca2+-ATP酶(sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase,SERCA)的活性来降低Ca2+的再摄取,这破坏了细胞内Ca2+的稳态并引起内质网应激标志物GRP78、ATF4、CHOP等水平升高,最终导致髓核细胞凋亡。
除衰老外,炎症浸润、营养缺乏、压力过载、高脂饮食等因素也在椎间盘退变的发病过程中扮演重要角色。内质网应激对细胞稳态的调控具有双向作用,适度的内质网应激可以增强细胞对不利环境的适应性。在肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的大鼠髓核细胞损伤模型中,CHEN等[83]研究发现内质网应激通过激活PERK/eIF2α和IRE1/XBP1通路促进细胞的存活和增殖,而沉默未折叠蛋白反应通路则显著提高了细胞的死亡率。然而,持续而强烈的炎症因子会形成组织炎症微环境并导致内质网应激过度激活,从而引发细胞分解代谢增加、氧化还原平衡失调、线粒体功能受损等情况,最终导致细胞凋亡的发生[74,84-85]。
虽然髓核细胞处于高代谢产物、低葡萄糖和低氧的组织微环境中,长期持续的组织内营养缺乏将超出细胞的适应能力极限,从而引发髓核细胞合成分解代谢失衡、细胞周期停滞,甚至细胞死亡[86-88]。CHANG等[89]发现短期葡萄糖饥饿处理所引发的内质网应激反应能够保护髓核细胞免受凋亡的影响,但长期的葡萄糖饥饿处理将导致内质网应激反应过度,并通过激活eIF2α/ATF4通路促进髓核细胞的凋亡。此外,压力过载引发的内质网应激在椎间盘退变的发病过程中发挥着重要作用。LIN等[78]研究表明,在机械压力下Ca2+从内质网释放,通过三磷酸肌醇受体/葡萄糖调节蛋白 75/电压依赖性阴离子通道1(inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor/glucose-regulated protein 75/ voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1,IP3R/GRP75/VDAC1)复合体进入线粒体并扰乱其功能,激活PARP/凋亡诱导因子(apoptosis inducing factor,AIF)通路导致髓核细胞凋亡。这一过程中,过量的活性氧是内质网应激的主要激活剂,导致线粒体内Ca2+的积累并诱发细胞程序性死亡。高胆固醇血症是全球公共卫生问题,尤其在高脂肪饮食和不健康生活方式的影响下日益严重[90]。研究发现,与正常饮食相比,高胆固醇饮食大鼠表现出更严重的椎间盘退变症状。值得注意的是,这种效应可以通过降低胆固醇的药物阿托伐他汀来消除[91]。
与细胞凋亡不同,Gasdermin基因家族介导的细胞焦亡是一种新型的促炎性细胞程序性死亡方式[92]。固醇调节元件结合蛋白1(sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1,SREBP1)是脂质代谢的重要调节因子,YAN等[91]研究结果显示,胆固醇过度积累可通过mSREBP1(SREBP1的成熟形式)介导的内质网应激引发髓核细胞凋亡并促进细胞外基质降解。此外,LI等[93]发现活性氧和内质网应激相关蛋白ATF3的增加可导致髓核细胞发生铁死亡,因此ATF3被认为是椎间盘退变有潜力的治疗靶点。
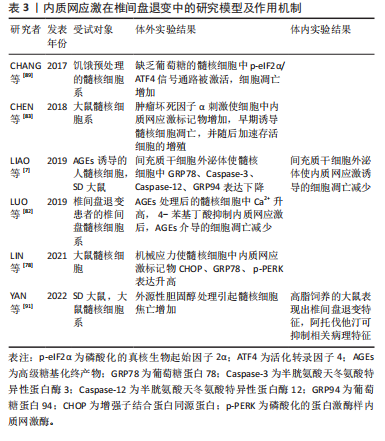
内质网应激在椎间盘退变中的研究模型及作用机制,见表3。
2.6 内质网应激与治疗 鉴于内质网应激在骨骼疾病的致病过程中具有重要作用,近年来,许多研究人员已开始专注于药物开发和探索治疗方法,并已初步取得了一些成果。外泌体是一种直径在50-150 nm之间的球形小囊泡,由双层脂质包裹而成,其主要功能是介导细胞间的信息交流[94-95]。这些小囊泡包含蛋白质、核糖核酸和脂质等多种生物活性物质,广泛存在于体液中[94-95]。多项研究表明,来自间充质干细胞的外泌体在特定的骨微环境中可以调节细胞增殖和分化,有助于减少细胞凋亡并维持细胞外基质的平衡[96]。LIAO等[7]发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体可以抑制内质网应激反应并减少CHOP的表达水平,从而抑制大鼠髓核细胞的凋亡。通过构建大鼠椎间盘退变模型,XIE等[97]研究发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体中的miR-31-5p在抑制ATF6相关的内质网应激反应中发挥重要作用,有助于抑制终板软骨细胞的凋亡和钙化。TAO等[98]研究表明,富血小板血浆中的外泌体可以通过激活成骨细胞中的蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,PKB/Akt)/Bad/B淋巴细胞瘤2(B-cell lymphoma 2,Bcl-2)信号通路,促进抗凋亡因子Bcl-2的表达并抑制内质网应激反应相关的细胞凋亡。此外,HAYASHI等[99]观察到肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的人牙龈间充质干细胞外泌体miR-1260b通过抑制ATF6β的表达,从而降低破骨细胞调控因子RANKL的表达水平,抑制破骨细胞的生成。
中药在防治退行性骨骼疾病方面拥有悠久的历史,其不良反应较少,并具有治疗范围广、作用靶点多等优势[100-102]。小檗碱是从黄连中提取的一种异喹啉类化合物。通过构建髓核细胞损伤模型,LUO等[103]发现小檗碱能够调节胞内Ca2+稳态并抑制内质网应激反应,进而减轻髓核细胞的凋亡。槲皮素(quercitrin)是存在于植物中的黄酮类化合物,具有多种生物活性。槲皮素可显著降低钛颗粒诱导的PERK、IRE1α、GRP78、CHOP、Caspase-12和Caspase-3的表达水平,从而抑制成骨细胞凋亡[104]。天麻素(gastrodin)是一种从传统中药天麻中提取的生物活性化合物。LIU等[105]发现天麻素可以改善骨微结构并减轻地塞米松诱导的大鼠骨质疏松症,它通过抑制地塞米松引起的内质网应激,降低GRP78、CHOP和p-eIF2α的表达水平,同时通过激活核因子E2相关因子2(nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2,NRF2)途径来保护成骨细胞。栀子苷(geniposide)是从传统中药杜仲中提取到的一种环烯醚萜苷类化合物。最近的研究表明,栀子苷通过激活细胞外调节蛋白激酶(extracellular regulated protein kinases,ERK)和NRF2信号通路,提高成骨标志物骨桥蛋白、成骨细胞特异性转录因子和Runt相关转录因子2的表达水平,降低ATF4和CHOP表达,从而抑制地塞米松诱导的内质网应激,改善线粒体凋亡并促进成骨分化[106-107]。
另外,很多脂质和蛋白质因子也可通过调控内质网应激系统来影响骨骼代谢。二十碳五烯酸是一种内源性omega-3脂肪酸,在哺乳动物的生长发育中发挥重要作用[108]。LIN等[109]在体外实验中发现,二十碳五烯酸能够抑制内质网应激并促进髓核细胞的存活;体内实验也表明,二十碳五烯酸可以改善大鼠针刺模型中椎间盘退变的进展。牛磺熊去氧胆酸是一种亲水性胆汁酸,WANG等[110]研究发现牛磺熊去氧胆酸能够有效抑制压力引发的内质网应激,从而减少髓核细胞的坏死性凋亡。此外,LIU等[111]发现相较于直接暴露于内质网应激诱导剂衣霉素的软骨细胞,首先使用衣霉素预处理,然后加入牛磺熊去氧胆酸的软骨细胞表现出内质网应激标记物水平下降、Ⅱ型胶原蛋白表达增加、细胞增殖恢复等现象。4-苯基丁酸是一种具有分子伴侣作用的短链芳香族脂肪酸,通常被视为内质网应激的修复剂。TANG等[112]研究显示,4-苯基丁酸能够抑制骨关节炎大鼠模型中的内质网应激,减少细胞凋亡和软骨损伤。此外,LEE等[113]和LUO等[82]研究表明,4-苯基丁酸可以抑制白细胞介素1β处理后骨髓间充质干细胞中内质网应激介导的破骨细胞分化,并通过抑制内质网应激来保护髓核细胞免受AGEs诱导的细胞凋亡。此外,YANG等[114]发现,作为内源性生长因子的颗粒蛋白前体参与调节雌激素受体α与雌激素的结合,从而调控雌激素对骨形成和骨吸收的能力。颗粒蛋白前体与雌二醇协同激活雌激素受体α,抑制MC3T3-E1细胞中的PERK/p-eIF2α信号通路,促进成骨分化并抑制破骨细胞的形成。骨膜蛋白是一种细胞外基质蛋白,MENG等[115]研究表明骨膜蛋白通过阻断eIF2α-ATF4信号通路,起到了保护成骨细胞的作用。

| [1] ZHANG P, MCGRATH B, LI S, et al. The PERK eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase is required for the development of the skeletal system, postnatal growth, and the function and viability of the pancreas. Mol Cell Biol. 2002;22(11):3864-3874. [2] RUIZ-ROMERO C, CARREIRA V, REGO I, et al. Proteomic analysis of human osteoarthritic chondrocytes reveals protein changes in stress and glycolysis. Proteomics. 2008;8(3):495-507. [3] MURAKAMI T, SAITO A, HINO S, et al. Signalling mediated by the endoplasmic reticulum stress transducer OASIS is involved in bone formation. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(10):1205-1211. [4] SAITO A, HINO S, MURAKAMI T, et al. Regulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress response by a BBF2H7-mediated Sec23a pathway is essential for chondrogenesis. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11(10):1197-1204. [5] TANG Q, ZHENG G, FENG Z, et al. Trehalose ameliorates oxidative stress-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and ER stress via selective autophagy stimulation and autophagic flux restoration in osteoarthritis development. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(10):e3081. [6] PINKAEW D, CHATTOPADHYAY A, KING MD, et al. Fortilin binds IRE1α and prevents ER stress from signaling apoptotic cell death. Nat Commun. 2017;8(1):18. [7] LIAO Z, LUO R, LI G, et al. Exosomes from mesenchymal stem cells modulate endoplasmic reticulum stress to protect against nucleus pulposus cell death and ameliorate intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Theranostics. 2019;9(14):4084-4100. [8] ZHENG Z, ZHANG X, HUANG B, et al. Site-1 protease controls osteoclastogenesis by mediating LC3 transcription. Cell Death Differ. 2021;28(6):2001-2018. [9] WEN ZQ, LIN J, XIE WQ, et al. Insights into the underlying pathogenesis and therapeutic potential of endoplasmic reticulum stress in degenerative musculoskeletal diseases. Mil Med Res. 2023;10(1):54. [10] HILLARY RF, FITZGERALD U. A lifetime of stress: ATF6 in development and homeostasis. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25(1):48. [11] TANG Q, LIU Q, LI Y, et al. CRELD2, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and human diseases. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023;14:1117414. [12] PATTERSON SE, DEALY CN. Mechanisms and models of endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrodysplasia. Dev Dyn. 2014;243(7):875-893. [13] SOVOLYOVA N, HEALY S, SAMALI A, et al. Stressed to death - mechanisms of ER stress-induced cell death. Biol Chem. 2014;395(1):1-13. [14] TAN L, HARPER L, MCNULTY MA, et al. High-fat diet induces endoplasmic reticulum stress to promote chondrocyte apoptosis in mouse knee joints. FASEB J. 2020;34(4):5818-5826. [15] HUANG R, HUI Z, WEI S, et al. IRE1 signaling regulates chondrocyte apoptosis and death fate in the osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2022; 237(1):118-127. [16] WU Z, LI M, ZHENG W, et al. Silencing of both ATF4 and PERK inhibits cell cycle progression and promotes the apoptosis of differentiating chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(1):101-111. [17] BREWER JW. Regulatory crosstalk within the mammalian unfolded protein response. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2014;71(6):1067-1079. [18] HE Y, SUN S, SHA H, et al. Emerging roles for XBP1, a sUPeR transcription factor. Gene Expr. 2010;15(1):13-25. [19] MENDES CS, LEVET C, CHATELAIN G, et al. ER stress protects from retinal degeneration. EMBO J. 2009;28(9):1296-1307. [20] CYBULSKY AV. Endoplasmic reticulum stress, the unfolded protein response and autophagy in kidney diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2017; 13(11):681-696. [21] WU T, JIANG Y, SHI W, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress: a novel targeted approach to repair bone defects by regulating osteogenesis and angiogenesis. J Transl Med. 2023;21(1):480. [22] ROJAS M, VASCONCELOS G, DEVER TE. An eIF2α-binding motif in protein phosphatase 1 subunit GADD34 and its viral orthologs is required to promote dephosphorylation of eIF2α. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015;112(27):E3466-3475. [23] HETZ C, ZHANG K, KAUFMAN RJ. Mechanisms, regulation and functions of the unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(8):421-438. [24] WEN Z, SUN Q, SHAN Y, et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Osteoarthritis: A Novel Perspective on the Pathogenesis and Treatment. Aging Dis. 2023;14(2):283-286. [25] LIU Y, ZHU H, YAN X, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress participates in the progress of senescence and apoptosis of osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;491(2):368-373. [26] RELLMANN Y, EIDHOF E, HANSEN U, et al. ER Stress in ERp57 Knockout Knee Joint Chondrocytes Induces Osteoarthritic Cartilage Degradation and Osteophyte Formation. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;23(1):182. [27] KUNG LHW, MULLAN L, SOUL J, et al. Cartilage endoplasmic reticulum stress may influence the onset but not the progression of experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):206. [28] CARBALLO CB, NAKAGAWA Y, SEKIYA I, et al. Basic Science of Articular Cartilage. Clin Sports Med. 2017;36(3):413-425. [29] BRIGGS MD, DENNIS EP, DIETMAR HF, et al. New developments in chondrocyte ER stress and related diseases. F1000Res. 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-290. [30] NAIDOO N. The endoplasmic reticulum stress response and aging. Rev Neurosci. 2009;20(1):23-37. [31] TAN L, REGISTER TC, YAMMANI RR. Age-Related Decline in Expression of Molecular Chaperones Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Chondrocyte Apoptosis in Articular Cartilage. Aging Dis. 2020;11(5): 1091-1102. [32] WEI G, LU K, UMAR M, et al. Risk of metabolic abnormalities in osteoarthritis: a new perspective to understand its pathological mechanisms. Bone Res. 2023;11(1):63. [33] BANSAL S, BURMAN A, TRIPATHI AK. Advanced glycation end products: Key mediator and therapeutic target of cardiovascular complications in diabetes. World J Diabetes. 2023;14(8):1146-1162. [34] YAMABE S, HIROSE J, UEHARA Y, et al. Intracellular accumulation of advanced glycation end products induces apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress in chondrocytes. FEBS J. 2013;280(7):1617-1629. [35] TAN L, YAMMANI RR. Nupr1 regulates palmitate-induced apoptosis in human articular chondrocytes. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(2): BSR20181473. [36] LIPPIELLO L, WALSH T, FIENHOLD M. The association of lipid abnormalities with tissue pathology in human osteoarthritic articular cartilage. Metabolism. 1991;40(6):571-576. [37] NAZLI SA, LOESER RF, CHUBINSKAYA S, et al. High fat-diet and saturated fatty acid palmitate inhibits IGF-1 function in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2017;25(9):1516-1521. [38] HAYWOOD J, YAMMANI RR. Free fatty acid palmitate activates unfolded protein response pathway and promotes apoptosis in meniscus cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(5):942-945. [39] HWANG HS, KIM HA. Chondrocyte Apoptosis in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):26035-26054. [40] LI Q, WEN Y, WANG L, et al. Hyperglycemia-induced accumulation of advanced glycosylation end products in fibroblast-like synoviocytes promotes knee osteoarthritis. Exp Mol Med. 2021;53(11):1735-1747. [41] RASHEED Z, HAQQI TM. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces the expression of COX-2 through activation of eIF2α, p38-MAPK and NF-κB in advanced glycation end products stimulated human chondrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1823(12):2179-2189. [42] IYER S, ADAMS DJ. Bone and the Unfolded Protein Response: In Sickness and in Health. Calcif Tissue Int. 2023;113(1):96-109. [43] ZHONG M, WU Z, CHEN Z, et al. Advances in the interaction between endoplasmic reticulum stress and osteoporosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023;165:115134. [44] BOYLE WJ, SIMONET WS, LACEY DL. Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 2003;423(6937):337-342. [45] SIDDIQUI JA, PARTRIDGE NC. Physiological Bone Remodeling: Systemic Regulation and Growth Factor Involvement. Physiology (Bethesda). 2016;31(3):233-245. [46] SUZUKI R, FUJIWARA Y, SAITO M, et al. Intracellular Accumulation of Advanced Glycation End Products Induces Osteoblast Apoptosis Via Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. J Bone Miner Res. 2020;35(10):1992-2003. [47] HINO S, KONDO S, YOSHINAGA K, et al. Regulation of ER molecular chaperone prevents bone loss in a murine model for osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2010;28(2):131-138. [48] CHALIL S, JASPERS RT, MANDERS RJ, et al. Increased endoplasmic reticulum stress in mouse osteocytes with aging alters Cox-2 response to mechanical stimuli. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(2):123-128.
[49] CHOTIYARNWONG P, MCCLOSKEY EV. Pathogenesis of glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and options for treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(8):437-447. [50] GUO Y, HAO D, HU H. High doses of dexamethasone induce endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis by promoting calcium ion influx-dependent CHOP expression in osteoblasts. Mol Biol Rep. 2021;48(12):7841-7851. [51] SATO AY, TU X, MCANDREWS KA, et al. Prevention of glucocorticoid induced-apoptosis of osteoblasts and osteocytes by protecting against endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress in vitro and in vivo in female mice. Bone. 2015;73:60-68. [52] MOHSIN S, BANIYAS MM, ALDARMAKI RS, et al. An update on therapies for the treatment of diabetes-induced osteoporosis. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2019;19(9):937-948. [53] WANG Y, GAO L, LI Y, et al. Nifedipine protects INS-1 β-cell from high glucose-induced ER stress and apoptosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2011;12(11): 7569-7580. [54] TAN J, ZHOU Y, LUO J, et al. High glucose inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells in periodontitis by activating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Ann Transl Med. 2022; 10(4):204. [55] LIU W, ZHU X, WANG Q, et al. Hyperglycemia induces endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent CHOP expression in osteoblasts. Exp Ther Med. 2013;5(5):1289-1292. [56] ZHOU R, MA Y, TAO Z, et al. Melatonin Inhibits Glucose-Induced Apoptosis in Osteoblastic Cell Line Through PERK-eIF2α-ATF4 Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:602307. [57] DIXON SJ, PATEL DN, WELSCH M, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of cystine-glutamate exchange induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and ferroptosis. Elife. 2014;3:e02523. [58] HONG SH, LEE DH, LEE YS, et al. Molecular crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis: emerging role of ER stress-induced p53-independent PUMA expression. Oncotarget. 2017;8(70): 115164-115178. [59] ZHAO Y, DU Y, GAO Y, et al. ATF3 Regulates Osteogenic Function by Mediating Osteoblast Ferroptosis in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. Dis Markers. 2022;2022:9872243. [60] YANG L, GUAN G, LEI L, et al. Palmitic acid induces human osteoblast-like Saos-2 cell apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018;23(6):1283-1294. [61] GILLET C, SPRUYT D, RIGUTTO S, et al. Oleate Abrogates Palmitate-Induced Lipotoxicity and Proinflammatory Response in Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Osteoblastic Cells. Endocrinology. 2015;156(11):4081-4093. [62] SATO Y, ISHIHARA N, NAGAYAMA D, et al. 7-ketocholesterol induces apoptosis of MC3T3-E1 cells associated with reactive oxygen species generation, endoplasmic reticulum stress and caspase-3/7 dependent pathway. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2017;10:56-60. [63] KREBS J, AGELLON LB, MICHALAK M. Ca(2+) homeostasis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress: An integrated view of calcium signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;460(1):114-121. [64] PERIN M, CHINIGÒ G, GENOVA T, et al. The Impact of Plasma Membrane Ion Channels on Bone Remodeling in Response to Mechanical Stress, Oxidative Imbalance, and Acidosis. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023;12(3):689. [65] CHENG Z, LIU Y, MA M, et al. Lansoprazole-induced osteoporosis via the IP3R- and SOCE-mediated calcium signaling pathways. Mol Med. 2022;28(1):21. [66] LI J, YANG S, LI X, et al. Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disuse osteoporosis. Bone. 2017;97:2-14. [67] GBD 2016 DISEASE AND INJURY INCIDENCE AND PREVALENCE COLLABORATORS. Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390(10100):1211-1259. [68] KATZ JN. Lumbar disc disorders and low-back pain: socioeconomic factors and consequences. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006;88 Suppl 2:21-24. [69] MAHER C, UNDERWOOD M, BUCHBINDER R. Non-specific low back pain. Lancet. 2017;389(10070):736-747. [70] HOLM S, MAROUDAS A, URBAN JP, et al. Nutrition of the intervertebral disc: solute transport and metabolism. Connect Tissue Res. 1981;8(2):101-119. [71] KAMALI A, ZIADLOU R, LANG G, et al. Small molecule-based treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current options and future directions. Theranostics. 2021;11(1):27-47. [72] GROH AMR, FOURNIER DE, BATTIÉ MC, et al. Innervation of the Human Intervertebral Disc: A Scoping Review. Pain Med. 2021;22(6):1281-1304. [73] LIANG H, LUO R, LI G, et al. The Proteolysis of ECM in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(3):1715. [74] FUJII T, FUJITA N, SUZUKI S, et al. The unfolded protein response mediated by PERK is casually related to the pathogenesis of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Res. 2018;36(5):1334-1345. [75] ZHANG YH, ZHAO CQ, JIANG LS, et al. Lentiviral shRNA silencing of CHOP inhibits apoptosis induced by cyclic stretch in rat annular cells and attenuates disc degeneration in the rats. Apoptosis. 2011; 16(6):594-605. [76] GRUBER HE, INGRAM JA, DAVIS DE, et al. Increased cell senescence is associated with decreased cell proliferation in vivo in the degenerating human annulus. Spine J. 2009;9(3):210-215. [77] ROUGHLEY PJ. Biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration: involvement of the extracellular matrix. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004; 29(23):2691-2699. [78] LIN H, PENG Y, LI J, et al. Reactive Oxygen Species Regulate Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and ER-Mitochondrial Ca2+ Crosstalk to Promote Programmed Necrosis of Rat Nucleus Pulposus Cells under Compression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8810698. [79] WANG B, KE W, WANG K, et al. Mechanosensitive Ion Channel Piezo1 Activated by Matrix Stiffness Regulates Oxidative Stress-Induced Senescence and Apoptosis in Human Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8884922. [80] SIVAN SS, TSITRON E, WACHTEL E, et al. Age-related accumulation of pentosidine in aggrecan and collagen from normal and degenerate human intervertebral discs. Biochem J. 2006;399(1):29-35. [81] KADOW T, SOWA G, VO N, et al. Molecular basis of intervertebral disc degeneration and herniations: what are the important translational questions? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473(6):1903-1912. [82] LUO R, SONG Y, LIAO Z, et al. Impaired calcium homeostasis via advanced glycation end products promotes apoptosis through endoplasmic reticulum stress in human nucleus pulposus cells and exacerbates intervertebral disc degeneration in rats. FEBS J. 2019; 286(21):4356-4373.
[83] CHEN L, LIU L, XIE ZY, et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Facilitates the Survival and Proliferation of Nucleus Pulposus Cells in TNF-α Stimulus by Activating Unfolded Protein Response. DNA Cell Biol. 2018;37(4):347-358.
[84] IURLARO R, MUÑOZ-PINEDO C. Cell death induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. FEBS J. 2016;283(14):2640-2652. [85] KRUPKOVA O, SADOWSKA A, KAMEDA T, et al. p38 MAPK Facilitates Crosstalk Between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and IL-6 Release in the Intervertebral Disc. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1706. [86] HUANG YC, URBAN JP, LUK KD. Intervertebral disc regeneration: do nutrients lead the way? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014;10(9):561-566. [87] FIELDS AJ, BALLATORI A, LIEBENBERG EC, et al. Contribution of the endplates to disc degeneration. Curr Mol Biol Rep. 2018;4(4):151-160. [88] JIANG L, YUAN F, YIN X, et al. Responses and adaptations of intervertebral disc cells to microenvironmental stress: a possible central role of autophagy in the adaptive mechanism. Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55(5-6):311-321. [89] CHANG H, CAI F, ZHANG Y, et al. Early-stage autophagy protects nucleus pulposus cells from glucose deprivation-induced degeneration via the p-eIF2α/ATF4 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;89:529-535. [90] YIN W, LI Z, ZHANG W. Modulation of Bone and Marrow Niche by Cholesterol. Nutrients. 2019;11(6):1394. [91] YAN J, LI S, ZHANG Y, et al. Cholesterol Induces Pyroptosis and Matrix Degradation via mSREBP1-Driven Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;9:803132. [92] YU P, ZHANG X, LIU N, et al. Pyroptosis: mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):128. [93] LI Y, PAN D, WANG X, et al. Silencing ATF3 Might Delay TBHP-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Repressing NPC Ferroptosis, Apoptosis, and ECM Degradation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:4235126. [94] HUA S, BARTOLD PM, GULATI K, et al. Periodontal and Dental Pulp Cell-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles: A Review of the Current Status. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021;11(7):1858. [95] WORTZEL I, DROR S, KENIFIC CM, et al. Exosome-Mediated Metastasis: Communication from a Distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347-360. [96] FONTANA G, SEE E, PANDIT A. Current trends in biologics delivery to restore intervertebral disc anabolism. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;84: 146-158. [97] XIE L, CHEN Z, LIU M, et al. MSC-Derived Exosomes Protect Vertebral Endplate Chondrocytes against Apoptosis and Calcification via the miR-31-5p/ATF6 Axis. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:601-614. [98] TAO SC, YUAN T, RUI BY, et al. Exosomes derived from human platelet-rich plasma prevent apoptosis induced by glucocorticoid-associated endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat osteonecrosis of the femoral head via the Akt/Bad/Bcl-2 signal pathway. Theranostics. 2017;7(3): 733-750. [99] HAYASHI C, FUKUDA T, KAWAKAMI K, et al. miR-1260b inhibits periodontal bone loss by targeting ATF6β mediated regulation of ER stress. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:1061216. [100] 曹天媛,倪志明,刘新宇,等.中医药调控BMSCs成骨分化防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2023,29(11):1669-1674. [101] 李昱林,俞海鹏,唐华菁,等.小檗碱促进骨再生的机制、安全性及在骨组织工程中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2024,28(35):5702-5708. [102] 张旭明,孙春全,赵晓晓,等.如意珍宝丸治疗骨关节炎的临床综合评价[J].中国中药杂志,2023,48(21):5957-5964. [103] LUO R, LIAO Z, SONG Y, et al. Berberine ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by modulating ER stress and autophagy in human nucleus pulposus cells. Life Sci. 2019;228:85-97. [104] ZHANG L, TIAN Z, LI W, et al. Inhibitory effect of quercetin on titanium particle-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS)-related apoptosis and in vivoosteolysis. Biosci Rep. 2017;37(4):BSR20170961. [105] LIU S, ZHOU L, YANG L, et al. Gastrodin alleviates glucocorticoid induced osteoporosis in rats via activating the Nrf2 signaling pathways. Oncotarget. 2018;9(14):11528-11540. [106] XIE B, WU J, LI Y, et al. Geniposide Alleviates Glucocorticoid-Induced Inhibition of Osteogenic Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells by ERK Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2019;10:411. [107] XIAO Y, REN Q, ZHENG Y, et al. Geniposide ameliorated dexamethasone-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial apoptosis in osteoblasts. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;291:115154. [108] GUPTA S. Brain food: Clever eating. Nature. 2016;531(7592):S12-13. [109] LIN Z, NI L, TENG C, et al. Eicosapentaenoic Acid-Induced Autophagy Attenuates Intervertebral Disc Degeneration by Suppressing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress, Extracellular Matrix Degradation, and Apoptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:745621. [110] WANG W, QING X, WANG B, et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic Acid Protects Nucleus Pulposus Cells from Compression-Induced Apoptosis and Necroptosis via Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018;2018:6719460. [111] LIU C, CAO Y, YANG X, et al. Tauroursodeoxycholic acid suppresses endoplasmic reticulum stress in the chondrocytes of patients with osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Med. 2015;36(4):1081-1087. [112] TANG YH, YUE ZS, ZHENG WJ, et al. 4-Phenylbutyric acid presents therapeutic effect on osteoarthritis via inhibiting cell apoptosis and inflammatory response induced by endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 2018;65(4):540-546. [113] LEE EG, SUNG MS, YOO HG, et al. Increased RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis by interleukin-1β and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Joint Bone Spine. 2014;81(6):520-526. [114] YANG Y, FENG N, LIANG L, et al. Progranulin, a moderator of estrogen/estrogen receptor α binding, regulates bone homeostasis through PERK/p-eIF2 signaling pathway. J Mol Med (Berl). 2022;100(8):1191-1207. [115] MENG X, ZHU Y, TAO L, et al. Periostin has a protective role in melatonininduced cell apoptosis by inhibiting the eIF2αATF4 pathway in human osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):1003-1012. |
| [1] | 马 驰, 王 宁, 陈 拥, 魏志晗, 刘逢纪, 朴成哲. 3D打印个体化截骨导板结合定制钢板在开放楔形胫骨高位截骨中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1863-1869. |
| [2] | 余 帅, 刘家伟, 朱 彬, 潘 檀, 李兴龙, 孙广峰, 于海洋, 丁 亚, 王宏亮. 小分子药物治疗骨关节炎的热点问题及应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1913-1922. |
| [3] | 赵济宇, 王少伟. 叉头框转录因子O1信号通路与骨代谢[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1923-1930. |
| [4] | 孙韫頔, 程露露, 万海丽, 常 赢, 熊雯娟, 夏 渊. 神经肌肉训练对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛和功能影响的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1945-1952. |
| [5] | 邓柯淇, 李光第, GOSWAMI ASHUTOSH, 刘星余, 何孝勇. 基于生物信息学对骨关节炎铁超载关键基因的筛选与验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(9): 1972-1980. |
| [6] | 王秋月, 靳 攀, 蒲 锐. 运动干预与细胞焦亡在骨关节炎中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1667-1675. |
| [7] | 陈跃平, 陈 锋, 彭清林, 陈荟伊, 董盼锋. 三七治疗骨关节炎机制:基于UHPLC-QE-MS、网络药理学及分子动力学模拟[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1751-1760. |
| [8] | 尹 路, 蒋川锋, 陈俊杰, 易 明, 王子赫, 石厚银, 汪国友, 沈骅睿. 沙苑子苷A对关节软骨细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1541-1547. |
| [9] | 王佩光, 张小文, 麦美斯, 黎璐茜, 黄 浩. 广义估计方程评估浮针法联合穴位埋线治疗不同分期膝骨关节炎的疗效[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(8): 1565-1571. |
| [10] | 杨治航, 孙祖延, 黄文良, 万 喻, 陈仕达, 邓 江. 神经生长因子促进兔骨髓间充质干细胞软骨分化并抑制肥大分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1336-1342. |
| [11] | 章镇宇, 梁秋健, 杨 军, 韦相宇, 蒋 捷, 黄林科, 谭 桢. 新橙皮苷治疗骨质疏松症的靶点及对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(7): 1437-1447. |
| [12] | 贺光辉, 原 杰, 柯燕琴, 丘小婷, 张晓玲. Hemin调控小鼠软骨细胞氧化应激的线粒体途径[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1183-1191. |
| [13] | 黄小彬, 葛继荣, 李生强, 谢丽华, 黄景文, 何艳艳, 薛立鹏. 不同滋阴补肾法干预去势大鼠破骨通路的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1214-1219. |
| [14] | 马浩宇, 乔鸿超, 郝茜茜, 史冬博. 不同运动强度与骨关节炎发病风险的效应分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(6): 1305-1311. |
| [15] | 项 攀, 车艳军, 罗宗平. 压应力激活SOST/Wnt/β-catenin通路诱导软骨终板细胞退变[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2025, 29(5): 951-957. |
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1 资料来源
1.1.1 检索人 第一作者在2023年12月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 2000年1月至2023年12月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science数据库;中国知网、万方、维普数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“内质网应激,骨骼疾病,未折叠蛋白反应,骨关节炎,骨质疏松症,椎间盘退变,自噬,凋亡,铁死亡,焦亡”;英文检索词为“endoplasmic reticulum stress,bone disease,unfolded protein response,osteoarthritis,osteoporosis,intervertebral disc degeneration,autophagy,apoptosis,ferroptosis,pyroptosis”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著、综述、荟萃分析、研究论文、基础实验等。
1.1.6 检索策略 以 PubMed 数据库及中国知网为例,检索策略见图1。
1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 ①探讨内质网应激信号通路的文献;②探讨内质网应激信号通路参与调控常见退行性骨骼疾病发病机制方面的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 ①重复性研究,较陈旧的文献;②与题目内容不一致、可信度较低的文献。
1.3 质量评估 利用计算机和手工检索方法,对文章标题、摘要和关键词进行初步筛选,然后对相关文献进行详细阅读。在筛选过程中,剔除与研究主题无关、内容重复或可信度较低的文献,并优先选择近5年内发表的文献。经过筛选,共排除1 580篇文献,最终纳入115篇文献,其中中文文献3篇(来源于中国知网、万方、维普数据库),英文文献112篇(来源于PubMed、Web of Science数据库)。文献检索流程见图2。
3.1 既往他人在该领域研究的贡献和存在的问题 骨关节炎、骨质疏松症以及椎间盘退变等骨骼系统疾病在老年人中的发病率逐渐上升,给社会和个人健康带来了沉重负担[9,25-26]。以往的研究指出,内质网应激与骨骼系统疾病的进展密切相关。在细胞内,内质网主要负责对蛋白质进行折叠和翻译后修饰,其功能易受到各种理化因素的影响而失衡,引起内质网应激的激活。细胞中内质网应激可以通过IRE1α、PERK和ATF6等多条信号传导途径来调节相关骨细胞的功能和骨代谢的平衡。适度的内质网应激有助于细胞的存活并使其适应外界环境的变化,然而,过度持续的内质网应激将会促进骨关节炎、骨质疏松症和椎间盘退变等疾病的发生[9,12-13]。尽管已有大量研究对内质网应激在骨骼系统疾病中的作用进行探讨,但仍存在一些问题亟待解决。首先,内质网应激在调节骨代谢中的具体作用机制尚未完全阐明,对于部分调节机制的研究存在争议,进一步的研究仍需要探索参与骨重塑的细胞内质网应激反应的详细机制,以及在细胞铁死亡、凋亡、焦亡等途径之间的相互作用问题。此外,未来的研究应该深入探讨内质网应激在骨疾病治疗中的潜在靶点,为预防和治疗常见退行性骨骼疾病提供新的途径和依据。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 文章综述了近年来常见退行性骨骼疾病的内质网应激研究进展。除了突出强调内质网应激在骨骼疾病发生和发展中的作用外,还特别指出了内质网应激作为潜在治疗靶点的研究进展。此综述详细探讨了内质网应激在骨关节炎、骨质疏松症、椎间盘退变等方面的作用,包括在软骨细胞、成骨细胞、髓核细胞等细胞中调节凋亡、铁死亡、焦亡、自噬等过程。此外,综述还涵盖了内质网应激对细胞外基质形成与降解、炎症反应等病理生理过程的影响,这些作用最终导致了相关骨病的发生和发展。这些研究为内质网应激在相关临床转化研究中的巨大潜能提供了强有力的支持,为患者的治疗方案带来了新的治疗前景。
3.3 综述的局限性 内质网应激在致病过程中的机制十分复杂,在多个通路之间存在联系和相互作用。目前,铁死亡、焦亡、自噬与凋亡的相互串扰是一个新兴领域,它们之间的相互作用影响着包括骨关节炎、骨质疏松症、椎间盘退变在内的多种疾病的病理变化。然而,目前相关领域的研究集中在体内和体外实验,深度和广度均不足。另外,由于篇幅限制,文章未能将现存的所有调节因子及其相互联系列举和论述。
3.4 综述的重要意义 文章综述了内质网应激在骨关节炎、骨质疏松症、椎间盘退变等常见骨骼疾病中的联系及相关机制。内质网应激在相关骨病发生过程中表现出双重作用,一方面通过清除处于病理状态或受损的细胞来维持机体稳态和延续;另一方面,它也可能对正常细胞造成损伤,从而引发病理过程。通过分析疾病危险因素、理化环境变化等外部因素,以及细胞组织结构、机体发育规律等内部因素,探讨了内质网应激与相关骨骼疾病致病过程的关联,有助于加深对常见骨骼疾病发病机制的理解。另外,该文总结了近年来关于内质网应激作为治疗靶点的研究,旨在为相关治疗策略带来新的见解,更好地实现预防和治疗相关骨病的目标。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 ①针对内质网应激中单一的自噬、凋亡等信号通路的研究显著多于相互作用的研究, 铁死亡、焦亡、自噬与凋亡在骨骼疾病中的相互调控作用值得深入探索;②基于内质网应激治疗的研究绝大部分尚处于实验室阶段,其不良反应和并发症还未可知,有待向临床转化;③当前的研究仍然受到一些技术上的限制。传统的研究方法通常限于对整体组织水平的分析,难以揭示细胞间的差异和相互作用。未来,应该运用新技术,例如单细胞测序技术、空间转录组学技术、类器官技术等,来揭示内质网应激在退行性骨骼疾病中的作用机制,为疾病的治疗和预防提供更有效的方法。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||