中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (9): 1417-1421.doi: 10.12307/2023.206
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
肌骨超声评价呼吸训练改善慢性非特异性下背痛患者多裂肌的形态学改变
李 超1,张佩佩2,徐朦婷3,李琳琳1,丁江涛3,刘西花1,毕鸿雁1
- 1山东中医药大学附属医院康复科,山东省济南市 250011;2山东中医药大学第二附属医院康复医学科,山东省济南市 250001;3山东中医药大学康复医学院,山东省济南市 250301
Respiratory training improves morphological changes of the multifidus muscle in patients with chronic nonspecific lower back pain assessed by musculoskeletal ultrasound
Li Chao1, Zhang Peipei2, Xu Mengting3, Li Linlin1, Ding Jiangtao3, Liu Xihua1, Bi Hongyan1
- 1Department of Rehabilitation, Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250011, Shandong Province, China; 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250001, Shandong Province, China; 3School of Rehabilitation Medicine, Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jinan 250301, Shandong Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
核心稳定性:核心区域肌肉群可被描述为一个规整的立方体,位于整个肌群前面的是腹部肌群,在其对面是人体的臀部以及背部肌群,其上下分别是横隔肌和盆底肌。核心稳定的要点或原则是在保持脊柱中立稳定的同时,为人体的关节活动提供防护作用,并有稳定的结构防护基础,核心稳定性是人体的主动肌群、被动肌群、神经三者在日常工作中的有效协作,这种有效合作才使得机体的脊柱运动持续保持在一个合适范围之内。
腹式呼吸训练:该方法即训练腹式呼吸,强调膈肌运动,目的是改善异常呼吸模式,减少其它辅助呼吸肌的用功,改善呼吸效率,降低呼吸能耗。患者仰卧位或半坐位或坐位,先将双手置于腹部以感觉腹式呼吸时腹部的动作;治疗师站在患者右侧,右手平放于患者上腹部。吸气时腹部放松,治疗师手上抬,患者经鼻缓慢深吸气,隆起腹部。最高点时暂3 s;呼气时治疗师手下压,患者缩唇将气缓慢吹出,同时收缩腹肌,促进横膈上抬。
背景:已有研究证实腰椎稳定训练可以改善慢性下背痛患者多裂肌的肌肉形态,呼吸训练是否影响慢性下背痛患者的多裂肌形态暂无临床研究。
目的:观察呼吸训练对慢性非特异性下背痛患者的腰椎稳定肌(多裂肌)肌肉厚度与横截面积改变的影响。
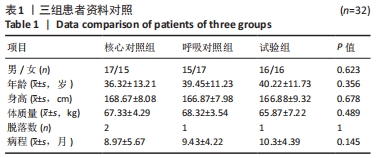
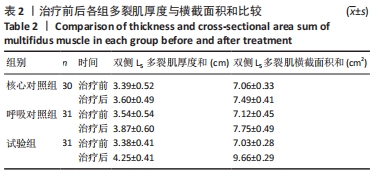
方法:96例符合纳入标准的慢性非特异性下背痛患者随机分为试验组(n=32)、呼吸对照组(n=32)和核心对照组(n=32),呼吸对照组接受呼吸训练,核心对照组接受核心稳定训练,试验组接受呼吸训练合并核心稳定训练,治疗1次/d,20 min/次,5 d/周,持续10周。3组患者治疗前后均采用肌骨超声观察记录患者腰椎稳定肌(多裂肌)的肌肉厚度与横截面积,对3组患者治疗前后多裂肌的形态学变化进行评价。
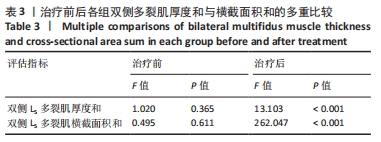
结果与结论:①治疗后双侧L5多裂肌厚度和呼吸对照组与核心对照组无明显差异,试验组显著大于其他两组;治疗后双侧L5多裂肌横截面积和试验组>呼吸对照组>核心对照组,差异有显著性意义(P < 0.001);②应用肌骨超声观察治疗前后3组患者多裂肌的形态学变化,证实呼吸训练对腰椎多裂肌的厚度和横截面积均有改善作用,同时肌骨超声技术作为新的疗效观察工具,可以作为慢性非特异性下背痛患者评估及辅助治疗的有效手段。
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0886-675X (李超)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: