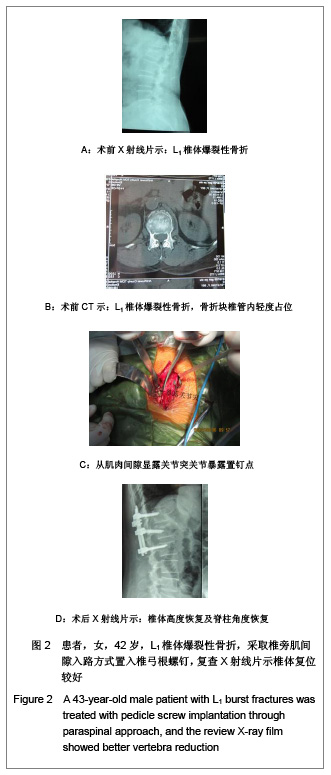
| [1] Wiltse LL, Bateman JG, Hutchinson RH, et al.The paraspinal sacrospinalis-splitting approach to the lumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1968;50(5):919-926.[2] Vialle R, Wicart P, Drain O,et al. The Wiltse paraspinal approach to the lumbar spine revisited: an anatomic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;445:175-180.[3] Mao ZG,Zhu JM,Fan SW. Zhejiang Linchuang Yixue. 2008; 10(4):502. 毛兆光,祝介明,范顺武.椎旁肌间隙入路在腰椎骨折内固定术中的应用[J].浙江临床医学,2008,10(4):502-503.[4] Li QC,Hu HL,Liu BG,et al. Zhongguo Jizhu Jisui Zazhi. 2011; 21(4):303-307. 黎庆初,胡辉林,刘宝戈,等.多裂肌间隙入路微创手术治疗腰椎滑脱症[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,21(4):303-307.[5] Huskisson EC. Measurement of pain. Lancet. 1974;2(7889): 1127-1131.[6] Fukui M, Chiba K, Kawakami M,et al. Japanese Orthopaedic Association Back Pain Evaluation Questionnaire. Part 2. Verification of its reliability : The Subcommittee on Low Back Pain and Cervical Myelopathy Evaluation of the Clinical Outcome Committee of the Japanese Orthopaedic Association. J Orthop Sci. 2007;12(6):526-532.[7] Stein J, Baker E, Pine ZM. Medial paraspinal muscle electromyography: techniques of examination. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1993;74(5):497-500.[8] Fang XQ,Hu ZJ,Fan SW,et al. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2009; 29(4):315-319. 方向前,胡志军,范顺武,等.胸腰段骨折经肌间隙入路与传统入路内固定的比较研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2009,29(4):315-319.[9] Kang CH, Shin MJ, Kim SM, et al. MRI of paraspinal muscles in lumbar degenerative kyphosis patients and control patients with chronic low back pain. Clin Radiol. 2007;62(5):479-486.[10] Kim K, Isu T, Sugawara A, et al. Comparison of the effect of 3 different approaches to the lumbar spinal canal on postoperative paraspinal muscle damage. Surg Neurol. 2008; 69(2):109-113.[11] Zheng J,Li KN,Liu L,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(39):7307-7310. 郑江,李开南,刘莉,等. 腰椎后路经皮微创与传统开放手术影响竖脊肌形态学改变的比较[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(39):7307-7310.[12] Watkins MB.Posterolateral bonegrafting for fusion of the lumbar and lumbosacral spine. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1959; 41-A(3):388-396.[13] Zhao HY,Wang YF. Zhongguo Dangdai Yiyao. 2010;17(5): 13-16. 赵海燕,王蕴峰.血清肌酸激酶活性测定和临床应用[J].中国当代医药,2010,17(5):13-16.[14] Kotil K, Tunckale T, Tatar Z, et al. Serum creatine phosphokinase activity and histological changes in the multifidus muscle: a prospective randomized controlled comparative study of discectomy with or without retraction. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(2):121-125.[15] Thesleff S, Ward MR. Studies on the mechanism of fibrillation potentials in denervated muscle. J Physiol. 1975;244(2): 313-323.[16] Kramer M, Katzmaier P, Eisele R, et al. Surface electromyography-verified muscular damage associated with the open dorsal approach to the lumbar spine. Eur Spine J. 2001;10(5):414-420.[17] Leinonen V, Määttä S, Taimela S, et al. Paraspinal muscle denervation, paradoxically good lumbar endurance, and an abnormal flexion-extension cycle in lumbar spinal stenosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2003;28(4):324-331.[18] Warren A, Prasad V, Thomas M. Pre-operative planning when using the Wiltse approach to the lumbar spine. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2010;92(1):74-75.[19] Zhang Y,Yin QS,Xu GZ,et al. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2001;8(4):334-336. 张余,尹庆水,徐国洲,等.胸腰椎椎弓根钉内固定术并发症的分析[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2001,8(4):334-336.[20] Crossman K, Mahon M, Watson PJ, et al. Chronic low back pain-associated paraspinal muscle dysfunction is not the result of a constitutionally determined "adverse" fiber-type composition.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2004;29(6):628-634. |