[1] ARMSTRONG D, ALVAREZ R, BAKKUM-GAMEZ J, et al. Ovarian Cancer, Version 2.2020, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2021;19(2): 191-226.
[2] SUN Q, BAI X, SOFIAS A, et al. Cancer nanomedicine meets immunotherapy: opportunities and challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2020;41(7):954-958.
[3] YANG C, XIA B, ZHANG Z, et al. Immunotherapy for Ovarian Cancer: Adjuvant, Combination, and Neoadjuvant. Front Immunol. 2020;11:577869.
[4] BANTA K, XU X, CHITRE A, et al. Mechanistic convergence of the TIGIT and PD-1 inhibitory pathways necessitates co-blockade to optimize anti-tumor CD8 T cell responses. Immunity. 2022;55(3):512-526.e519.
[5] WEISS S, DJUREINOVIC D, JESSEL S, et al. A Phase I Study of APX005M and Cabiralizumab with or without Nivolumab in Patients with Melanoma, Kidney Cancer, or Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Resistant to Anti-PD-1/PD-L1. Clin Cancer Res. 2021;27(17):4757-4767.
[6] WU M, HUANG Q, XIE Y, et al. Improvement of the anticancer efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade via combination therapy and PD-L1 regulation. J Hematol Oncol. 2022;15(1):24.
[7] SAXENA R, WANG Y, MIER J. CXCR4 inhibition modulates the tumor microenvironment and retards the growth of B16-OVA melanoma and Renca tumors. Melanoma Res. 2020;30(1):14-25.
[8] LI Z, WANG Y, SHEN Y, et al. Targeting pulmonary tumor microenvironment with CXCR4-inhibiting nanocomplex to enhance anti-PD-L1 immunotherapy. Sci Adv. 2020;6(20):eaaz9240.
[9] 徐桂兰,宋建生,杨世疆.超声微泡沉默S100A4基因对胃癌干细胞干性和上皮间质转化的调控[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(25):4025-4031.
[10] BARZEGAR-FALLAH A, GANDHI K, RIZWAN S, et al. Harnessing Ultrasound for Targeting Drug Delivery to the Brain and Breaching the Blood-Brain Tumour Barrier. Pharmaceutics. 2022;14(10):2231.
[11] OMATA D, UNGA J, SUZUKI R, et al. Lipid-based microbubbles and ultrasound for therapeutic application. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2020;154-155:236-244.
[12] XUE V, CHUNG J, TANG P, et al. USMB-shMincle: a virus-free gene therapy for blocking M1/M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2021;23:26-37.
[13] LI N, TANG J, YANG J, et al. Tumor perfusion enhancement by ultrasound stimulated microbubbles potentiates PD-L1 blockade of MC38 colon cancer in mice. Cancer Lett. 2021;498:121-129.
[14] ILOVITSH T, FENG Y, FOIRET J, et al. Low-frequency ultrasound-mediated cytokine transfection enhances T cell recruitment at local and distant tumor sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(23):12674-12685.
[15] TAN X, YI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction Alleviates Immunosuppression Induced by CD71 Erythroid Progenitor Cells and Promotes PDL-1 Blockade Immunotherapy in the Lewis Lung Cancer Model. Front Oncol. 2021;11: 768222.
[16] MA Y, HAN J, JIANG J, et al. Ultrasound targeting of microbubble-bound anti PD-L1 mAb to enhance anti-tumor effect of cisplatin in cervical cancer xenografts treatment. Life Sci. 2020;262:118565.
[17] YAMAGUCHI K, MATSUMOTO Y, SUZUKI R, et al. Enhanced antitumor activity of combined lipid bubble ultrasound and anticancer drugs in gynecological cervical cancers. Cancer Sci. 2021;112(6):2493-2503.
[18] DONG L, LI N, WEI X, et al. A Gambogic Acid-Loaded Delivery System Mediated by Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction: A Promising Therapy Method for Malignant Cerebral Glioma. Int J Nanomedicine. 2022;17:2001-2017.
[19] 李翠仙,黄备建,陆清,等.靶向血管内皮生长因子受体2/整合素α_vβ_3微泡体内评价肾细胞癌血管生成的实验研究[J].中华超声影像学杂志,2022,31(4): 338-344.
[20] 关丽娜,魏圆圆,窦静,等.优化靶向载基因超声纳米泡效能:实验研究[J].中国医学影像技术,2022,38(9):1281-1285.
[21] BONIFÁCIO V. Ovarian Cancer Biomarkers: Moving Forward in Early Detection. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1219:355-363.
[22] HAN Y, SUN J, WEI H, et al. Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction: Modulation in the Tumor Microenvironment and Application in Tumor Immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 2022;13:937344.
[23] YANG Y, LI Q, GUO X, et al. Mechanisms underlying sonoporation: Interaction between microbubbles and cells. Ultrason Sonochem. 2020;67:105096.
[24] 曾宏兴,郑德俊,苑伟,等. 超声靶向爆破载藤黄酸微泡对人结肠癌HCT116细胞增殖和凋亡的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2021,38(11):2163-2166.
[25] SHI D, GUO L, SUN X, et al. UTMD inhibit EMT of breast cancer through the ROS/miR-200c/ZEB1 axis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):6657.
[26] DAASSI D, MAHONEY KM, FREEMAN GJ. The importance of exosomal PDL1 in tumour immune evasion. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20:209-215.
[27] SHI Y, RIESE DJ,SHEN J. The Role of the CXCL12/CXCR4/CXCR7 Chemokine Axis in Cancer. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:574667.
[28] HAO S, XU S, LI L, et al. Tumour inhibitory activity on pancreatic cancer by bispecific nanobody targeting PD-L1 and CXCR4. BMC Cancer. 2022;22(1):1092.
[29] BIASCI D, SMORAGIEWICZ M, CONNELL C, et al. CXCR4 inhibition in human pancreatic and colorectal cancers induces an integrated immune response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(46):28960-28970.
[30] 邓海怡,王李强,杨伊霖,等.双免疫联合治疗在晚期非小细胞肺癌中的一线应用[J].中国肺癌杂志,2022,25(2):102-110.
[31] LU G, QIU Y, SU X. Targeting CXCL12-CXCR4 Signaling Enhances Immune Checkpoint Blockade Therapy Against Triple Negative Breast Cancer. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021;157: 105606.
[32] SCHOEN S, KILINC M, LEE H, et al. Towards controlled drug delivery in brain tumors with microbubble-enhanced focused ultrasound. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022;180: 114043.
[33] YOO S, MITTELSTEIN D, HURT R, et al. Focused ultrasound excites cortical neurons via mechanosensitive calcium accumulation and ion channel amplification. Nat Commun. 2022;13(1):493.
|
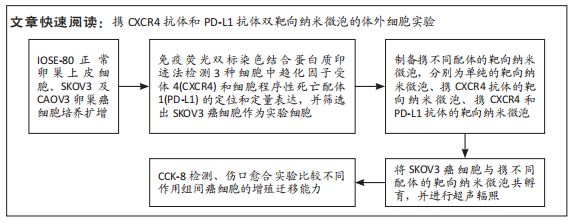
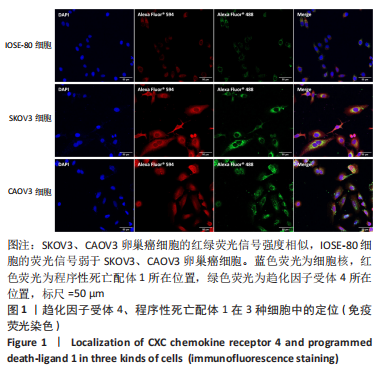
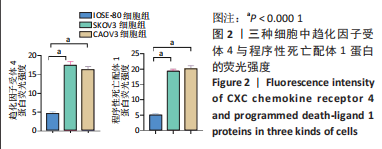
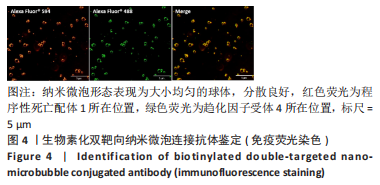
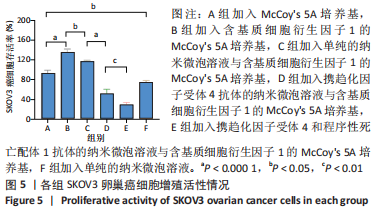
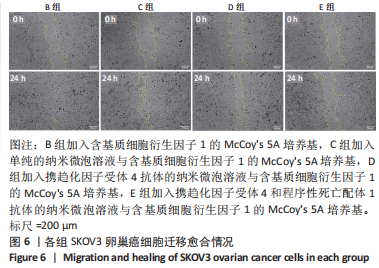
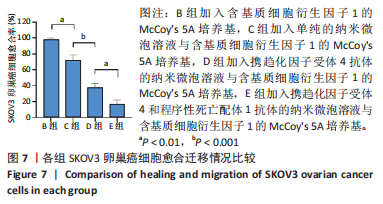
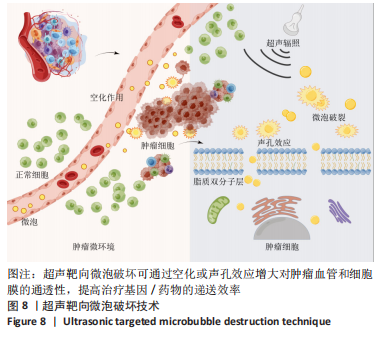 超声靶向微泡破坏突破了血管的限制,与血管外组织或肿瘤的标记物结合,从而有利于早期诊断、临床分期和疾病治疗。通过双标记荧光免疫法,此次实验发现3种细胞均可表达CXCR4和PD-L1蛋白。SKOV3、CAOV3卵巢癌细胞中出现了较强的绿色及红色荧光信号,且两种癌细胞的荧光强度相似,而IOSE-80细胞的荧光强度则弱于两种癌细胞。此外,这也验证了CXCR4、PD-L1与其抗体的结合通路,从而可在体内免疫循环中使失活的T细胞重新活跃起来,增强抗肿瘤作用。DAASSI等[26]、SHI等[27]研究认为CXCR4主要位于细胞膜上,PD-L1主要位于细胞膜和细胞质中,此次实验双重染色结果与之相似。蛋白质印迹法检测结果显示,SKOV3、CAOV3卵巢癌细胞中CXCR4、PD-L1蛋白的表达量均显著高于IOSE-80细胞,而两种癌细胞之间无显著差异,这为CXCR4、PD-L1成为卵巢癌治疗的靶点提供了可能。此外,HAO等[28]证明了抗PD-L1/CXCR4双功能纳米体对肿瘤细胞的抑制作用与CXCR4的表达有关,因此筛选SKOV3癌细胞作为实验细胞。此次实验也发现,卵巢癌细胞过表达的CXCR4和PD-L1蛋白在正常卵巢上皮细胞表面也存在,因此在以其为靶点的治疗策略中,为避免对正常组织的影响以保证特异性,可利用超声靶向微泡破坏技术精确定位到肿瘤组织,仅局部释放药物以减少对正常组织的损害,实现更高的治疗效率。
超声靶向微泡破坏突破了血管的限制,与血管外组织或肿瘤的标记物结合,从而有利于早期诊断、临床分期和疾病治疗。通过双标记荧光免疫法,此次实验发现3种细胞均可表达CXCR4和PD-L1蛋白。SKOV3、CAOV3卵巢癌细胞中出现了较强的绿色及红色荧光信号,且两种癌细胞的荧光强度相似,而IOSE-80细胞的荧光强度则弱于两种癌细胞。此外,这也验证了CXCR4、PD-L1与其抗体的结合通路,从而可在体内免疫循环中使失活的T细胞重新活跃起来,增强抗肿瘤作用。DAASSI等[26]、SHI等[27]研究认为CXCR4主要位于细胞膜上,PD-L1主要位于细胞膜和细胞质中,此次实验双重染色结果与之相似。蛋白质印迹法检测结果显示,SKOV3、CAOV3卵巢癌细胞中CXCR4、PD-L1蛋白的表达量均显著高于IOSE-80细胞,而两种癌细胞之间无显著差异,这为CXCR4、PD-L1成为卵巢癌治疗的靶点提供了可能。此外,HAO等[28]证明了抗PD-L1/CXCR4双功能纳米体对肿瘤细胞的抑制作用与CXCR4的表达有关,因此筛选SKOV3癌细胞作为实验细胞。此次实验也发现,卵巢癌细胞过表达的CXCR4和PD-L1蛋白在正常卵巢上皮细胞表面也存在,因此在以其为靶点的治疗策略中,为避免对正常组织的影响以保证特异性,可利用超声靶向微泡破坏技术精确定位到肿瘤组织,仅局部释放药物以减少对正常组织的损害,实现更高的治疗效率。