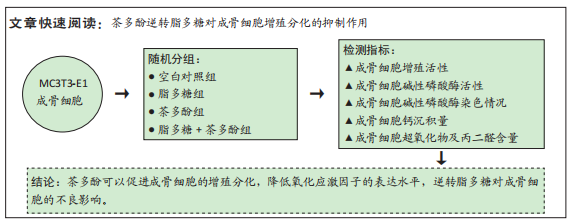
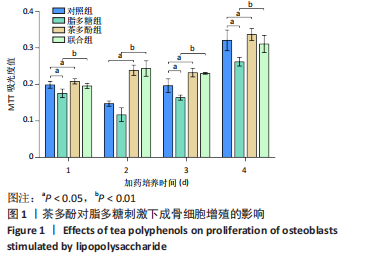
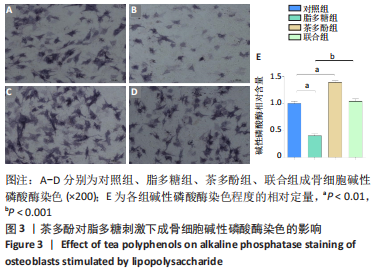
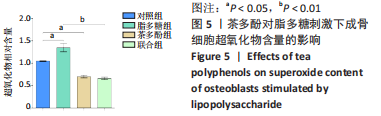
[1] ASCONE G, DI CEGLIE I, WALGREEN B, et al. High LDL levels lessen bone destruction during antigen-induced arthritis by inhibiting osteoclast formation and function. Bone. 2020;130:115140.
[2] ROBERTS JL, MELLA-VELAZQUEZ G, DAR HY, et al. Deletion of IL-17ra in osteoclast precursors increases bone mass by decreasing osteoclast precursor abundance. Bone. 2022;157:116310.
[3] 张晓音,吴旻,李雨萌,等.脂多糖的效应及其机理研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2015,36(12):133-136.
[4] 张倩璐,江婷,赵国军.脂多糖抑制成骨细胞分化作用研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2019,35(21):2743-2746.
[5] DAIGANG L, JINING Q, JINLAI L, et al. LPS-stimulated inflammation inhibits BMP-9-induced osteoblastic differentiation through crosstalk between BMP/MAPK and Smad signaling. Exp Cell Res. 2016;341(1):54-60.
[6] 刘子歌,田佳宁,袁衡,等.白藜芦醇对LPS诱导的MC3T3-E1成骨细胞的骨保护作用[J].江苏医药,2021,47(3):222-226.
[7] MA J, WANG Z, ZHAO J, et al. Resveratrol Attenuates Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-Induced Inhibition of Osteoblast Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:2045-2052.
[8] ZHOU CC, XU RS, WU ZP, et al. Osteogenesis, Osteoclastogenesis and their Crosstalk in Lipopolysaccharide-induced Periodontitis in Mice. Chin J Dent Res. 2021;24(1):33-39.
[9] GUO C, YANG RJ, JANG K, et al. Protective Effects of Pretreatment with Quercetin Against Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Apoptosis and the Inhibition of Osteoblast Differentiation via the MAPK and Wnt/β-Catenin Pathways in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(4):1547-1561.
[10] WANG Q, YANG X, ZHU C, et al. Advances in the Utilization of Tea Polysaccharides: Preparation, Physicochemical Properties, and Health Benefits. Polymers (Basel). 2022;14(14):2775.
[11] YE Y, WARUSAWITHARANA H, ZHAO H, et al. Tea Polyphenols Attenuates Inflammation via Reducing Lipopolysaccharides Level and Inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB Pathway in Obese Mice. Plant Foods Hum Nutr. 2022;77(1):105-111.
[12] KUMARI A, KUMAR D, GULATI A, et al. Mechanistic studies on polyphenol rich fractions of Kangra tea by HPTLC and NMR for their antioxidant activities. J Food Sci Technol. 2022;59(7):2751-2763.
[13] TRUONG VL, JEONG WS. Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory roles of tea polyphenols in inflammatory bowel diseases. Food Sci Biotechnol. 2022;11(3): 502-511.
[14] 曹振,潘光玉,郭勇.茶多酚对骨组织细胞的影响及其在组织工程中的应用进展[J].国际生物医学工程杂志,2020,43(3):239-243.
[15] 范芹,管晓燕,李小娜,等.TP 对脂多糖介导人牙周膜成纤维细胞细胞间黏附分子-1 表达的影响[J]. 口腔医学研究,2018,34(10):1089.
[16] GUO C, WANG SL, XU ST, et al. SP600125 reduces lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis and restores the early-stage differentiation of osteoblasts inhibited by LPS through the MAPK pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2015;35(5):1427-1434.
[17] LIU R, ZHONG Y, CHEN R, et al. Bacterial infections exacerbate myeloma bone disease. J Transl Med. 2022;20(1):16.
[18] CHEN ZY, GAO S, ZHANG YW, et al. Antibacterial biomaterials in bone tissue engineering. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(11):2594-2612.
[19] BANDOW K, MAEDA A, KAKIMOTO K, et al. Molecular mechanisms of the inhibitory effect of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on osteoblast differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;402(4):755-761.
[20] HUANG X, XIE M, XIE Y, et al. The roles of osteocytes in alveolar bone destruction in periodontitis. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):479.
[21] 郑秀梅,黄文霞.巨噬细胞介导的炎性微环境对牙周膜细胞增殖和成骨分化的影响[J].口腔疾病防治,2018,26(5):297-303.
[22] BAEK KH, OH KW, LEE WY, et al. Association of oxidative stress with postmenopausal osteoporosis and the effects of hydrogen peroxide on osteoclast formation in human bone marrow cell cultures. Calcif Tissue Int. 2010;87(3): 226-235.
[23] KONG Y, ZHANG Y, CAI Y, et al. METTL3 mediates osteoblast apoptosis by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress during LPS-induced inflammation. Cell Signal. 2022;95:110335.
[24] CHANG Y, HU CC, WU YY, et al. Ibudilast Mitigates Delayed Bone Healing Caused by Lipopolysaccharide by Altering Osteoblast and Osteoclast Activity. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(3):1169.
[25] WANG Y, ZHANG L, WANG K, et al. Circulating Exosomes from Mice with LPS-Induced Bone Loss Inhibit Osteoblast Differentiation. Calcif Tissue Int. 2022; 111(2):185-195.
[26] LIU S, DU J, LI D, et al. Oxidative stress induced pyroptosis leads to osteogenic dysfunction of MG63 cells. J Mol Histol. 2020;51(3):221-232.
[27] YANG Y, SUN Y, MAO WW, et al. Oxidative stress induces downregulation of TP53INP2 and suppresses osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs during osteoporosis through the autophagy degradation pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2021;166:226-237.
[28] ZHAO Y, GAO J, ZHANG Y, et al. Cyclosporine A Promotes Bone Remodeling in LPS-Related Inflammation via Inhibiting ROS/ERK Signaling: Studies In Vivo and In Vitro. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:8836599.
[29] TSIKAS D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal Biochem. 2017;524:13-30.
[30] ZHANG H, LIU L, JIANG C, et al. MMP9 protects against LPS-induced inflammation in osteoblasts. Innate Immun. 2020;26(4):259-269.
[31] CHEN M, LIN X, ZHANG L, et al. Effects of nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway on periodontal ligament stem cells under lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation. Bioengineered. 2022;13(3):7951-7961.
[32] GUO C, YUAN L, WANG JG, et al. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces the apoptosis and inhibits osteoblast differentiation through JNK pathway in MC3T3-E1 cells. Inflammation. 2014;37(2):621-631.
[33] XING Q, YE Q, FAN M, et al. Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide inhibits the osteoblastic differentiation of preosteoblasts by activating Notch1 signaling. J Cell Physiol. 2010;225(1):106-114.
[34] ZHANG Y, GU X, LI D, et al. METTL3 Regulates Osteoblast Differentiation and Inflammatory Response via Smad Signaling and MAPK Signaling. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;21(1):199.
[35] RAMESH P, JAGADEESAN R, SEKARAN S, et al. Flavonoids: Classification, Function, and Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Bone Remodelling. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:779638.
[36] HUANG HT, CHENG TL, LIN SY, et al. Osteoprotective Roles of Green Tea Catechins. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(11):1136.
[37] 谢睿锋,李岩,王东.不同浓度表儿茶素没食子酸酯对体外培养成骨细胞的影响[J].中国现代医生,2018,56(11):34-37,42.
[38] OCHI H, HARA Y, TAGAWA M, et al. The roles of TNFR1 in lipopolysaccharide-induced bone loss: dual effects of TNFR1 on bone metabolism via osteoclastogenesis and osteoblast survival. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(5):657-663.
|