[1] LEBOFF MS, GREENSPAN SL, INSOGNA KL, et al. The clinician’s guide to prevention and treatment of osteoporosis. Osteoporos Int. 2022;33(10):2049-2102.
[2] MA ML, MA ZJ, HE YL, et al. Efficacy of vitamin K2 in the prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Front Public Health. 2022;10:979649.
[3] XU H, LIU T, HU L, et al. Effect of caffeine on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108650.
[4] WANG H, YANG L, CHAO J. Antiosteoporosis and bone protective effect of dieckol against glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in rats. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:932488.
[5] WU D, CLINE-SMITH A, SHASHKOVA E, et al. T-Cell Mediated Inflammation in Postmenopausal Osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2021; 12:687551.
[6] YANG K, QIU X, CAO L, et al. The role of melatonin in the development of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:975181.
[7] WANG X, ZHANG X, HAN Y, et al. Role of the major histocompatibility complex class II protein presentation pathway in bone immunity imbalance in postmenopausal osteoporosis. Front Endocrinol. 2022; 13:876067.
[8] LIM SY. Romosozumab for the treatment of osteoporosis in women: Efficacy, safety, and cardiovascular risk. Womens Health. 2022;18:17455057221125577.
[9] ROZENBERG S, AL-DAGHRI N, AUBERTIN-LEHEUDRE M, et al. Is there a role for menopausal hormone therapy in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis?. Osteoporos Int. 2020;31(12):2271-2286.
[10] FISCHER V, HAFFNER-LUNTZER M. Interaction between bone and immune cells: Implications for postmenopausal osteoporosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2022;123:14-21.
[11] 麦合木提江•穆海麦提,买买提沙吾提阿吉•买买提,唐军伟,等.has-miR-100-5p靶向含7A的锌指和BTB结构域是绝经后骨质疏松的潜在靶标[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(32):5168-5172.
[12] YUAN F, PENG W, YANG C, et al. Teriparatide versus bisphosphonates for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis: A meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2019;66:1-11.
[13] AIBAR-ALMAZÁN A, VOLTES-MARTÍNEZ A, CASTELLOTE-CABALLERO Y, et al. Current Status of the Diagnosis and Management of Osteoporosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(16):9465.
[14] SILVA BC, MADEIRA M, D’ALVA CB, et al. Definition and management of very high fracture risk in women with postmenopausal osteoporosis: a position statement from the Brazilian Society of Endocrinology and Metabolism (SBEM) and the Brazilian Association of Bone Assessment and Metabolism (ABRASSO). Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2022;66(5):591-603.
[15] 许萍,杨成武,黄淑芸,等.安石榴苷基于调整肠道菌群改善APP/PS1阿尔兹海默病小鼠认知功能的实验研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2022,38(18):2181-2186.
[16] BERDOWSKA I, MATUSIEWICZ M, FECKA I. Punicalagin in Cancer Prevention-Via Signaling Pathways Targeting. Nutrients. 2021;13(8): 2733.
[17] ALALAWI S, ALBALAWI F, RAMJI DP. The Role of Punicalagin and Its Metabolites in Atherosclerosis and Risk Factors Associated with the Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(10):8476.
[18] BHATNAGAR A, KEKATPURE AL. Postmenopausal Osteoporosis: A Literature Review. Cureus. 2022;14(9):e29367.
[19] SUN D, PENG Y, GE S, et al. USP1 Inhibits NF-κB/NLRP3 Induced Pyroptosis through TRAF6 in Osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 Cells. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2022;22(4):536-545.
[20] ALI D, TENCEROVA M, FIGEAC F, et al. The pathophysiology of osteoporosis in obesity and type 2 diabetes in aging women and men: The mechanisms and roles of increased bone marrow adiposity. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:981487.
[21] YANG X, CHANG T, YUAN Q, et al. Changes in the composition of gut and vaginal microbiota in patients with postmenopausal osteoporosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:930244.
[22] ZHENG L, ZHUANG Z, LI Y, et al. Bone targeting antioxidative nano-iron oxide for treating postmenopausal osteoporosis. Bioact Mater. 2021;14:250-261.
[23] JEONG HG, KIM MK, LIM HJ, et al. Up-to-Date Knowledge on Osteoporosis Treatment Selection in Postmenopausal Women. J Menopausal Med. 2022;28(3):85-91.
[24] XU J, CAO K, LIU X, et al. Punicalagin Regulates Signaling Pathways in Inflammation-Associated Chronic Diseases. Antioxidants. 2021; 11(1):29.
[25] LO J, LIU CC, LI YS, et al. Punicalagin Attenuates LPS-Induced Inflammation and ROS Production in Microglia by Inhibiting the MAPK/NF-κB Signaling Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. J Inflamm Res. 2022;15:5347-5359.
[26] AL-KHAWALDE AAA, ABUKHALIL MH, JGHEF MM, et al. Punicalagin Protects against the Development of Methotrexate-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice via Activating Nrf2 Signaling and Decreasing Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, and Cell Death. Int J Mol Sci. 2022; 23(20):12334.
[27] ZHANG Y, TAN X, CAO Y, et al. Punicalagin Protects against Diabetic Liver Injury by Upregulating Mitophagy and Antioxidant Enzyme Activities. Nutrients. 2022;14(14):2782.
[28] ZHANG Z, JI C, WANG YN, et al. Maresin1 Suppresses High-Glucose-Induced Ferroptosis in Osteoblasts via NRF2 Activation in Type 2 Diabetic Osteoporosis. Cells. 2022;11(16):2560.
[29] LONG Z, DOU P, CAI W, et al. MiR-181a-5p promotes osteogenesis by targeting BMP3. Aging (Albany NY). 2023;15(3):734-747.
[30] OUYANG J, XIAO Y, REN Q, et al. 7-Ketocholesterol Induces Oxiapoptophagy and Inhibits Osteogenic Differentiation in MC3T3-E1 Cells. Cells. 2022;11(18):2882.
[31] ZHOU M, GRAVES DT. Impact of the host response and osteoblast lineage cells on periodontal disease. Front Immunol. 2022;13:998244.
[32] NAGASHIMA D, ISHIBASHI Y, KAWAGUCHI S, et al. Human Recombinant Lactoferrin Promotes Differentiation and Calcification on MC3T3-E1 Cells. Pharmaceutics. 2022;15(1):60.
[33] TAN AQ, ZHENG YF. The Roles of SNHG Family in Osteoblast Differentiation. Genes . 2022;13(12):2268.
[34] KAN T, HE Z, DU J, et al. Irisin promotes fracture healing by improving osteogenesis and angiogenesis. J Orthop Translat. 2022;37:37-45.
[35] DARJANKI CM, PRAHASANTI C, FITRIA AE, et al. RUNX2 and ALP expression in osteoblast cells exposed by PMMA-HAp combination: An in vitro study. J Oral Biol Craniofac Res. 2023;13(2):277-282.
[36] WANG MY, AN MF, FAN MS, et al. FAEE exerts a protective effect against osteoporosis by regulating the MAPK signalling pathway. Pharm Biol. 2022;60(1):467-478.
[37] DAMANI JJ, DE SOUZA MJ, VANEVERY HL, et al. The Role of Prunes in Modulating Inflammatory Pathways to Improve Bone Health in Postmenopausal Women. Adv Nutr. 2022;13(5):1476-1492.
[38] KERSCHAN-SCHINDL K, PAPAGEORGIOU M, FÖGER-SAMWALD U, et al. Assessment of Bone Microstructure by Micro CT in C57BL/6J Mice for Sex-Specific Differentiation. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):14585.
[39] BROWN JP, ENGELKE K, KEAVENY TM, et al. Romosozumab improves lumbar spine bone mass and bone strength parameters relative to alendronate in postmenopausal women: results from the Active-Controlled Fracture Study in Postmenopausal Women With Osteoporosis at High Risk (ARCH) trial. J Bone Miner Res. 2021;36(11): 2139-2152.
[40] WEE H, KHAJURIA DK, KAMAL F, et al. Assessment of Bone Fracture Healing Using Micro-Computed Tomography. J Vis Exp. 2022;(190): 10.3791/64262.
[41] XIE H, HUA Z, GUO M, et al. Gut microbiota and metabonomics used to explore the mechanism of Qing’e Pills in alleviating osteoporosis. Pharm Biol. 2022;60(1):785-800.
[42] KUNIOKA CT, MANSO MC, CARVALHO M. Association between Environmental Cadmium Exposure and Osteoporosis Risk in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;20(1):485.
[43] LI Y, ZHANG R, REN M, et al. Experimental study on the effects of simvastatin in reversing the femoral metaphyseal defects induced by sodium valproate in normal and ovariectomized rats. Heliyon. 2022; 8(9):e10480.
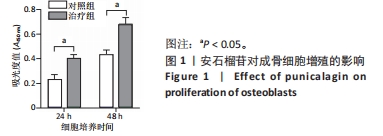
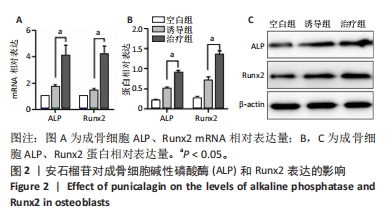
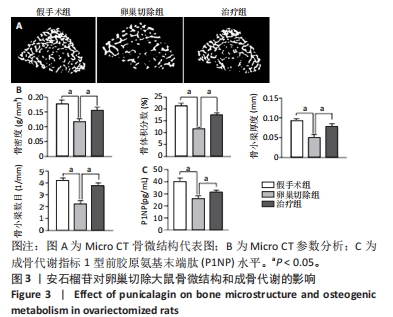
|