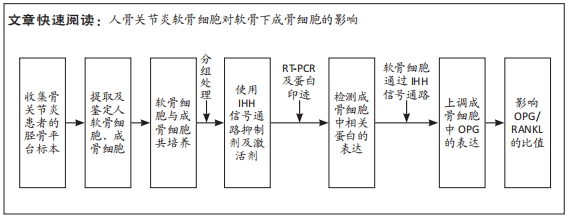
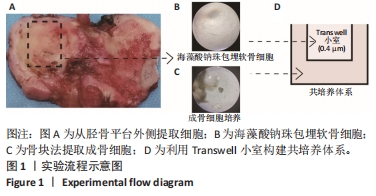
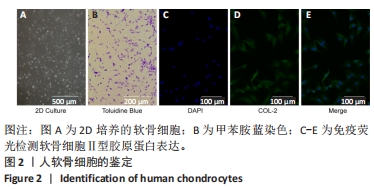
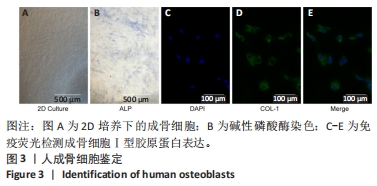
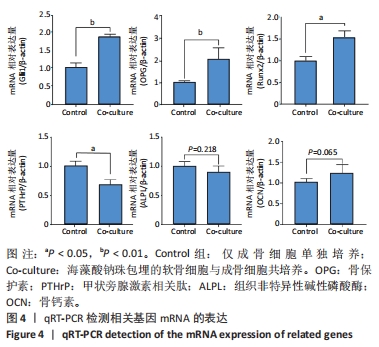
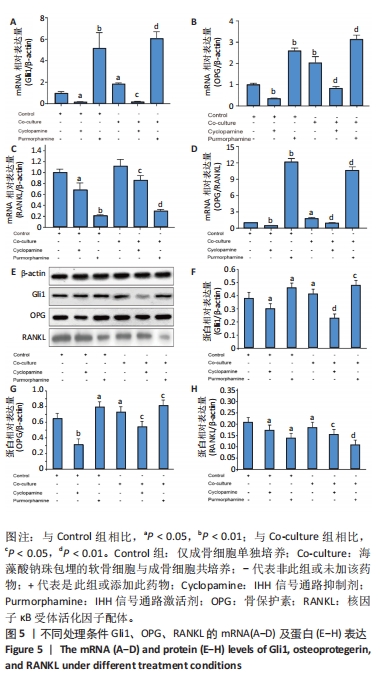
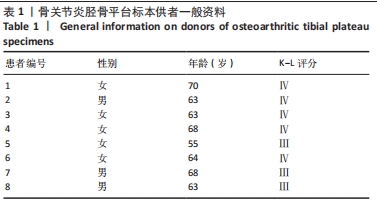
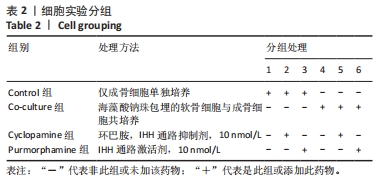
[1] NELSON AE. Osteoarthritis year in review 2017: clinical.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2018;26(3):319-325.
[2] O’NEILL TW, MCCABE PS, MCBETH J. Update on the epidemiology, risk factors and disease outcomes of osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018;32(2):312-326.
[3] AHO OM, FINNILA M, THEVENOT J, et al. Subchondral bone histology and grading in osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 2017;12(3):e0173726.
[4] HUGLE T, GEURTS J. What drives osteoarthritis?-synovial versus subchondral bone pathology. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2017;56(9): 1461-1471.
[5] STEWART HL, KAWCAK CE. The Importance of Subchondral Bone in the Pathophysiology of Osteoarthritis. Front Vet Sci. 2018;5:178.
[6] LI G, YIN J, GAO J, et al. Subchondral bone in osteoarthritis: insight into risk factors and microstructural changes. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013; 15(6):223.
[7] BURR DB, GALLANT MA. Bone remodelling in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2012;8(11):665-673.
[8] SANCHEZ C, DEBERG MA, PICCARDI N, et al. Subchondral bone osteoblasts induce phenotypic changes in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(11):988-997.
[9] SANCHEZ C, DEBERG MA, PICCARDI N, et al. Osteoblasts from the sclerotic subchondral bone downregulate aggrecan but upregulate metalloproteinases expression by chondrocytes. This effect is mimicked by interleukin-6, -1beta and oncostatin M pre-treated non-sclerotic osteoblasts. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(11):979-987.
[10] 朴星银,蒋传路.胶质瘤相关Hedgehog信号通路的研究进展[J].中国微侵袭神经外科杂志,2012,11(17):526-528.
[11] LIN AC, SEETO BL, BARTOSZKO JM, et al. Modulating hedgehog signaling can attenuate the severity of osteoarthritis. Nat Med. 2009;15(12): 1421-1425.
[12] MAEDA Y, SCHIPANI E, DENSMORE MJ, et al. Partial rescue of postnatal growth plate abnormalities in Ihh mutants by expression of a constitutively active PTH/PTHrP receptor. Bone. 2010;46(2):472-478.
[13] HOFBAUER LC, KUHNE CA, VIERECK V. The OPG/RANKL/RANK system in metabolic bone diseases. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2004; 4(3):268-275.
[14] SCHARSTUHL A, GLANSBEEK HL, VAN BEUNINGEN HM, et al. Inhibition of endogenous TGF-beta during experimental osteoarthritis prevents osteophyte formation and impairs cartilage repair. J Immunol. 2002; 169(1):507-514.
[15] TCHETINA EV, SQUIRES G, POOLE AR. Increased type II collagen degradation and very early focal cartilage degeneration is associated with upregulation of chondrocyte differentiation related genes in early human articular cartilage lesions. J Rheumatol. 2005;32(5):876-886.
[16] SALTZMAN BM, RIBOH JC. Subchondral Bone and the Osteochondral Unit: Basic Science and Clinical Implications in Sports Medicine. Sports Health. 2018;10(5):412-418.
[17] ANDERSON HC, CHACKO S, ABBOTT J, et al. The loss of phenotypic traits by differentiated cells in vitro. VII. Effects of 5-bromodeoxyuridine and prolonged culturing on fine structure of chondrocytes. Am J Pathol. 1970;60(2):289-312.
[18] VON DER MARK K, GAUSS V, VON DER MARK H, et al. Relationship between cell shape and type of collagen synthesised as chondrocytes lose their cartilage phenotype in culture. Nature. 1977;267(5611): 531-532.
[19] REICHENBERGER E, AIGNER T, VON DER MARK K,et al. In situ hybridization studies on the expression of type X collagen in fetal human cartilage. Dev Biol. 1991;148(2):562-572.
[20] FUKUI N, PURPLE CR, SANDELL LJ. Cell biology of osteoarthritis: the chondrocyte’s response to injury. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2001;3(6): 496-505.
[21] SUN MM, BEIER F. Chondrocyte hypertrophy in skeletal development, growth, and disease. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2014;102(1): 74-82.
[22] PITSILLIDES AA, BEIER F. Cartilage biology in osteoarthritis--lessons from developmental biology. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(11):654-663.
[23] MORT JS, BILLINGTON CJ. Articular cartilage and changes in arthritis: matrix degradation. Arthritis Res. 2001;3(6):337-341.
[24] MOULIN D, SALONE V, KOUFANY M, et al. MicroRNA-29b Contributes to Collagens Imbalance in Human Osteoarthritic and Dedifferentiated Articular Chondrocytes. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:9792512.
[25] HDUD IM, EL-SHAFEI AA, LOUGHNA P, et al. Expression of Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid (TRPV) channels in different passages of articular chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(4):4433-4445.
[26] WANG D, REN H, LI C, et al. Orexin A prevents degradation of the articular matrixes in human primary chondrocyte culture. Mol Immunol. 2018;101:102-107.
[27] FINGER F, SCHORLE C, ZIEN A, et al. Molecular phenotyping of human chondrocyte cell lines T/C-28a2, T/C-28a4, and C-28/I2. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(12):3395-3403.
[28] SAAS J, LINDAUER K, BAU B, et al. Molecular phenotyping of HCS-2/8 cells as an in vitro model of human chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2004;12(11):924-934.
[29] SCHULZE S, WEHRUM D, DIETER P, et al. A supplement-free osteoclast-osteoblast co-culture for pre-clinical application. J Cell Physiol. 2018; 233(6):4391-4400.
[30] SUN Q, CHOUDHARY S, MANNION C, et al. Ex vivo construction of human primary 3D-networked osteocytes. Bone. 2017;105:245-252.
[31] ROSENBERG N, ROSENBERG O, WEIZMAN A, et al. In vitro Effects of the Specific Mitochondrial TSPO Ligand Ro5 4864 in Cultured Human Osteoblasts. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2018;126(2):77-84.
[32] FLORENCIO-SILVA R, SASSO GR, SASSO-CERRI E, et al. Biology of Bone Tissue: Structure, Function, and Factors That Influence Bone Cells.Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:421746.
[33] SANCHEZ C, DEBERG MA, BELLAHCENE A, et al. Phenotypic characterization of osteoblasts from the sclerotic zones of osteoarthritic subchondral bone. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(2):442-455.
[34] NAKAOKA R, HSIONG SX, MOONEY DJ. Regulation of chondrocyte differentiation level via co-culture with osteoblasts. Tissue Eng. 2006; 12(9):2425-2433.
[35] SIMONET WS, LACEY DL, DUNSTAN CR, et al. Osteoprotegerin: a novel secreted protein involved in the regulation of bone density. Cell. 1997; 89(2):309-319.
[36] YASUDA H, SHIMA N, NAKAGAWA N, et al. Identity of Osteoclastogenesis Inhibitory Factor (OCIF) and Osteoprotegerin (OPG): A Mechanism by which OPG/OCIF Inhibits Osteoclastogenesis in Vitro 1. Endocrinology. 1998;139(3):1329-1337.
[37] SCHNEEWEIS LA, WILLARD D, MILLA ME. Functional Dissection of Osteoprotegerin and Its Interaction with Receptor Activator of NF-κB Ligand. J Biol Chem. 2005;280(50):41155-41164.
[38] REID P, HOLEN I. Pathophysiological roles of osteoprotegerin (OPG). Eur J Cell Biol. 2009;88(1):1-17.
[39] GEUSENS P. Emerging treatments for postmenopausal osteoporosis–focus on denosumab. Clin Interv Aging. 2009;4:241-250.
[40] SILVA I, BRANCO JC. Rank/Rankl/opg:literature review. Acta Reumatol Port. 2011;36(3):209-218.
[41] TYROVOLA JB. The “Mechanostat” Principle and the Osteoprotegerin-OPG/RANKL/RANK System PART II. The Role of the Hypothalamic-Pituitary Axis. J Cell Biochem. 2017;118(5):962-966.
[42] HOFBAUER LC, KHOSLA S, DUNSTAN CR, et al. The roles of osteoprotegerin and osteoprotegerin ligand in the paracrine regulation of bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res. 2000;15(1):2-12.
[43] UPTON AR, HOLDING CA, DHARMAPATNI AA, et al. The expression of RANKL and OPG in the various grades of osteoarthritic cartilage. Rheumatol Int. 2012;32(2):535-540.
[44] MAK KK, BI Y, WAN C, et al. Hedgehog signaling in mature osteoblasts regulates bone formation and resorption by controlling PTHrP and RANKL expression. Developmental Cell. 2008;14(5):674-688.
[45] LIANG W, LI X, GAO B, et al. Observing the development of the temporomandibular joint in embryonic and post-natal mice using various staining methods. Exp Ther Med. 2016;11(2):481-489.
[46] MAEDA Y, NAKAMURA E, NGUYEN MT, et al. Indian Hedgehog produced by postnatal chondrocytes is essential for maintaining a growth plate and trabecular bone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(15): 6382-6387.
[47] HUANGFU D, ANDERSON KV. Signaling from Smo to Ci/Gli: conservation and divergence of Hedgehog pathways from Drosophila to vertebrates.Development. 2006;133(1):3-14.
[48] DIDIASOVA M, SCHAEFER L, WYGRECKA M. Targeting GLI Transcription Factors in Cancer. Molecules. 2018;23(5):1003.
[49] LEIJTEN JC, BOS SD, LANDMAN EB, et al. GREM1, FRZB and DKK1 mRNA levels correlate with osteoarthritis and are regulated by osteoarthritis-associated factors. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(5):R126.
[50] ALI SA, AL-JAZRAWE M, MA H, et al. Regulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis by Hedgehog Signaling in Osteoarthritic Cartilage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016;68(1):127-137.
|