[1] ZHAO X, MENG F, HU S, et al. The Synovium Attenuates Cartilage Degeneration in KOA through Activation of the Smad2/3-Runx1 Cascade and Chondrogenesis-related miRNAs. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2020;22:832-845.
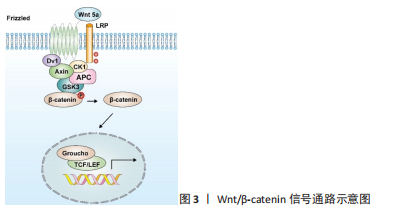
[2] ZHOU Y, WANG T, HAMILTON JL, et al. Wnt/β-catenin Signaling in Osteoarthritis and in Other Forms of Arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2017; 19(9):53.
[3] 刘朝晖,马剑雄,张顺,等.膝骨关节炎的现状及治疗方法的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2020,13(8):688-693.
[4] GUNARATNE R, PRATT DN, BANDA J, et al. Patient Dissatisfaction Following Total Knee Arthroplasty: A Systematic Review of the Literature. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(12):3854-3860.
[5] HE Z, LIU M, ZHANG Q, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway is activated in the progress of mandibular condylar cartilage degeneration and subchondral bone loss induced by overloaded functional orthopedic force (OFOF). Heliyon. 2022;8(10):e10847.
[6] 王华敏,宓轶群,刚嘉鸿.信号通路在膝骨关节炎实验研究中的进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(2):267-272.
[7] BERGWITZ C, WENDLANDT T, KISPERT A, et al. Wnts differentially regulate colony growth and differentiation of chondrogenic rat calvaria cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2001;1538(2-3):129-140.
[8] YUASA T, OTANI T, KOIKE T, et al. Wnt/β-catenin signaling stimulates matrix catabolic genes and activity in articular chondrocytes: its possible role in joint degeneration. Lab Invest. 2008;88(3):264-274.
[9] SHANG X, BÖKER KO, TAHERI S, et al. The Interaction between microRNAs and the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(18):9887.
[10] ZHENG W, LIN P, MA Y, et al. Psoralen promotes the expression of cyclin D1 in chondrocytes via the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(5): 1377-1384.
[11] DING QH, YE CY, CHEN EM, et al. Emodin ameliorates cartilage degradation in osteoarthritis by inhibiting NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling in-vitro and in-vivo. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:222-230.
[12] ZHONG G, LIANG R, YAO J, et al. Artemisinin Ameliorates Osteoarthritis by Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(6):2575-2590.
[13] LIU F, LI L, LU W, et al. Scutellarin ameliorates cartilage degeneration in osteoarthritis by inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin and MAPK signaling pathways. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;78:105954.
[14] 颜春鲁,李盛华,安方玉,等.富硒黄芪皂苷对大鼠退变软骨细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控机制研究[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2018, 34(10):1210-1213.
[15] 徐翀,申利民,苑文杰.当归多糖通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞氧化应激损伤与炎症反应[J].陕西中医,2022,43(6):700-703,770.
[16] 肖强,郭子龙,杨晓宏.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路探讨川芎嗪延缓膝骨关节炎软骨退变的机制[J].中医药导报,2022,28(2):37-42,52.
[17] LU J, ZHANG T, SUN H, et al. Protective effects of dioscin against cartilage destruction in a monosodium iodoacetate (MIA)-indcued osteoarthritis rat model. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;108:1029-1038.
[18] 马玮玮,李瑛.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的淫羊藿苷治疗膝骨关节炎机制研究现状[J].湖北中医杂志,2022,44(6):63-66.
[19] 刘摇摇,刘湘宁,田银平,等.淫羊藿苷对骨骼系统药理作用机制的研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理,2020,31(12):1516-1520.
[20] HU L, LUO D, ZHANG H, et al. Polydatin inhibits IL-1β-mediated chondrocyte inflammation and ameliorates cartilage degradation: Involvement of the NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways. Tissue Cell. 2022;78:101865.
[21] JIMI E, FEI H, NAKATOMI C. NF-κB Signaling Regulates Physiological and Pathological Chondrogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6275.
[22] 郑晓慧,董博,袁普卫,等.NF-κB信号通路在骨性关节炎软骨破坏中的研究进展[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2021,27(7):540-544.
[23] CHOI MC, JO J, PARK J, et al. NF-κB Signaling Pathways in Osteoarthritic Cartilage Destruction. Cells. 2019;8(7):734.
[24] JI B, GUO W, MA H, et al. Isoliquiritigenin suppresses IL-1β induced apoptosis and inflammation in chondrocyte-like ATDC5 cells by inhibiting NF-κB and exerts chondroprotective effects on a mouse model of anterior cruciate ligament transection. Int J Mol Med. 2017;40(6):1709-1718.
[25] JIANG LB, MENG DH, LEE SM, et al. Dihydroartemisinin inhibits catabolism in rat chondrocytes by activating autophagy via inhibition of the NF-κB pathway. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38979.
[26] RAN J, MA C, XU K, et al. Schisandrin B ameliorated chondrocytes inflammation and osteoarthritis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signal pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018;12:1195-1204.
[27] WANG J, WANG X, CAO Y, et al. Therapeutic potential of hyaluronic acid/chitosan nanoparticles for the delivery of curcuminoid in knee osteoarthritis and an in vitro evaluation in chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 2018;42(5): 2604-2614.
[28] 胡芯源,曹珊,陈文明,等.连翘苷元通过抑制TLR4介导的NF-κB信号通路减轻大鼠骨关节炎软组织损伤和基质降解[J].免疫学杂志,2021, 37(2):115-121.
[29] 李宁博,骆晓飞,尹夏,等.杜仲多糖通过抑制NF-κB通路减轻IL-1β诱导的软骨细胞损伤[J].中国骨伤,2022,35(7):661-668.
[30] HE L, PAN Y, YU J, et al. Decursin alleviates the aggravation of osteoarthritis via inhibiting PI3K-Akt and NF-kB signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107657.
[31] JIA Y, HE W, ZHANG H, et al. Morusin Ameliorates IL-1β-Induced Chondrocyte Inflammation and Osteoarthritis via NF-κB Signal Pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:1227-1240.
[32] 黄竞杰,杨俊兴,陈浩雄.牛膝总皂苷治疗膝骨关节炎的药理研究进展[J].中药新药与临床药理,2021,32(4):592-595.
[33] 张燕丽,田园,付起凤,等.白芍的化学成分和药理作用研究进展[J].中医药学报,2021,49(2):104-109.
[34] WAN H, LI C, YANG Y, et al. Loganin attenuates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation, cartilage degeneration, and rat synovial inflammation by regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB. J Int Med Res. 2022;50(8): 3000605221104764.
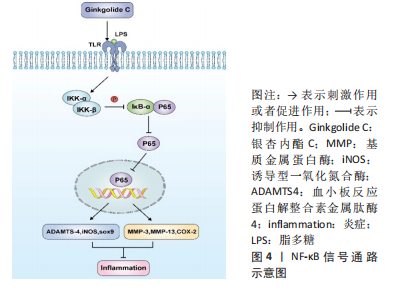
[35] MA T, JIA L, ZHAO J, et al. Ginkgolide C slows the progression of osteoarthritis by activating Nrf2/HO-1 and blocking the NF-κB pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:1027553.
[36] 王迷娜,刘璐,赵洛鹏,等.膝骨关节炎炎性因子及信号通路的研究进展[J].中国骨伤,2020,33(4):388-392.
[37] HAN F, JIANG H, QU W, et al. KLF11 protects chondrocytes via inhibiting p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2020;24(12):6505-6516.
[38] 王象鹏,谢文鹏,毕亦飞,等.基于p38 MAPK信号通路分析槲皮素保护骨性关节炎关节软骨的机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(7): 169-177.
[39] 赵宝祥.基于IL-1β/MAPKs通路探讨威灵仙总皂苷对骨关节炎软骨细胞凋亡的影响[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2016.
[40] 苏友新,闫虎,陈宝军,等.壮骨健膝方含药血清中药物成分骨碎补柚皮苷对IL-1β诱导兔退变软骨细胞“caveolin-p38MAPK”信号通路的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2014,34(12):1492-1498.
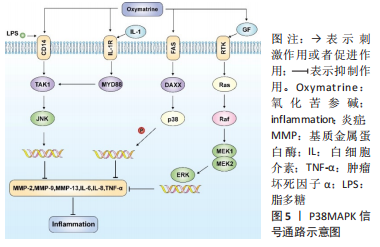
[41] JIANG Y, SANG W, WANG C, et al. Oxymatrine exerts protective effects on osteoarthritis via modulating chondrocyte homoeostasis and suppressing osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(8):3941-3954.
[42] HOSSAIN MA, ALAM MJ, KIM B, et al. Ginsenoside-Rb1 prevents bone cartilage destruction through down-regulation of p-Akt, p-P38, and p-P65 signaling in rabbit. Phytomedicine. 2022;100:154039.
[43] CHEN Y, SHOU K, GONG C, et al. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Osteoarthritis by Suppressing the Activation of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Biomed Res Int. 2018;2018:8384576.
[44] WANG X, PAN J, LIU D, et al. Nicorandil alleviates apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy through PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(8): 5349-5359.
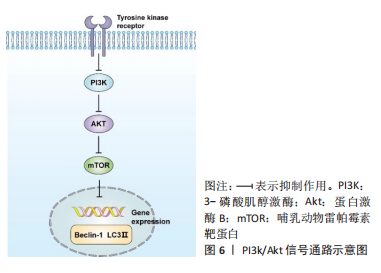
[45] 邓欢,吕艺蓁,刘宣,等.PI3K/AKT信号通路调控骨关节疾病软骨细胞自噬及损伤的机制[J]. 西安交通大学学报(医学版),2022,43(2):309-314.
[46] 商连斌,金连峰,王哲,等.续断总皂苷对膝骨关节炎大鼠软骨组织中PI3K/AKT/mTOR信号通路影响的实验研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2021,48(5): 188-191,后插2.
[47] 姚旭,王清华,茹艺,等.芍药苷抑制PI3K/AKT信号促进细胞自噬治疗骨关节炎[J].吉林中医药,2020,40(8):1076-1079.
[48] TANG Y, LI Y, XIN D, et al. Icariin alleviates osteoarthritis by regulating autophagy of chondrocytes by mediating PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):2984-2999.
[49] 杨阳,何宇,史于传,等.白杨素通过PI3K/AKT信号通路抑制LPS诱导的软骨细胞自噬[J].中国药理学通报,2021,37(5):662-668.
[50] 杨鑫,李源力,蒋萍,等.杨梅素通过PI3K/AKT/NF-κB信号通路对骨性关节炎发展的影响[J].暨南大学学报(自然科学与医学版),2020,41(1): 48-57.
[51] 段志远,于强,周驰,等.蛇床子素对膝骨关节炎大鼠的作用及对PI3K/Akt/NF-κB信号通路的影响[J].解剖科学进展,2021,27(1):111-114..
[52] 郑洁,袁普卫,赵莉平,等.青藤碱通过PI3K/AKt-mTOR信号通路调节膝OA兔软骨自噬水平机制研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(8): 30-33.
[53] LI J, JIANG M, YU Z, et al. Artemisinin relieves osteoarthritis by activating mitochondrial autophagy through reducing TNFSF11 expression and inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling in cartilage. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2022; 27(1):62.
[54] SUN K, LUO J, JING X, et al. Hyperoside ameliorates the progression of osteoarthritis: An in vitro and in vivo study. Phytomedicine. 2021;80:153387.
[55] PARK SK, DAHMER MK, QUASNEY MW. MAPK and JAK-STAT signaling pathways are involved in the oxidative stress-induced decrease in expression of surfactant protein genes. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(2):334-346.
[56] YANG Y, LIU Y, YU H, et al. Sesquiterpenes from Kadsura coccinea attenuate rheumatoid arthritis-related inflammation by inhibiting the NF-κB and JAK2/STAT3 signal pathways. Phytochemistry. 2022;194:113018.
[57] 李旭升,陈慧,甄平,等.JAK2/STAT3信号通路介导姜黄素在骨性关节炎软骨细胞代谢中的影响[J].中国骨伤,2016,29(12):1104-1109.
[58] 刘军,何晓乐,甄平,等.JAK2/STAT3信号通路介导薯蓣皂苷元对骨性关节炎软骨细胞代谢的影响[J].浙江大学学报(医学版),2016,45(5): 452-459.
[59] 高伟静,林朋朝.黄芪多糖通过JAK2/STAT3通路调控人膝骨关节炎软骨细胞增殖与凋亡[J].医学研究杂志,2022,51(2):67-71,91.
[60] 胡炯,王伟东,王昌兴,等.染料木素调控JAK2/STAT3信号通路改善骨性关节炎大鼠软骨代谢的作用研究[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2018,23(4):383-388.
[61] 谢平金,罗臻,卢启贵,等.川芎嗪和过表达miR-20b-5p干预早期膝骨关节炎模型大鼠滑膜,软骨和软骨下骨血管新生的组织学变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):237-245.
[62] 韩宪富,李宁,谢兴文,等.TLR4/MyD88信号通路在膝骨关节炎滑膜炎中的作用[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(11):1690-1694.
[63] 郑洁,赵莉平,胡亚莉,等.青藤碱对兔膝骨关节炎模型软骨Toll样受体2、4及髓样分化因子88表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2018,25(9):49-51. |