中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 121-130.doi: 10.12307/2023.781
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
益气活血开窍类中药及复方调控干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的作用
应春苗1,潘小龙1,刘飞祥2,陈 娜1,樊飞燕1,张运克1,2
- 1河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 450046;2河南中医药大学第一附属医院,河南省郑州市 450000
-
收稿日期:2022-11-29接受日期:2023-01-04出版日期:2024-01-08发布日期:2023-06-29 -
通讯作者:张运克,博士,教授,主任医师,博士生导师,博士后合作导师,河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 450046;河南中医药大学第一附属医院,河南省郑州市 450000 -
作者简介:应春苗,女,1996年生,河南省漯河市人,汉族,河南中医药大学在读硕士,主要从事中医药防治神经内科疾病的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(81974564),项目名称:基于PKCθ/NF-kB信号转导调控的麝香黄芪复方滴丸调节MSCs透过脑缺血后血脑屏障迁移及分化机制,项目负责人:张运克;国家自然科学基金(82104730),项目名称:基于转录组学探讨左归丸调节OXT/OXTR前馈环路抗绝经 后骨质疏松阐释“诸髓皆属于脑”的机制,项目负责人:刘飞祥;中原英才计划—科技创新领军人才项目(224200510027),项目名称:负载芪芎左归饮的 MSCs 外泌体修复衰老后脑缺血神经血管单元的研究,项目负责人:张运克
Effect of traditional Chinese medicine and compounds for supplementing qi and activating blood circulation and inducing resuscitation on regulating stem cells to promote nerve repair of acute ischemic stroke
Ying Chunmiao1, Pan Xiaolong1, Liu Feixiang2, Chen Na1, Fan Feiyan1, Zhang Yunke1, 2
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; 2The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-29Accepted:2023-01-04Online:2024-01-08Published:2023-06-29 -
Contact:Zhang Yunke, MD, Professor, Chief physician, Doctoral supervisor, Post-doctoral cooperative supervisor, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China; The First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China -
About author:Ying Chunmiao, Master candidate, Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450046, Henan Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81974564 (to ZYK); the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82104730 (to LFX); the Zhongyuan Talent Program - Science and Technology Innovation Leading Talent Project, No. 224200510027 (to ZYK)
摘要:
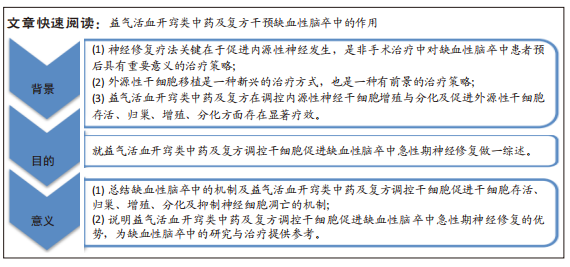
文题释义:
益气活血开窍类中药及复方:气虚血瘀证是缺血性脑卒中的最主要证候,缺血性脑卒中导致脑内血脉淤堵,脑窍闭塞,益气修复既损之脑神,活血疏通淤塞之脉道,开窍以启闭醒神,益气活血开窍类中药及复方对于改善缺血性脑卒中引起的脑髓失养、神机失用等神经损伤具有重要意义。缺血性脑卒中急性期:指发病后2周以内,伴有神志障碍者可至1个月。在缺血性脑卒中急性期,神经修复存在一个相对较长的时间窗,在此时间窗内调节大脑重塑,对于改善受损的神经功能起到至关重要的作用。
目的:综述益气活血开窍类中药及复方促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的机制,以期为缺血性脑卒中的新药研究及治疗提供参考。
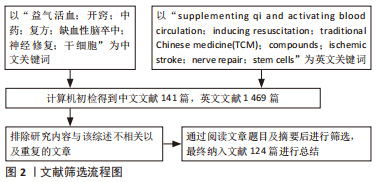
方法:检索中国知网和PubMed数据库2010-2022年期间关于益气活血开窍类中药及复方促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的文献,以“益气活血;开窍;中药;复方;缺血性脑卒中;神经修复;干细胞”为中文检索词,以“supplementing qi and activating blood circulation;inducing resuscitation;traditional Chinese medicine (TCM);compounds;ischemic stroke;nerve repair;stem cells”为英文检索词。排除陈旧及重复的观点,将检索到的文献进行分析整理,共纳入124篇文献进行分析。
结果与结论:①梳理了干细胞、缺血性脑卒中的定义及缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复途径。②总结了益气活血开窍类中药及复方促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的作用机制,主要包括促进干细胞增殖、提高干细胞活力及存活率、促进干细胞归巢、诱导干细胞向神经元分化、抑制神经细胞凋亡、促进轴突再生、调控血管新生及重塑、提高神经营养因子水平及修复血脑屏障完整性。③通过现有的研究总结了益气活血开窍类中药及复方促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的相关因子及信号通路,如Nestin蛋白表达、DCX蛋白表达、脑源性神经营养因子、血管内皮生长因子及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路、Notch信号通路、PI3k/Akt信号通路、BDNF/TrkB信号通路和ERK/MAPK信号通路等,为今后缺血性脑卒中特效药物及新的临床治疗方法的研究提供相关参考。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2480-2441 (应春苗) ;https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1500-1535 (张运克)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
应春苗, 潘小龙, 刘飞祥, 陈 娜, 樊飞燕, 张运克. 益气活血开窍类中药及复方调控干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 121-130.
Ying Chunmiao, Pan Xiaolong, Liu Feixiang, Chen Na, Fan Feiyan, Zhang Yunke. Effect of traditional Chinese medicine and compounds for supplementing qi and activating blood circulation and inducing resuscitation on regulating stem cells to promote nerve repair of acute ischemic stroke[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 121-130.
14 d内为急性期时间窗,患者一旦错过急性期神经修复时间,神经将产生不可逆转性损伤。干细胞疗法作为一种替代疗法,能够补充缺血性脑卒中丢失神经元。长期以来研究证实,缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复是一个多因素复杂的过程(见图3),脑缺血损伤发生后,内源性神经干细胞激活增殖迁移至受损区域,补充坏死神经元,然而内源性神经干细胞再生能力有限,外源性干细胞在国内外治疗卒中事件已进行大量实验,明确缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复相关机制,促进干细胞增殖、存活、迁移及神经轴突的重塑,为神经修复提供所需内环境以改善神经损伤。
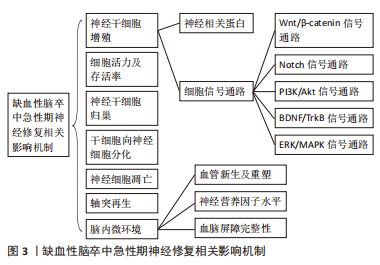
2.1.1 神经干细胞增殖对神经修复的影响
(1)神经相关蛋白:巢蛋白(Nestin)是一种独特的中间丝蛋白,主要分布在脑室下区、海马区等,并且主要在大脑神经干细胞和小脑分子层的星形胶质细胞中表达[19]。研究表明,Nestin能够增强脑组织对抗缺血缺氧能力,促进神经细胞增殖与存活、细胞骨架的稳定和重建,有利于神经组织修复[20]。郭筱琪[21]研究发现,Nestin水平降低时神经干细胞的增殖明显降低。神经元微管相关蛋白(doublecortin,DCX)在发育中及成人大脑神经发生过程中起到调控神经前体细胞分化的作用,用于表达短暂增殖的神经前体细胞,反映神经发生的水平高低和强度的变化,是神经细胞再生比较可靠的特异性标志物[22]。Tau蛋白有助于稳定微管结构,维持神经元的形态,可溶性高磷酸化tau蛋白的积累形成神经纤维缠结,破坏结合微管的能力,促进异常tau蛋白聚集,介导神经退行性病变[23]。ALI等[24]研究发现,脑缺血/再灌注可诱导tau蛋白过度磷酸化,导致微管稳定性降低,神经元活性降低,最终细胞死亡。
(2)细胞信号通路:Wnt/β-catenin、Notch、磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase,PI3K )/蛋白激酶B(protein kinase B,Akt)、脑源性神经营养因子(brain-derived neurotrophic factor,BDNF)/酪氨酸激酶受体B(tyrosine kinase receptor B, TrkB)、丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinases,MAPK)/细胞外信号调节激酶(extracellular signal-regulated kinase,ERK)等信号通路与缺血性脑卒中急性期内源性神经发生及外源性干细胞体内增殖密切相关,是促进缺血性脑卒中神经修复的潜在靶点。
Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在神经源性谱系的细胞中具有不同的活性,并调节神经祖细胞增殖和新生神经元成熟[25]。Wnt3a配体与由低密度脂蛋白受体相关蛋白5/6(LRP5/6)共受体介导的Wnt-Frizzled相互作用,导致糖原合酶激酶3(glycogen synthase kinase-3β,GSK3β)的磷酸化和失活,进而促进缺血性卒中后神经发生[26]。研究表明,Wnt/β-catenin信号通路与神经细胞增殖密切相关[27]。
Notch信号通路在参与维持神经干细胞的增殖、调节脑区神经干细胞维持和分化的平衡中发挥重要作用,是最保守的信号通路之一[28]。研究表明,在缺氧条件下Notch-1上调并激活,Notch1细胞内结构域(Notch1 intracellular domain,NICD)和Hes-1表达增加,促进神经细胞的增殖[29]。另有研究证实,Hes1的超振荡对神经祖细胞增殖至关重要[30]。
PI3K/Akt信号通路介导神经祖细胞增殖和生长,在大脑皮质神经发育中起到重要作用[31]。Akt作为PI3K的下游介质,在外源性ATP刺激下,PI3K-Akt-mTOR通路被激活,下游p70S6K磷酸化水平显著上调,磷酸化GSK3,促进神经元的发育、分化、存活和再生[32]。
BDNF/TrkB信号通路激活在中枢神经系统中具有多效作用,能够促进神经增殖、神经元的存活及分化[33]。BDNF通过与TrkB受体相结合,激活TrkB下游的两条信号通路——PI3K/Akt和MAPK/ERK通路,调节某些转录因子的水平和活性,进而调控神经系统中神经元的神经传递、神经再生、形态和功能性以及突触可塑性[34-35]。
ERK/MAPK信号通路在细胞增殖、转化、分化和凋亡过程中起到重要作用[36]。BDNF[37]、表皮生长因子[38]、血管内皮生长因子(vascular endothelial growth factor,VEGF)等生长因子能够激活ERK/MAPK信号通路上游蛋白Ras蛋白[39],Ras活化Raf蛋白激酶,激活下游丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(mitogen-activated protein kinase,MEK)(MEK1和MEK2)和MAPK,磷酸化激活下游的ERK激酶ERK-1和ERK-2,最终通过调节转录调节因子的活性将细胞增殖和分化信号传递给细胞核[36,40-41]。MAPK有助于神经干细胞的维持,可被苏氨酸和酪氨酸残基的磷酸化激活,以响应脑缺血,MAPK磷酸化能够促进齿状回区神经元存活[42]。
2.1.2 细胞活力及存活率对神经修复的影响 研究表明,ERK与许多细胞活动有关,如细胞死亡、活力和增殖,Akt与细胞存活和生长有关,ERK和Akt均能通过磷酸化多个靶点促进细胞存活[43]。脑组织缺血后,线粒体损伤引发一系列事件,缺血引起的线粒体去极化启动过多的活性氧生产,减少ATP生成,增加pten诱导的假定激酶1(PTEN-induced putative kinase 1,PINK1)的积累[44],因此,线粒体对于神经元细胞的兴奋性和存活是必不可少的。HUANG等[45]研究证实,在颈中动脉闭塞动物模型中注射星形细胞来源的线粒体可增加磷酸化的AKT水平,从而促进细胞存活。另有研究证明,在缺氧条件下培养的星形胶质细胞产生了功能性细胞外线粒体,提高了ATP水平和神经活性[46]。
2.1.3 干细胞归巢对神经修复的影响 神经细胞向梗死周围区域迁移的促进可能是由于化学引诱剂和神经营养分子的增加,其中,基质细胞衍生因子1(stromal cell-derived factor-1,SDF-1)/CXC趋化因子受体4(CXC chemokine receptor 4,CXCR4)信号轴在脑缺血后引导神经母细胞向缺血部位迁移中发挥重要作用。研究证实,在缺血性脑卒中动物模型中,SDF-1α mRNA和蛋白主要存在于缺血半暗影区,在3-7 d达到峰值,并在移植后至少14 d保留,在缺氧条件下骨髓间充质干细胞中CXCR4的表达升高。SDF-1及其受体CXCR4在相互作用下可以诱导干细胞沿着嗅-丘脑和海马-皮质的路径迁移到脑缺血病变归巢至缺血组织[47]。另有研究证实,脑内注射SDF-1或CXCR4过表达同样促进移植骨髓间充质干细胞向缺血病变迁移[48]。
2.1.4 干细胞向神经细胞分化对神经修复的影响 线粒体酶和细胞代谢因子是调节神经干细胞发育和分化的潜在治疗靶点,参与线粒体功能的代谢物,如ATP、ADP、AMP和自由基,与神经元和其他细胞中的PI3K/Akt信号通路密切相关,Akt磷酸化GSK3促进细胞增殖和分化[49]。此外,默信息调节因子2相关酶1(sirtuin1,SIRT1)是一种去乙酰化酶,在整个成人大脑中广泛表达[50],它能够与Wnt信号传导、钙信号及葡萄糖稳态中涉及的一组蛋白质靶标相互作用,通过使各种组蛋白和非组蛋白以及转录因子脱乙酰化,参与神经干细胞的增殖和分化[51]。
2.1.5 神经细胞凋亡对神经修复的影响 脑缺血引起的细胞凋亡是神经元死亡的另一个主要原因。缺血相关的凋亡因子包括Bcl-2蛋白家族和caspase蛋白酶家族,Bcl-2蛋白能够促进缺血后皮质、海马和纹状体中未成熟和成熟神经元的存活[52]。Caspase 蛋白酶家族的成员在细胞凋亡的启动(Caspase-2、-8、-9 和-10)和执行细胞凋亡(Caspase-3、-6 和 -7)中发挥重要作用[53]。Bcl-2和Bax参与了细胞凋亡的控制,Caspase-3是细胞凋亡的关键行刑者;Bcl-2是一种凋亡抑制剂,在抗凋亡机制中发挥重要作用,而Bax和Caspase-3是促凋亡相关蛋白,其过表达能够催化细胞凋亡[54]。
2.1.6 轴突再生对神经修复的影响 缺血性脑卒中后,会出现轴突的快速和剧烈的损失以及轴突的延迟变性,中风后轴突再生在神经发生和功能恢复中起到重要作用[55]。Rho/ROCK通路调节多种关键细胞功能,如树突状树化、生长锥发育、轴突引导、神经元存活和神经元死亡[56]。Rho/ROCK信号通路包括3种主要的髓磷脂抑制剂(Nogo-A,-B和-C),髓磷脂相关糖蛋白(myelin-associated glycoprotein,Mag)和少突胶质细胞髓磷脂糖蛋白(oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein,Omgp),其中Nogo-A是抑制轴突再生和神经修复的关键因子,缺血刺激可激活中枢神经元中的Nogo-A,通过GTPase信号级联激活Rho/ROCK信号通路,最终抑制轴突生发[57]。Rho家族(GTPases,包括Cdc42,RacG,TPases和RhoA)在极化生长过程中起核心作用,此外,Cdc42参与细胞骨架形成、细胞极化、增殖和迁移[58]。缺血性脑卒中发生后这些蛋白调节细胞骨架重组,导致生长锥的崩溃,抑制神经突起的生长,参与调节与细胞增殖相关的基因表达,限制轴突再生和神经元存活[59]。
2.1.7 缺血性脑卒中急性期脑内微环境对神经修复的影响
(1)血管新生及重塑:血管新生受多种血管生长因子的特异性调节而激活,其中最有效的缺氧诱导血管生成因子和血管生成素[60]。VEGF由内皮细胞和周细胞分泌,其家族成员配体有3个受体蛋白激酶VEGFR1(flt1),VEGFR2(kinase insert domain receptor-Flk-1)和VEGFR3以及2个非酶受体(neutrophilin-1 and neutrophilin-2)[61]。缺氧能够增强VEGF R1的转录,刺激VEGF R2与蛋白酪氨酸磷酸酶结合,共同参与VEGF诱导信号的产生和调节[62]。血管生成素家族主要由Ang-1,Ang-2,Ang-3,Ang-4等4种配体及Tie1和Tie2两种受体组成,其中Ang-1和Ang-2与血管生成关系更为密切。研究证实,Ang1能够激活酪氨酸激酶Tie2受体,从而介导血管生长和血管新生、抑制细胞通透性和炎症、激活内皮细胞迁移[63]。
(2)神经营养因子水平:神经营养因子是一类分泌蛋白,由BDNF、VEGF、神经生长因子、成纤维细胞生长因子、胶质细胞源性神经营养因子和神经营养因子3等共同组成[64]。它们是中枢神经系统发育和功能的重要调节剂,能够减少宿主内源性神经元的细胞死亡,促进轴突连接并增强移植的神经干细胞存活和植入[65]。
(3)血脑屏障完整性:血脑屏障是调节神经微环境的一种动态结构,能够严格限制循环与脑实质之间的离子和液体运动,保护神经回路正常功能、突触传递和重构、血管生成和神经生成所需的神经微环境[66]。血脑屏障的紧密连接是血脑屏障通透性的主要决定因素[67]。紧密连接主要是由跨膜蛋白claudin、occludin和连接黏附分子形成的,通过与闭锁蛋白(zonula occludens,ZO)、扣带蛋白、AF-6和7H6在内的跨膜蛋白相互作用实现紧密连接的稳定性和功能[68]。claudin-1、claudin-3和claudin-5最有可能负责控制细胞旁通路,Claudin-5是脑内皮中最丰富的亚型,决定血脑屏障紧密连接的密封特性[69]。早期研究表明,增加Occludin蛋白的表达能够使TEER增强,细胞旁扩散减少,ZO-1在claudin、occludin和连接黏附分子的组合中发挥核心作用,连接黏附分子家族成员还在白细胞黏附和通过血脑屏障向脑实质转移中发挥重要作用[70]。
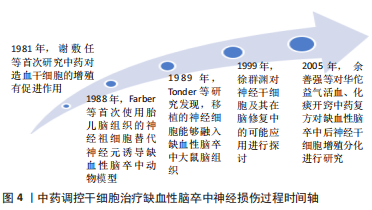
2.2 益气活血开窍类中药及复方调控干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复相关机制 近年来,中药调控干细胞治疗缺血性脑卒中的研究逐渐深入发展(见图4)。张运克教授团队多年来对益气活血经典名方补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大脑中动脉闭塞(middle cerebral artery occlusion,MCAO)模型大鼠进行深入探讨,取得显著成果,为益气活血开窍中药及复方调控干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复提供借鉴参考。在此基础上,对当前益气活血开窍类中药及复方调控干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复相关机制研究进行归纳综述,为后续相关作用机制、益气活血中药及复方与干细胞的紧密结合探讨提供依据及参考。
2.2.1 益气活血开窍类中药有效成分
(1)益气活血类中药有效成分:见表1。
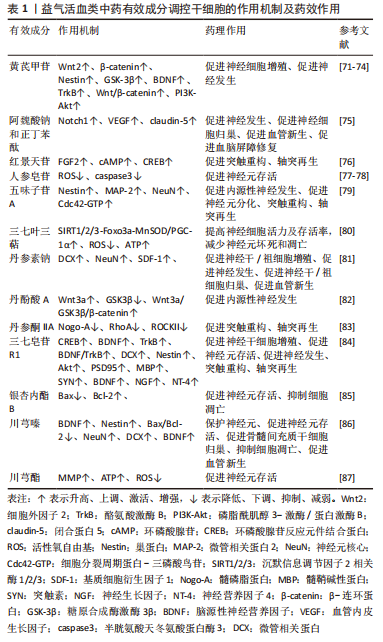
黄芪甲苷:SUN等[71]发现,中药黄芪有效活性成分黄芪甲苷能够上调β-catenin蛋白表达,增加Wnt2、GSK-3β含量,激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,激活中风小鼠海马体中的静止干细胞来促进中风后同侧海马的神经发生。SUN等[72]研究证实经黄芪甲苷处理后,脑卒中小鼠缺血皮质中p-PI3K和p-Akt的表达明显上调,促进神经细胞的增殖再生。NI等[73]发现,黄芪甲苷能够增强MCAO大鼠体内BDNF及TrkB表达水平,促进其体内神经干细胞增殖与神经发生。CHEN等[74]研究表明,黄芪甲苷VI能够磷酸化表皮生长因子受体和MAPK,促进短暂性脑缺血大鼠海马齿状回区、齿状回的颗粒下区内源性神经发生和神经干细胞增殖,且黄芪甲苷VI能够增强体外培养的神经干细胞自我更新和增殖。
阿魏酸钠和正丁苯酞:ZHAO等[75]研究发现,当归提取物阿魏酸钠和正丁苯酞联合脂肪源性干细胞治疗能够多途径促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复:①能够激活光化学诱导血栓性脑卒中大鼠脑内Notch1通路,促进局灶性缺血后的脑室下区神经发生;②显著增加梗死区毛细血管密度及周长,且VEGF的表达比单独脂肪源性干细胞治疗高2.3倍,表明当归提取物阿魏酸钠和正丁苯酞联合脂肪源性干细胞治疗具有协同增强新生血管的作用;③能够进一步增强脂肪源性干细胞脑内移植的功效,使得浸润到缺血性脑卒中大鼠脑梗死区的移植细胞数量最大化;④显著增加脑卒中模型大鼠脑内调节血脑屏障通透性的关键整合蛋白claudin-5蛋白,保持内皮紧密连接,明显减少血脑屏障渗漏;而单纯脂肪源性干细胞治疗则有增加血脑屏障渗漏趋势,二者联合治疗,既明显改善局部脑血流量,也并未加剧血脑屏障渗漏。
红景天苷:LI等[76]发现,中药红景天提取物红景天苷能够增加MCAO大鼠脑组织内成纤维细胞生长因子2表达,通过其介导的cAMP/PKA/CREB通路促进树突和突触的可塑性。
人参皂苷:NI等[77]证实,中药人参有效成分人参皂苷能够抑制缺血条件下活性氧过度产生,保护线粒体完整性,促进缺血性脑卒中小鼠脑内神经元存活。LI等[78]发现,人参皂苷能够下调缺血性脑卒中大鼠促凋亡蛋白Caspase-3表达,抑制缺血性脑卒中急性期神经细胞凋亡,促进神经细胞存活。
五味子苷A:ZONG等[79]证实,中药五味子有效提取物五味子苷A治疗后缺血性脑损伤小鼠缺血区Nestin水平明显提高,梗死周围区域成熟神经元和未成熟神经细胞的数量显著增加,有效促进缺血性损伤后内源性神经干细胞增殖和神经元分化;并且五味子苷A能够上调缺血性脑损伤小鼠体内Cdc42-GTP的活性,促进神经祖细胞的细胞周期和细胞骨架重排,参与神经元轴突的生长并介导f-肌动蛋白的神经纤维骨架的形成,最终促进轴突和新神经纤维进入半暗带。
三七叶三萜:XIE等[80]发现,中药三七有效活性成分三七叶三萜通过作用于NAMPT-NAD+通路及其下游关键的SIRT1/2/3-Foxo3a-MnSOD/PGC-1α信号通路,显著保持氧化还原平衡,抑制过量活性氧水平,减轻线粒体损伤,显著提高缺血缺氧条件下神经元的存活率。
丹参素钠:研究证实,中药丹参提取物丹参素钠治疗:①能够显著增加缺血性脑卒中动物脑内DCX蛋白含量,增加梗死周围区域成熟神经元数量,促进神经干细胞增殖及神经发生;②能够增强局灶性脑缺血小鼠脑内SDF-1的表达,促进脑缺血后神经干细胞的归巢;③能够显著上调缺血性脑卒中急性期VEGF表达,增加梗死灶周围新生微血管数量,促进血管神经修复[81]。
丹酚酸A:研究发现,中药丹参有效成分丹酚酸A能够显著增加脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑内Nestin表达,促进神经再生,且丹酚酸A能够上调Wnt3a抑制GSK3β活性,从而增加β-catenin的积累,促进缺血性脑卒中模型大鼠内源性神经发生[82]。
丹参酮IIA:WANG等[83]证实,中药丹参活性成分丹参酮IIA治疗能够明显降低局灶性脑缺血大鼠脑内Nogo-A、RhoA和ROCKII表达,促进轴突再生可能,发挥神经保护作用。
三七皂苷R1:ZHU等[84]研究发现,中药三七提取物三七皂苷R1:①能够显著增加脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑内Nestin和DCX表达,增加梗死周围区域成熟神经元数量,促进神经干细胞增殖及神经发生;②能够显著上调MCAO大鼠BDNF、p-TrkB、p-Akt和环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白(cAMP-response element binding protein,p-CREB)表达,发挥神经保护及促神经元作用;③能够上调脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠脑内髓鞘碱性蛋白(myelin basic protein,MBP)、突触素PSD95和神经递质SYN表达,促进轴突再生和树突重塑;④能够显著增加MCAO大鼠脑内BDNF、神经生长因子和神经营养因子4表达,促进神经发生及神经细胞存活。
银杏内酯B:YANG等[85]研究发现,中药银杏叶提取物银杏内酯B治疗能够显著上调MCAO大鼠脑内抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达,下调Bax表达,增加Bcl-2/Bax比率,抑制神经细胞凋亡。
川芎嗪:LIN等[86]发现,川芎嗪联合骨髓间充质干细胞显著上调缺血性脑卒中大鼠脑内缺血性脑SDF-1和CXCR4的表达,缺血半暗带骨髓间充质干细胞数量明显增加,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向缺血区域的归巢;川芎嗪联合干细胞治疗能够刺激缺血性脑卒中大鼠脑组织缺血区域BDNF的分泌,使得BDNF表达水平显著升高;川芎嗪联合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗后,缺血性脑卒中大鼠脑内新生神经元数目、DCX数目、星形胶质细胞数量和微血管密度均显著增加,可协同促进缺血性脑卒中后的血管新生和神经新生。
川芎酯:WU等[87]证实,中药川芎活性成分川芎酯能够显著增加缺血性脑卒中大鼠基质金属蛋白酶和ATP产生,降低活性氧的产生,促进神经细胞存活。
(2)开窍类中药有效成分:见表2。
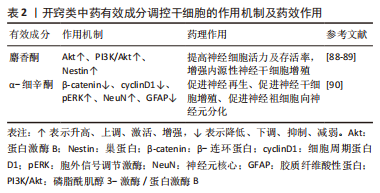
麝香酮:ZHOU等[88]研究发现,中药麝香提取物麝香酮能够呈剂量依赖性增强缺血性脑卒中大鼠体内Akt表达,神经细胞数目明显增加,显著提高细胞活力。麝香酮治疗后,MCAO大鼠缺血区Nestin水平明显提高,梗死周围区域成熟神经元和未成熟神经细胞的数量显著增加[89]。
α-细辛酮:LEE等[90]发现,石菖蒲提取物α-细辛酮能够提高缺血性脑卒中小鼠体内β-catenin蛋白和cyclinD1蛋白含量,增强pERK因子表达,促进小鼠内源性神经干细胞增殖分化;经石菖蒲提取物α-细辛酮处理后,缺血性脑卒中小鼠脑内神经元细胞数目明显增多,并且新生神经细胞成熟率是其他细胞的5.93倍,是星形胶质细胞的2.45倍,即α-细辛酮显著增强神经元样细胞的分化,限制星形胶质细胞样分化。
2.2.2 益气活血开窍类中药单体
(1)益气活血类中药单体:见表3。
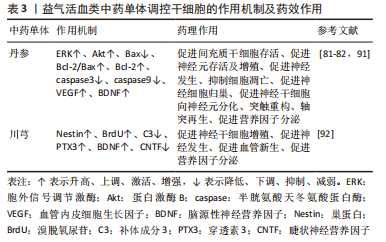
丹参:KIM等[91]发现,中药丹参处理的间充质干细胞治疗后MCAO大鼠脑缺血区域细胞移植存活率约为单纯间充质干细胞移植的2.5倍,且MCAO大鼠脑内p-Akt和p-ERK表达水平显著提高,ERK和Akt磷酸化增强,表明丹参能够促进间充质干细胞在缺血性脑卒中区域的归巢和沉降,有助于间充质干细胞存活。ZHANG等[82]研究证实,①丹参能够增加缺血性脑卒中大鼠脑内神经干/祖细胞从齿状回的颗粒下区到缺血区域的迁移距离,促进神经干/祖细胞归巢;②丹参治疗能够刺激神经祖细胞分化为成熟的神经元并整合到纹状体中现有的神经元回路中;③经丹参处理的Bax和Caspase-3因子表达水平比对照组降低了8.6-12倍,而丹参提取物处理组抗凋亡因子Bcl-2水平比对照组高2.0倍,即丹参能够显著上调抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达,下调Bax表达,增加Bcl-2/Bax比率,下调缺血性脑卒中促凋亡蛋白Caspase-3和Caspase9表达,抑制缺血性脑卒中急性期神经细胞凋亡,促进神经细胞存活;④丹参治疗14 d,能够刺激缺血性脑卒中模型大鼠神经轴突萌发,并在缺血性纹状体中重建新的轴突连接,进而有助于中风后神经功能的恢复。WEI等[81]发现,丹参治疗能够明显增加局灶性脑缺血小鼠脑组织完全梗死区相关营养因子VEGF、BDNF表达。
川芎:YU等[92]在神经发生的评估中发现,①川芎能够增加MCAO大鼠齿状回和齿状回的颗粒下区两个区域的神经前体细胞和新生神经元数量;②川芎能够增加MCAO大鼠脑组织内BDNF的表达,并且川芎能够减少睫状神经营养因子的表达;③川芎与冰片联合治疗对VEGF的改善明显优于单纯冰片治疗;④补体成分3(complement component 3,C3)和pentraxin3(PTX3)分别被广泛用作星形胶质细胞从A1表型到A2表型的标志物,缺血性损伤能够诱导齿状回和齿状回的颗粒下区中C3的增加[93]。川芎能够降低C3表达,而且增强两个区域的PTX3表达,有效逆转缺血性损伤时反应性星形胶质细胞从A1表型到A2表型过程,抑制星形胶质细胞分化。
(2)开窍类中药单体:见表4。

牛黄:DU等[94]研究证实,①中药牛黄治疗能够显著上调抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达,下调Bax表达,增加Bcl-2/Bax比率,并且缺血性脑卒中促凋亡蛋白Caspase-3表达,抑制缺血性脑卒中急性期神经细胞凋亡;②牛黄能够显著上调缺血性脑卒中急性期VEGF表达,增加梗死灶周围新生微血管数量;③牛黄能够增加Occludin、Claudin-5、ZO-1蛋白表达,修复紧密连接蛋白,保护血脑屏障[94]。
皂荚:LUO等[95]研究发现,皂荚治疗能够显著上调抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达,下调Bax表达,增加Bcl-2/Bax比率,抑制缺血性脑卒中大鼠神经细胞凋亡,减轻神经元损伤。
冰片:YU等[92]实验发现,①冰片能够上调MCAO大鼠VEGF和VEGF R2表达,且川芎与冰片联合对VEGF的改善明显优于单纯冰片治疗;②冰片能够增加MCAO大鼠脑组织内BDNF的表达;③在冰片治疗下,内皮细胞间紧密连接恢复,内皮与基底膜间隙明显缩小,血脑屏障结构得到明显改善,促进胞饮作用,有助于小分子药物穿透血脑屏障并流入大脑;此外,冰片能够显著抑制缺血性脑卒中大鼠齿状回和齿状回的颗粒下区两个区域claudin-5、JAM-3、occludin和ZO-1的下降,清除其降低血脑屏障通透性和改善超微结构的机制。
安息香:XIE等[96]发现,安息香治疗能够显著上调抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达,下调Bax表达,增加Bcl-2/Bax比率,下调缺血性脑卒中促凋亡蛋白Caspase-3表达,抑制缺血性脑卒中急性期神经细胞凋亡,促进神经细胞存活。CHEN等[97]研究证实,安息香治疗能够明显增强MCAO大鼠缺血脑组织中VEGF和Ang-1表达,促进缺血区域血管再生。
2.2.3 益气活血开窍类中药复方 见表5。

补阳还五汤:中药复方补阳还五汤主要成分有黄芪、赤芍、川芎、当归尾、地龙、桃仁、红花,乃益气活血经典名方。张运克等[98]研究证实,益气活血方补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗能显著增加缺血性脑卒中大鼠模型体内神经元细胞NSE表达和细胞轴突GFAP蛋白表达,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向神经元方向分化。此外, 张运克等[99]研究发现,补阳还五汤治疗能显著上调抗凋亡因子Bcl-2表达,下调Bax表达,增加Bcl-2/Bax比率,抑制缺血性脑卒中急性期神经细胞凋亡,促进神经细胞存活。另有研究证实,补阳还五汤联合间充质干细胞治疗能够上调MCAO大鼠VEGF表达,诱导缺血区血管再生,促进神经发生;且补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞治疗能够增加Occludin、Claudin、JAM-A、ZO-1蛋白表达,协同促进血脑屏障修复与神经修复[100-101]。
脑脉通:中药复方脑脉通主要有效成分有人参、川芎、大黄、葛根,冯静静等[102]发现,益气活血开窍类中药复方脑脉通联合骨髓间充质干细胞能够显著增加脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑内Nestin表达,促进神经再生。
麝香黄芪复方滴丸:麝香黄芪复方滴丸是在补阳还五汤原方基础上加入芳香开窍药麝香、冰品化裁而成。张运克等[103-104]研究证实,益气活血开窍中药复方麝香黄芪复方滴丸显著上调缺血性脑卒中大鼠模型缺血区域Occludin、Claudin-5、JAM-A、ZO-1的蛋白表达,维持血脑屏障紧密连接完整性,发挥脑保护作用。
三化汤:三化汤主要由大黄、枳实、羌活、厚朴组成,共奏通腑开窍之功用。FU等[105]发现,三化汤治疗可显著降低再灌注后p-tau蛋白水平,而t-tau蛋白和mRNA水平无明显变化,提示三化汤通过减少tau磷酸化发挥神经保护和促进神经发生的作用;且三化汤能够在缺血性脑卒中急性期上调齿状回的颗粒下区神经细胞和星形胶质细胞数量,促进神经前体细胞向未成熟神经元分化。
健脾益智胶囊:中药复方健脾益智胶囊主要由人参、黄芪、白术、制何首乌、菖蒲、远志、水蛭组成,具有健脾益气、活血开窍之功效[106]。冯珂等[107]发现,健脾益智胶囊能够明显提高MCAO大鼠Notch1、Jagged1蛋白表达及其基因的表达,以及提高Notch下游靶向蛋白Hes1的表达,激活Notch促进MCAO大鼠海马神经干细胞增殖。且健脾益智胶囊能够显著增强缺血性脑卒中模型大鼠体内碱性成纤维细胞生长因子2、BDNF、表皮生长因子的表达,促进神经干细胞的增殖、分化[108]。
白脉散:蒙药白脉散是由人参、牛黄、冰片等19味药物组成的治疗中风的民族方药,陈小玉[109]研究发现,白脉散能够增强双侧颈总动脉夹闭模型小鼠脑内Notch1基因表达,激活Notch通路,提高神经干细胞增殖活性。
益气活血方:益气活血方主要成分为黄芪、三七、川芎、红花,孟庆萍等[110]证实益气活血方能够上调MCAO大鼠模型缺血侧额顶叶皮质Hes-1和Hes-5蛋白表达,增强Notch信号转导通路Hes-1和Hes-5效应分子活性功能,促进脑缺血损伤后内源性神经干细胞增殖。
保元胶囊:中药复方保元胶囊主要成分有黄芪、丹参、猪苓、枸杞等,具有益气养血活血之功效。DU等[111]发现,保元胶囊能够上调海马中p-Akt、p-GSK-3β和AMPK的表达,并下调β-catenin,调节PI3K-Akt信号通路促进神经干细胞增殖;且保元胶囊能够呈剂量依赖性地增加MCAO小鼠脑内ATP和AMP含量,降低神经干细胞中的ADP含量,增强Akt和p-GSK3β的磷酸化,促进神经干细胞向神经元方向分化。
芪仙通络方:芪仙通络方为国医大师刘祖贻治疗缺血性脑卒中之经验方,由黄芪、丹参、水蛭、山楂、葛根、淫羊藿、枸杞子、制首乌共同组成,具有补肾益气、活血通络之功效,寿雅琨[112]研究证实,芪仙通络方能够明显上调BDNF表达和p-CREB表达,促进TrkB磷酸化,促进神经细胞增殖与突触重构。林秀慧等[113]研究发现,芪仙通络方能够显著上调缺血性脑卒中急性期VEGF表达,增加梗死灶周围新生微血管数量,促进神经修复。另有研究证实,芪仙通络方能够上调缺血性脑卒中大鼠脑内BDNF水平,促进其内源性神经发生[114]。
脑疏宁:脑疏宁由益母草、川牛膝、三七、白茅根、生大黄、连翘、水蛭、石菖蒲共同组成,具有益气活血、通腑开窍之功效。荆莉等[115]证实,脑疏宁能够增加体外培养的神经干细胞p-ERK1/2蛋白表达,促进ERK1/2磷酸化,激活ERK/MAPK信号通路,促进神经干细胞的增殖。
银杏活脑胶囊:鲁启洪[116]研究发现,银杏活脑胶囊能够显著上调缺血性脑卒中急性期VEGF表达,增加梗死灶周围新生微血管数量,促进神经修复。
肾脑复元汤:益气补肾、活血通络中药复方肾脑复元汤联合人脐带间充质干细胞治疗能够明显抑制缺血缺氧后线粒体cyt-C释放,减少Caspase-9、Caspase-3表达,发挥脑保护作用[117]。胡国恒等[118]证实,肾脑复元汤联合人脐带间充质干细胞治疗能够增强MCAO大鼠VEGF表达,显著改善神经功能损伤。李映辰等[119]研究发现,肾脑复元汤联合人脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗,能够有效促进脑缺血再灌注后损伤大鼠脑内神经营养因子BDNF及碱性成纤维细胞生长因子表达。

| [1] HANKEY GJ. Stroke. Lancet. 2017;389(10069):641-654. [2] VIRANI SS, ALONSO A, BENJAMIN EJ, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2020 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2020;141(9):e139-e596. [3] MARKUS TM, TSAI SY, BOLLNOW MR, et al. Recovery and brain reorganization after stroke in adult and aged rats. Ann Neurol. 2005;58(6): 950-953. [4] HERMANN DM, CHOPP M. Promoting brain remodelling and plasticity for stroke recovery: therapeutic promise and potential pitfalls of clinical translation. Lancet Neurol. 2012;11(4):369-380. [5] TANG H, LI Y, TANG W, et al. Endogenous Neural Stem Cell-induced Neurogenesis after Ischemic Stroke: Processes for Brain Repair and Perspectives. Transl Stroke Res. 2022 Sep 3. doi: 10.1007/s12975-022-01078-5. [6] 田超,袁梦晨,王晓峰,等.醒脑开窍药治疗中风病实验研究进展[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2018,16(15):2158-2161. [7] 范晓迪,张业昊,刘建勋.益气活血法在缺血性脑卒中后神经修复中的生物学基础研究进展[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(15):216-222. [8] WANG M, LIU J X, YAO MJ, et al. Advances in research on pharmacological and neuroprotective effects of traditional Chinese medicine after cerebral ischemia. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020;45(3):513-517. [9] TØNDER N, SØRENSEN T, ZIMMER J, et al. Neural grafting to ischemic lesions of the adult rat hippocampus. Exp Brain Res. 1989;74(3):512-526. [10] TOMAN NG, GRANDE AW, LOW WC. Neural Repair in Stroke. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(9-10):1123-1126. [11] KAWABORI M, SHICHINOHE H, KURODA S, et al. Clinical Trials of Stem Cell Therapy for Cerebral Ischemic Stroke. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(19):7380. [12] FAIZ M, SACHEWSKY N, GASCÓN S, et al. Adult Neural Stem Cells from the Subventricular Zone Give Rise to Reactive Astrocytes in the Cortex after Stroke. Cell Stem Cell. 2015;17(5):624-634. [13] IKHSAN M, PALUMBO A, ROSE D, et al. Neuronal Stem Cell and Drug Interactions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis: Concise Review. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(11):1202-1211. [14] 谢仁敷,麻柔,廖军鲜,等.中药对体内扩散盒小鼠造血干细胞作用观察[J].中医杂志,1981(5):76-78. [15] 姜超,赵文树,孙申田.中医药对神经干细胞影响的研究概况[J].中医药信息,2006(5):14-15. [16] 樊飞燕,张运克.益气活血中药联合骨髓间充质干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中血管新生的作用与机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(13):2060-2069. [17] 孙作艳,岳少乾,唐巍巍,等.芳香开窍药对脑卒中保护作用的实验研究进展[J].天津中医药,2018,35(1):77-80. [18] ZHAO YH. Essential Role of Chinese Medicines in Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Chin J Integr Med. 2019;25(10): 723-727. [19] ERNST C, CHRISTIE BR. The putative neural stem cell marker, nestin, is expressed in heterogeneous cell types in the adult rat neocortex. Neuroscience. 2006; 138(1):183-188. [20] BERNAL A, ARRANZ L. Nestin-expressing progenitor cells: function, identity and therapeutic implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2018;75(12):2177-2195. [21] 郭筱琪.Nestin巢蛋白对神经干细胞和星形胶质细胞增殖分化的影响[D].苏州:苏州大学,2019. [22] LIU XS, CHOPP M, ZHANG XG, et al. Gene profiles and electrophysiology of doublecortin-expressing cells in the subventricular zone after ischemic stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2009;29(2):297-307. [23] CHEN X, JIANG H. Tau as a potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke. Aging (Albany NY). 2019;11(24):12827-12843. [24] ALI T, KIM MO. Melatonin ameliorates amyloid beta-induced memory deficits, tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration via PI3/Akt/GSk3β pathway in the mouse hippocampus. J Pineal Res. 2015;59(1):47-59. [25] ROSENBLOOM AB, TARCZYŃSKI M, LAM N, et al. β-Catenin signaling dynamics regulate cell fate in differentiating neural stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020;117(46):28828-28837. [26] SHRUSTER A, BEN-ZUR T, MELAMED E, et al. Wnt signaling enhances neurogenesis and improves neurological function after focal ischemic injury. PLoS One. 2012; 7(7):e40843. [27] 王先斌,汤红艳,李兴统,等.Wnt信号通路与神经发生、神经退行性变过程中的表述及作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(28):4587-4592. [28] 王凯,赵斌,王栓科,等.Notch信号转导通路在神经修复与再生中的激活效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(23):4351-4354. [29] ZHANG Y, HE K, WANG F, et al. Notch-1 signaling regulates astrocytic proliferation and activation after hypoxia exposure. Neurosci Lett. 2015; 603:12-18. [30] ROESE-KOERNER B, STAPPERT L, BRÜSTLE O. Notch/Hes signaling and miR-9 engage in complex feedback interactions controlling neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation. Neurogenesis (Austin). 2017;4(1):e1313647. [31] WANG L, ZHOU K, FU Z, et al. Brain Development and Akt Signaling: the Crossroads of Signaling Pathway and Neurodevelopmental Diseases. J Mol Neurosci. 2017;61(3):379-384. [32] SONG G, OUYANG G, BAO S. The activation of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med. 2005;9(1):59-71. [33] GUO W, NAGAPPAN G, LU B. Differential effects of transient and sustained activation of BDNF-TrkB signaling. Dev Neurobiol. 2018;78(7):647-659. [34] EYILETEN C, SHARIF L, WICIK Z, et al. The Relation of the Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor with MicroRNAs in Neurodegenerative Diseases and Ischemic Stroke. Mol Neurobiol. 2021;58(1):329-347. [35] ZHAO H, ALAM A, SAN CY, et al. Molecular mechanisms of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuro-protection: Recent developments. Brain Res. 2017;1665:1-21. [36] KOLCH W. Meaningful relationships: the regulation of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway by protein interactions. Biochem J. 2000;351 Pt 2(Pt 2):289-305. [37] VANDAMME D, HERRERO A, AL-MULLA F, et al. Regulation of the MAPK pathway by raf kinase inhibitory protein. Crit Rev Oncog. 2014;19(6):405-415. [38] LIU Y, LU JB, CHEN Q, et al. Involvement of MAPK/ERK kinase-ERK pathway in exogenous bFGF-induced Egr-1 binding activity enhancement in anoxia-reoxygenation injured astrocytes. Neurosci Bull. 2007;23(4):221-228. [39] GUO YJ, PAN WW, LIU SB, et al. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19(3):1997-2007. [40] TEERTAM SK, PRAKASH BABU P. Differential role of SIRT1/MAPK pathway during cerebral ischemia in rats and humans. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):6339. [41] O’NEILL E, KOLCH W. Conferring specificity on the ubiquitous Raf/MEK signalling pathway. Br J Cancer. 2004;90(2):283-288. [42] XING L, LARSEN RS, BJORKLUND GR, et al. Layer specific and general requirements for ERK/MAPK signaling in the developing neocortex. Elife. 2016;5:e11123. [43] ROUX PP, BLENIS J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: a family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2004;68(2):320-344. [44] GALLUZZI L, KEPP O, KROEMER G. Mitochondria: master regulators of danger signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(12):780-788. [45] HUANG PJ, KUO CC, LEE HC, et al. Transferring Xenogenic Mitochondria Provides Neural Protection Against Ischemic Stress in Ischemic Rat Brains. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(5):913-927. [46] HAYAKAWA K, ESPOSITO E, WANG X, et al. Transfer of mitochondria from astrocytes to neurons after stroke. Nature. 2016;535(7613):551-555. [47] WANG Y, DENG Y, ZHOU GQ. SDF-1alpha/CXCR4-mediated migration of systemically transplanted bone marrow stromal cells towards ischemic brain lesion in a rat model. Brain Res. 2008;1195:104-112. [48] SHYU WC, LIN SZ, YEN PS, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha promotes neuroprotection, angiogenesis, and mobilization/homing of bone marrow-derived cells in stroke rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;324(2):834-849. [49] LE BELLE JE, OROZCO NM, PAUCAR AA, et al. Proliferative neural stem cells have high endogenous ROS levels that regulate self-renewal and neurogenesis in a PI3K/Akt-dependant manner. Cell Stem Cell. 2011;8(1): 59-71. [50] 闫海清,贵永堃,任瑞芳,等.沉默信息调节因子2相关酶1对急性脑梗死大鼠的神经保护作用及其机制[J].中华实验外科杂志,2020, 37(2):261-262. [51] BARTOLI-LEONARD F, WILKINSON FL, LANGFORD-SMITH A, et al. The Interplay of SIRT1 and Wnt Signaling in Vascular Calcification. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2018; 5:183. [52] ZHANG TJ, HANG J, WEN DX, et al. Hippocampus bcl-2 and bax expression and neuronal apoptosis after moderate hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass in rats. Anesth Analg. 2006;102(4):1018-1025. [53] KURANAGA E. Beyond apoptosis: caspase regulatory mechanisms and functions in vivo. Genes Cells. 2012;17(2):83-97. [54] YI X, YIN XM, DONG Z. Inhibition of Bid-induced apoptosis by Bcl-2. tBid insertion, Bax translocation, and Bax/Bak oligomerization suppressed. J Biol Chem. 2003; 278(19):16992-16999. [55] HINMAN JD. The back and forth of axonal injury and repair after stroke. Curr Opin Neurol. 2014;27(6):615-623. [56] KIMURA T, HORIKOSHI Y, KURIYAGAWA C, et al. Rho/ROCK Pathway and Noncoding RNAs: Implications in Ischemic Stroke and Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):11573. [57] LIU J, GAO HY, WANG XF. The role of the Rho/ROCK signaling pathway in inhibiting axonal regeneration in the central nervous system. Neural Regen Res. 2015;10(11):1892-1896. [58] GOVEK EE, WU Z, ACEHAN D, et al. Cdc42 Regulates Neuronal Polarity during Cerebellar Axon Formation and Glial-Guided Migration. iScience. 2018;1:35-48. [59] RAPPAZ B, LAI WSK, CORREIA JP, et al. FLIM FRET Visualization of Cdc42 Activation by Netrin-1 in Embryonic Spinal Commissural Neuron Growth Cones. PLoS One. 2016;11(8):e159405. [60] SHI X, DOYCHEVA DM, XU L, et al. Sestrin2 induced by hypoxia inducible factor1 alpha protects the blood-brain barrier via inhibiting VEGF after severe hypoxic-ischemic injury in neonatal rats. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;95: 111-121. [61] MELINCOVICI CS, BOŞCA AB, ŞUŞMAN S, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) - key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 2018;59(2):455-467. [62] WANG Z, TAO J, ZHANG Q, et al. Effect of oxygen and glucose deprivation on VEGF and its receptors in microvascular endothelial cells co-cultured with mast cells. Cell Biol Int. 2015;39(9):1016-1025. [63] SAHARINEN P, BRY M, ALITALO K. How do angiopoietins Tie in with vascular endothelial growth factors? Curr Opin Hematol. 2010;17(3):198-205. [64] JEONG CH, KIM SM, LIM JY, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells expressing brain-derived neurotrophic factor enhance endogenous neurogenesis in an ischemic stroke model. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:129145. [65] WANG F, TANG H, ZHU J, et al. Transplanting Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Treatment of Ischemic Stroke. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(12):1825-1834. [66] KEANEY J, CAMPBELL M. The dynamic blood-brain barrier. FEBS J. 2015; 282(21): 4067-4079. [67] BAUER H, TRAWEGER A. Tight Junctions of the Blood-Brain Barrier-A Molecular Gatekeeper. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2016;15(9):1016-1029. [68] STAMATOVIC SM, JOHNSON AM, KEEP RF, et al. Junctional proteins of the blood-brain barrier: New insights into function and dysfunction. Tissue Barriers. 2016;4(1):e1154641. [69] GREENE C, HANLEY N, CAMPBELL M. Claudin-5: gatekeeper of neurological function. Fluids Barriers CNS. 2019;16(1):3. [70] GREENE C, CAMPBELL M. Tight junction modulation of the blood brain barrier: CNS delivery of small molecules. Tissue Barriers. 2016;4(1): e1138017. [71] SUN L, ZHANG H, WANG W, et al. Astragaloside IV Exerts Cognitive Benefits and Promotes Hippocampal Neurogenesis in Stroke Mice by Downregulating Interleukin-17 Expression via Wnt Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:421. [72] SUN L, HAN R, GUO F, et al. Antagonistic effects of IL-17 and Astragaloside IV on cortical neurogenesis and cognitive behavior after stroke in adult mice through Akt/GSK-3β pathway. Cell Death Discov. 2020;6:74. [73] NI GX, LIANG C, WANG J, et al. Astragaloside IV improves neurobehavior and promotes hippocampal neurogenesis in MCAO rats though BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;130:110353. [74] CHEN X, WU H, CHEN H, et al. Astragaloside VI Promotes Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Enhances Neurological Function Recovery in Transient Cerebral Ischemic Injury via Activating EGFR/MAPK Signaling Cascades. Mol Neurobiol. 2019;56(4):3053-3067. [75] ZHAO YH, LIU NW, KE CC, et al. Combined treatment of sodium ferulate, n-butylidenephthalide, and ADSCs rehabilitates neurovascular unit in rats after photothrombotic stroke. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(1):126-142. [76] LI S, LU Y, DING D, et al. Fibroblast growth factor 2 contributes to the effect of salidroside on dendritic and synaptic plasticity after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(11):10951-10968. [77] NI XC, WANG HF, CAI YY, et al. Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits astrocyte activation and promotes transfer of astrocytic mitochondria to neurons against ischemic stroke. Redox Biol. 2022;54:102363. [78] LI XY, LIANG J, TANG YB, et al. Ginsenoside Rd prevents glutamate-induced apoptosis in rat cortical neurons. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2010;37(2):199-204. [79] ZONG W, GOUDA M, CAI E, et al. The Antioxidant Phytochemical Schisandrin A Promotes Neural Cell Proliferation and Differentiation after Ischemic Brain Injury. Molecules. 2021;26(24):7466. [80] XIE W, ZHU T, ZHOU P, et al. Notoginseng Leaf Triterpenes Ameliorates OGD/R-Induced Neuronal Injury via SIRT1/2/3-Foxo3a-MnSOD/PGC-1α Signaling Pathways Mediated by the NAMPT-NAD Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020; 2020:7308386. [81] WEI ZZ, CHEN D, LIU LP, et al. Enhanced Neurogenesis and Collaterogenesis by Sodium Danshensu Treatment After Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice. Cell Transplant. 2018;27(4):622-636. [82] ZHANG S, KONG D W, MA GD, et al. Long-term administration of salvianolic acid A promotes endogenous neurogenesis in ischemic stroke rats through activating Wnt3a/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2022;43(9):2212-2225. [83] WANG J, NI G, LIU Y, et al. Tanshinone IIA Promotes Axonal Regeneration in Rats with Focal Cerebral Ischemia Through the Inhibition of Nogo-A/NgR1/RhoA/ROCKII/MLC Signaling. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2020;14:2775-2787. [84] ZHU T, WANG L, XIE W, et al. Notoginsenoside R1 Improves Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Promoting Neurogenesis via the BDNF/Akt/CREB Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:615998. [85] YANG X, ZHENG T, HONG H, et al. Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract and Ginkgolide B against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation and glucose injury in a new in vitro multicellular network model. Front Med. 2018;12(3):307-318. [86] LIN L, CHU L, REN C, et al. Enhanced Migration of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells with Tetramethylpyrazine and Its Synergistic Effect on Angiogenesis and Neurogenesis After Cerebral Ischemia in Rats. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(13):871-881. [87] WU Q, LIU J, MAO Z, et al. Ligustilide attenuates ischemic stroke injury by promoting Drp1-mediated mitochondrial fission via activation of AMPK. Phytomedicine. 2022;95:153884. [88] ZHOU Z, DUN L, WEI B, et al. Musk Ketone Induces Neural Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation in Cerebral Ischemia via Activation of the PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway. Neuroscience. 2020;435:1-9. [89] 乔利军,向娇娇,崔志忠,等.麝香酮对脑缺血再灌注损伤大鼠神经再生作用的研究[J].中医药学报,2022(11):18-24. [90] LEE HJ, AHN SM, PAK ME, et al. Positive effects of α-asarone on transplanted neural progenitor cells in a murine model of ischemic stroke. Phytomedicine. 2018;51:151-161. [91] KIM R, LEE S, LEE CY, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza enhances the survival of mesenchymal stem cells under ischemic conditions. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2018; 70(9):1228-1241. [92] YU B, YAO Y, ZHANG X, et al. Synergic Neuroprotection Between Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort and Borneol Against Ischemic Stroke by Neurogenesis via Modulating Reactive Astrogliosis and Maintaining the Blood-Brain Barrier. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:666790. [93] ZAMANIAN JL, XU L, FOO LC, et al. Genomic analysis of reactive astrogliosis. J Neurosci. 2012;32(18):6391-6410. [94] DU X, LI C, ZHANG S, et al. Exploring the pharmacological mechanism of calculus bovis in cerebral ischaemic stroke using a network pharmacology approach. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022;284:114507. [95] LUO C, WU Y, CHEN X, et al. Chemical Composition, Protective Effects, and Mechanisms of Volatile Oil from Fructus Gleditsiae Abnormalis with Nasal Administration against Ischemic Injury in HFD and MCAO-Induced Rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021;2021:8880996. [96] XIE Q, MA R, GUO X, et al. Benzoinum from Styrax tonkinensis (Pierre) Craib ex Hart exerts a NVU protective effect by inhibiting cell apoptosis in cerebral ischaemia rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;265:113355. [97] CHEN H, REN M, LI H, et al. Neuroprotection of benzoinum in cerebral ischemia model rats via the ACE-AngI-VEGF pathway. Life Sci. 2020;260: 118418. [98] 张运克,高峰,张丹,等.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑组织NSE和GFAP表达的影响[J].中医杂志,2013, 54(23):2043-2045. [99] 张运克.补阳还五汤及拆方影响脑缺血再灌注大鼠细胞凋亡与Bcl-2、Bax蛋白的表达(英文)[J].中国临床康复,2006,10(43):196-199. [100] ZHANG YK, HAN XY, CHE ZY. Effects of buyang huanwu tang combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation on the expression of VEGF and Ki-67 in the brain tissue of the cerebral ischemia-reperfusion model rat. J Tradit Chin Med. 2010;30(4):278-282. [101] 张运克,车志英,李可.补阳还五汤联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑组织紧密连接蛋白的表达[J].中国组织工程研究,2019, 23(1):55-60. [102] 冯静静,刘昱言,刘轲,等.脑脉通联合骨髓间充质干细胞移植对脑缺血再灌注大鼠巢蛋白表达的影响[J].辽宁中医杂志,2021,48(11):181-185. [103] 张运克,傅小欧,李可.麝香黄芪复方滴丸对缺血再灌注损伤大鼠脑组织紧密连接蛋白表达影响[J]. 中华中医药学刊,2022,40(3):1-5. [104] 李梦頔,李一兴,张运克.麝香黄芪复方滴丸对体外缺血缺氧血脑屏障通透性及相关调节蛋白的影响[J].中华中医药学刊,2022,40(1):80-84. [105] FU DL, LI JH, SHI YH, et al. Sanhua Decoction, a Classic Herbal Prescription, Exerts Neuroprotection Through Regulating Phosphorylated Tau Level and Promoting Adult Endogenous Neurogenesis After Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Front Physiol. 2020;11:57. [106] 赵克非,李斌,张艳滨,等.健脾益智胶囊对大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠海马Hes1表达的影响[J].广西中医药,2018,41(3):70-73. [107] 冯珂,纪立金.健脾益智胶囊对大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠海马神经干细胞增殖及Notch1、Jagged1表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2013,28(4): 921-924. [108] 冯珂,纪立金.健脾益智胶囊对大脑中动脉栓塞大鼠海马BDNF、EGF、bFGF表达的影响[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(6):2686-2688. [109] 陈小玉.白脉散有效成分组调控神经干细胞增殖的分子机制研究[D].北京:中央民族大学,2013. [110] 孟庆萍,胡建鹏,王键,等.两种中药复方对局灶性脑缺血再灌注大鼠脑组织Hes-1、Hes-5表达的动态影响[J].安徽中医学院学报,2009, 28(5):52-55. [111] DU Q, DENG R, LI W, et al. Baoyuan Capsule promotes neurogenesis and neurological functional recovery through improving mitochondrial function and modulating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. 2021;93:153795. [112] 寿雅琨.基于BDNF/TrkB/CREB信号通路探讨芪仙通络方对MCAO大鼠突触重塑的影响及作用机制[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2020. [113] 林秀慧,吴志敏,王逸如,等.芪仙通络方对脑梗死恢复期患者神经功能恢复的影响及机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(23):118-124. [114] 林秀慧,周春吉,马珂,等.芪仙通络方对脑缺血大鼠内源性神经干细胞再生的影响及机制[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2017,23(24):141-147. [115] 荆莉,唐丽,李敏,等.脑疏宁对缺血性脑卒中神经再生作用的研究[J].中央民族大学学报(自然科学版),2020,29(3):71-79. [116] 鲁启洪.银杏活脑胶囊对大鼠缺血性脑卒中微血管增殖和神经干细胞再生的影响[J].湖北民族学院学报(医学版),2009,26(4):7-9. [117] 胡国恒,刘侃,尹美美,等.肾脑复元汤对MCAO大鼠脑保护作用及cyt-C,Caspase-9,Caspase-3的影响[J].中国中医急症,2017,26(3):384-386. [118] 胡国恒,侯小花,李映辰,等.肾脑复元汤联合人脐带间充质干细胞移植对MCAO大鼠神经功能恢复及VEGF表达的影响[J].中国中医急症, 2016,25(1):4-7. [119] 李映辰,王瑾茜,刘侃,等.肾脑复元汤联合人脐带间充质干细胞移植对脑缺血再灌注大鼠神经营养因子表达的影响[J].中草药,2016, 47(5):781-787. [120] VANDAMME D, HERRERO A, AL-MULLAF, et al. Regulation of the MAPK pathway by raf kinase inhibitory protein. Crit Rev Oncog. 2014;19(6):405-415. [121] SIMONYAN L, RENAULT TT, NOVAIS MJ, et al. Regulation of Bax/mitochondria interaction by AKT. FEBS Lett. 2016;590(1):13-21. [122] TRAZZI S, STEGER M, MITRUGNO VM, et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptors increase neuronal precursor proliferation through AKT/glycogen synthase kinase-3beta/beta-catenin signaling. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(13):10098-10109. [123] LI XT, LIANG Z, WANG TT, et al. Brain-derived Neurotrophic Factor Promotes Growth of Neurons and Neural Stem Cells Possibly by Triggering the Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/ AKT/Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β/β-catenin Pathway. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2017;16(7):828-836. [124] FEI Y, ZHAO B, ZHU J, et al. XQ-1H promotes cerebral angiogenesis via activating PI3K/Akt/GSK3β/β-catenin/VEGF signal in mice exposed to cerebral ischemic injury. Life Sci. 2021;272:119234. |
| [1] | 艾芳芳, 肖红燕, 汪 芳, 朱永朝, 马丽君. 枸杞多糖联合奥沙利铂可逆转结肠癌干细胞的耐药[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 74-79. |
| [2] | 范永晶, 王 姝, 金武龙. 颌骨来源骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的特点、优势与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [3] | 黄勇彬, 王 涛, 娄园一, 庞景群, 陈光华. 间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 107-112. |
| [4] | 杨 婷, 丁智斌, 江 楠, 韩红霞, 侯苗苗, 马存根, 宋丽娟, 李新毅. 星形胶质细胞调节缺血性脑卒中的胶质瘢痕形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 131-138. |
| [5] | 马岁录, 何志军, 刘 涛, 李 岩, 何元旭, 何 波, 王威威, 魏晓涛. 中药单体调控“细胞自噬”防治皮瓣坏死[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 153-158. |
| [6] | 彭英楠, 边志磊, 张素平, 李 丽, 曹伟杰, 万鼎铭. CD34+细胞数对单倍体造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 1-6. |
| [7] | 韦雨柔, 田佳庆, 何宪顺, 詹芝玮, 魏腾飞, 林天烨, 何 伟, 魏秋实. 慢病毒沉默Piezo1蛋白与人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化及TAZ的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 12-19. |
| [8] | 王宪峰, 王 锟, 孙 晗, 孙晓亮, 言力韬. 脐带间充质干细胞外泌体LncRNA H19修复软骨损伤的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 20-25. |
| [9] | 张元澍, 何 旭, 薛 源, 金叶盛, 汪 凯, 施 勤, 芮永军. 鸢尾素缓解棕榈酸对骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨抑制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 26-31. |
| [10] | 何莉君, 漆小娟. 脂肪间充质干细胞过表达骨形态发生蛋白2促进骨质疏松大鼠牙槽骨缺损修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 32-37. |
| [11] | 周明华, 胡晓宇. LncRNA SNHG4调控牙周膜干细胞成骨分化过程中的miR-152-3p[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 38-43. |
| [12] | 郑嵘炅, 邓泽润, 韩 丹, 孙丽华. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体调节大鼠肝细胞凋亡的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 44-49. |
| [13] | 郑明魁, 薛晨晖, 关晓明, 马 迅. 人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体降低脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的通透性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [14] | 孙 菁, 廖 健, 孙江龄, 程 萍, 冯红超. 重组人生长激素促进人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 56-61. |
| [15] | 何宛俞, 程乐平. 干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的策略与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
缺血性脑卒中归属于中医“中风”范畴,中风病程分为急性期、恢复期和后遗症期3个阶段,急性期指发病后2周以内,中脏腑可至1个月。气虚血瘀、脑窍闭塞乃缺血性脑卒中病机之本,补元益气修复既损之脑神,活血行血疏通淤塞之脉道,开窍通关以启闭醒神,改善缺血性脑卒中引起的脑髓失养、神机失用临床证候。大脑缺血受到损伤可激活内源性神经干细胞,增殖迁移到梗死区和梗死周围区域,在多种营养因子的调节下分化为功能神经元并融入局部神经回路,促进神经修复[5],由于其再生能力有限,内源性神经发生无法替代及充分补充损伤丢失的神经细胞。现代药理学实验及临床研究表明,在缺血性脑卒中急性期,醒脑开窍类中药(如麝香、冰片、苏合香、安息香、牛黄、石菖蒲等)通过调节缺血性脑卒中后血脑屏障通透性、抗氧化应激、抑制神经细胞凋亡等途径促进脑内神经单元修复[6]。以补阳还五汤为代表的益气活血类方药多途径、多靶点减轻缺血缺氧引起的神经元损伤,促进神经系统重塑,综合作用于神经血管单元促进内源性神经修复,改善缺血性脑卒中引起的神经功能损伤[7]。大量研究证实,益气活血开窍类中药及中药复方能够在缺血性脑卒中急性期通过抗神经细胞凋亡、促进内源性神经祖细胞增殖、调节神经分化等途径调节内源性神经发生,发挥神经保护作用,并且具有毒副作用小、作用靶点多等优势[8]。
干细胞是一种具有自我更新和分化能力的细胞,主要包括胚胎干细胞、间充质干细胞、神经干细胞和诱导多能干细胞。1989年,TØNDER等[9]研究发现,移植的神经细胞能够融入缺血性脑卒中大鼠脑组织。自此以来,干细胞用于中风后神经修复的研究逐渐深入,例如胚胎干细胞和诱导多能干细胞能够用于替代神经元细胞,发挥修复损伤大脑的能力,间充质干细胞和脐血干细胞能够改善神经病理学和神经缺陷[10]。这些干细胞能够增殖并分化为神经细胞,替代缺血性脑卒中后坏死的神经细胞,在改善缺血性脑卒中急性期的神经功能缺损中具有良好的神经功能修复效果[11],越来越多地应用于卒中后急性期神经功能修复的相关研究。
由于外源性干细胞在脑内的移植生存率仅有5%,并且存在内源性和外源性干细胞在体内存活率低、有效分化率低和抵达病灶发挥作用率低等问题[12],越来越多的学者建议利用药物及相关因子辅助干细胞移植以提高干细胞治疗作用[13]。中药调控干细胞疗法自20世纪80年代在中国最初用于白血病骨髓移植的治疗研究,2005年始,中药调控干细胞逐渐用于缺血性脑卒中后神经修复与再生[14-15]。具有活血化瘀、益气生血、醒脑开窍的益气活血开窍类中药及复方治疗缺血性脑卒中神经功能损伤历史悠久,故而利用益气活血开窍类中药调控干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的研究层出不穷[16-17]。体内体外研究发现,益气活血开窍类中药辅助干细胞移植治疗缺血性脑卒中更有利于提高移植细胞向病灶部位的迁移能力,促进干细胞归巢、增殖及分化,减轻干细胞移植的不良作用及免疫抑制等不良反应[18]。该文通过梳理缺血性脑卒中神经修复的相关信号通路和主要机制,阐述益气活血开窍类中药及复方调控干细胞促进缺血性卒中急性期神经修复作用及相关机制,以期为开拓缺血性脑卒中的治疗方法提供参考。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2022年12月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 重点文献检索时间范围自2010年1月至2022年12月,同时纳入少量远期经典文献。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中国知网、PubMed数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 以“supplementing qi and activating blood circulation;inducing resuscitation;traditional Chinese medicine (TCM);compounds;ischemic stroke;nerve repair;stem cells”为英文关键词,以“益气活血;开窍;中药;复方;缺血性脑卒中;神经修复;干细胞”为中文关键词。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 研究原著,综述,述评,荟萃分析。
1.1.6 手工检索情况 无。
1.1.7 检索策略 以PubMed数据库检索策略为例,见图1。

1.2 文献筛选标准 去除重复文献及与研究主题相关性差的文献,选择与研究目的、内容关系密切的文献。
1.3 质量评估及数据的提取 经资料收集者互相评估纳入文献的有效性和适用性,通过阅读文题和摘要进行初步筛选;排除中英文文献重复性研究,以及内容不相关的文献,最后纳入中英文文献共124篇进行综述,其中中文文献30篇来源于中国知网,英文文献94篇来源于PubMed数据库。文献筛选流程,见图2。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 中药及干细胞在缺血性脑卒中中的应用已被广泛探讨,中药调控干细胞增殖方面也有过探究,但随着研究的进一步深入,该综述从中药对缺血性脑卒中神经修复的相关机制研究进行归纳整理,进而对中药促进干细胞增殖、抑制细胞凋亡、调控干细胞分化、促进轴突再生及改善脑内微环境,促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的机制研究进行了论述。
3.3 综述的局限性 该综述文献检索以主题词结合自由词,时间跨度较长,可能会出现文献检索不全面等问题,而且文章主要综述基础实验研究成果,临床相关研究仍旧不足,但尽可能对该领域的重要研究成果及最新研究热点进行归纳论述。
3.4 综述的重要意义 该研究通过总结近年促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的益气活血开窍类中药及复方发现,益气活血开窍类中药及中药复方在缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复过程中发挥重要作用,通过调控干细胞增殖相关蛋白促进干细胞增殖,调控相关通路促进缺血性脑卒中后神经发生,通过改善脑内微环境,促进再生神经存活、抑制神经再生过程中不良事件的发生,从而参与缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复过程。通过综述益气活血开窍类中药在干细胞移植中发挥的协同调控作用及相关机制研究进展,希望能够为缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复相关新药研发及新的疗法研究提供新思路及一定的理论依据。
3.5 课题专家组对未来的建议 益气活血开窍类中药及中药复方调控干细胞促进缺血性卒中急性期神经修复研究确实取得了一些良好成果,从益气活血开窍类中药单体、中药有效成分及中药复方方面取得了较多进展,但对其药效及作用机制需要进一步研究探索。与需要急性干预的神经保护相比,神经修复治疗存在一个相对较长的时间窗,在此时间窗内,大脑重塑可以被治疗调节,这将有益于所有脑卒中患者。因此,通过益气活血开窍类中药及中药复方辅助干细胞治疗缺血性脑卒中,促进神经修复也必将是有前景的治疗方式。然而由于缺血性脑卒中后中枢神经系统反应的复杂性以及神经修复过程中的可塑性,采用何种治疗模式、提高治疗效率和治疗安全性,以及应用于临床的可行性仍旧是亟待探索与解决的问题,需要更深一步的研究。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
益气活血开窍类中药及复方:气虚血瘀证是缺血性脑卒中的最主要证候,缺血性脑卒中导致脑内血脉淤堵,脑窍闭塞,益气修复既损之脑神,活血疏通淤塞之脉道,开窍以启闭醒神,益气活血开窍类中药及复方对于改善缺血性脑卒中引起的脑髓失养、神机失用等神经损伤具有重要意义。缺血性脑卒中急性期:指发病后2周以内,伴有神志障碍者可至1个月。在缺血性脑卒中急性期,神经修复存在一个相对较长的时间窗,在此时间窗内调节大脑重塑,对于改善受损的神经功能起到至关重要的作用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
近年研究发现益气活血开窍类中药及复方可显著促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复,益气活血开窍类中药及复方通过调控内源性神经发生及促进外源性干细胞在体内的存活、迁移、增殖、分化来改善缺血性脑卒中急性期神经损伤。本文综述了益气活血开窍类中药及复方调控干细胞促进缺血性脑卒中急性期神经修复的相关因子及信号通路,以期为缺血性脑卒中新药研发及新的治疗方法提供依据与参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||