中国组织工程研究 ›› 2024, Vol. 28 ›› Issue (1): 107-112.doi: 10.12307/2023.769
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的应用前景
黄勇彬1,王 涛1,娄园一1,庞景群1,陈光华2
- 1广东医科大学,广东省湛江市 524000;2广东医科大学附属医院骨科中心,广东省湛江市 524000
-
收稿日期:2022-11-15接受日期:2023-01-04出版日期:2024-01-08发布日期:2023-06-28 -
通讯作者:陈光华,博士,主任医师,副教授,博士生导师,广东医科大学附属医院骨科中心,广东省湛江市 524000 -
作者简介:黄勇彬,男,1997年生,广东医科大学在读硕士,初级医师,主要从事创伤骨科、骨质疏松、肌肉萎缩等方面的研究。 -
基金资助:广东省基础与应用基础研究基金自然科学基金面上项目(2021A1515011434),项目负责人:陈光华
Application prospect of mesenchymal stem cells in promoting muscle tissue repair
Huang Yongbin1, Wang Tao1, Lou Yuanyi1, Pang Jingqun1, Chen Guanghua2
- 1Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China; 2Orthopedic Center of Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2022-11-15Accepted:2023-01-04Online:2024-01-08Published:2023-06-28 -
Contact:Chen Guanghua, MD, Chief physician, Associate professor, Doctoral supervisor, Orthopedic Center of Affiliated Hospital of Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China -
About author:Huang Yongbin, Master candidate, Junior physician, Guangdong Medical University, Zhanjiang 524000, Guangdong Province, China -
Supported by:General Program of the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation, No. 2021A1515011434 (to CGH)
摘要:

文题释义:
间充质干细胞:来源于胚胎发育的中胚层,具有多方向分化的潜能,在相关信号或外来因素的刺激下可分化为心肌、成骨、成脂、上皮等细胞。目前,已有大量研究证实间充质干细胞可用于治疗心血管疾病、肾病、糖尿病、肌腱损伤等。肌肉组织修复:肌肉组织结构破坏涉及肌膜的破坏、细胞骨架的损伤以及细胞内基质的异常,而肌肉组织修复包括坏死肌纤维的清除、肌纤维的再生、新生肌肉组织的重塑。
目的:综述间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的研究进展,为进一步临床应用提供理论依据。
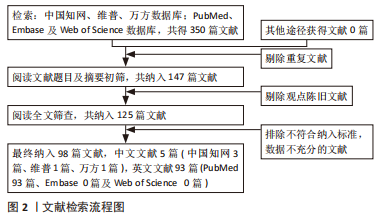
方法:检索中国知网、维普、万方、PubMed、Embase及Web of Science数据库从建库至2022年相关文献,检索词为“间充质干细胞,肌肉组织,肌肉损伤,肌肉萎缩,外泌体,支架”和“mesenchymal stem cells,muscle tissue,muscle injury,muscle atrophy,exosomes,scaffolds”。筛选间充质干细胞促进肌纤维增殖修复的文献,共纳入98篇文献进行综述分析。
结果与结论:①间充质干细胞促进肌纤维增殖修复的相关机制复杂,多以抗炎、抑制间质纤维化、抑制脂肪形成等方式促进肌纤维增殖修复;②基于间充质干细胞的相关生物支架、细胞共培养等可明显弥补间充质干细胞定植后存活率低的缺点;③当前间充质干细胞疗法仍有明显的局限性,未来间充质干细胞联合其他治疗方式应当成为主要的发展趋势。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6860-0489(黄勇彬) ;https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8877-1322(陈光华)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
黄勇彬, 王 涛, 娄园一, 庞景群, 陈光华. 间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的应用前景[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 107-112.
Huang Yongbin, Wang Tao, Lou Yuanyi, Pang Jingqun, Chen Guanghua. Application prospect of mesenchymal stem cells in promoting muscle tissue repair[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2024, 28(1): 107-112.
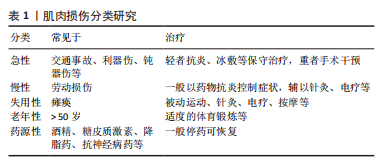
2.1.1 肌肉损伤的分类及表现 随着经济的迅猛发展,人均年龄普遍提高。相应地,人们遭遇肌肉损伤的可能性也逐渐加大,发生率为10%-55%[7],包括利器、交通事故所致的急性损伤,过度体育锻炼或超过正常日常活动水平肢体操作所致的慢性损伤,以及内分泌性、老年性、失用性、药源性、神经源性的肌少症等,结果造成骨骼肌质量和功能的丢失,见表1。骨骼肌占体质量的35%-45%[8],严重损伤者将失去劳动能力。目前该领域的治疗尚无突破性进展,极大影响患者的生活质量和生理心理健康。
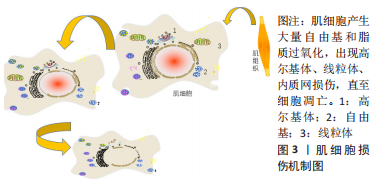
2.1.2 肌肉损伤的机制 一般来说,肌肉组织损伤修复通常需要经历3个阶段[7,9]:第一阶段是肌纤维的坏死和退化产生的炎性反应,例如嗜中性粒细胞等炎症细胞浸润及其细胞因子分泌所致的一系列连续反应过程,此阶段一般自损伤起始3 d内达到高峰[10],是组织破坏的主要阶段;第二阶段涉及成纤维细胞迁移修复以及神经血管的形成;第三阶段则是新生肌肉组织在运动过程中的逐渐成熟[11]。在这个过程中,原肌纤维坏死凋亡,新生细胞修复肌肉组织,然而具体机制在学术界颇具争议,有学者认为肌肉损伤起始于损伤后炎性反应所致的大量自由基和脂质过氧化,引起损伤肌细胞的能量代谢紊乱和细胞内钙稳态失调,最终造成肌纤维的坏死、凋亡[12],见图3。肌肉组织具有一定的维持体内平衡和损伤后增殖再生修复的能力,但是如果损伤超出机体自我修复能力,修复和重塑阶段将失去平衡,形成瘢痕组织,以取代受伤的骨骼肌,这将极大影响机体的运动能力,不利于功能恢复。
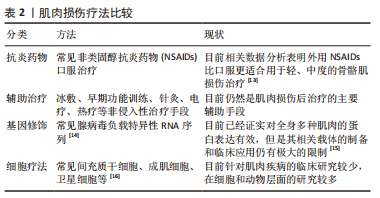
2.1.3 肌肉损伤现有的修复方法和手段 肌纤维再生修复涉及肌纤维数量和单位体积的修复,许多治疗策略已经被尝试修复肌肉组织,例如抗炎、冰敷、针灸、电疗等保守治疗较为常见,适度的早期锻炼也被发现可以一定程度上加快肌肉组织的再生愈合,但是相关治疗效果都不是十分理想,因为大多数情况下都只是组织的愈合,而没有恢复理想的肌力。为此,基因疗法和干细胞疗法逐渐应用于细胞或动物层面的肌肉损伤修复研究[3],并且展现了肌纤维增殖修复的良好优势,见表2。鉴于间充质干细胞的再生特性,开发新的方法用于辅助手术或药物等治疗手段以促进肌纤维增殖再生修复成为当下的研究热点。
2.2 间充质干细胞的来源及其生物学特性
2.2.1 间充质干细胞的来源 间充质干细胞可从骨髓、脂肪、脐带及其血液等组织中分离出来,特征包括易于分离、体外扩增能力和自我更新能力强,是潜在的具有分化为不同组织类型能力的多能基质细胞,可以经过诱导产生骨骼细胞、软骨细胞、脂肪细胞、心肌细胞以及神经细胞等,是组织再生和退化性相关疾病干细胞治疗的极佳来源[17-18]。间充质干细胞可以通过细胞因子等营养因子的分泌,调节包括肌肉骨骼组织、外周神经等组织功能[19-20],例如分泌血管内皮生长因子促进血管形成,分泌神经营养因子增加神经纤维髓鞘化和轴突再生。间充质干细胞还具有相当大的增殖和肌源性分化潜能,基于间充质干细胞的肌纤维增殖治疗已逐渐用于细胞或动物研究,发展迅速。
2.2.2 间充质干细胞的生物学特性 随着干细胞研究的快速发展,发现间充质干细胞的来源条件、质量和数量会对临床应用成功与否产生重要的影响[21]。最早是从骨髓中分离出间充质干细胞应用于骨骼再生研究,但是此方式存在创伤性大、收获后细胞数量少等问题,极大限制了临床应用。因此,脂肪、脐带等组织来源的间充质干细胞逐渐得到发展,相较于骨髓来源间充质干细胞,具有组织采集容易、原始细胞产量高、体外增殖能力强等明显优势,目前已成为骨髓间充质干细胞的一个有吸引力的替代品[22-23]。
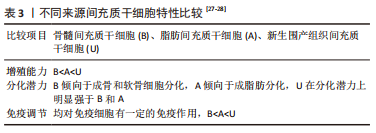
学者们最初认为不同来源间充质干细胞具有相似的特性:都表达间充质干细胞特有的标记物谱,例如 CD73(SH3),CD90,CD105(SH2)[24],都能够在体外向成骨、成脂、成肌和成软骨细胞系分化[25],但是深入研究后发现分化潜力、增殖代谢能力等方面存在明显差异,见表3。间充质干细胞的增殖能力会随着传代数的增加而不断下降,但是不同来源的间充质干细胞具有不同的衰老速度(新生围产组织间充质干细胞<脂肪组织间充质干细胞<骨髓间充质干细胞),因此,目前临床上更多地采用具有“零岁细胞”之称的围产组织来源间充质干细胞,例如脐带、羊膜、胎盘等[26]。
因此,利用间充质干细胞进行研究时,可以根据不同间充质干细胞特性进行合理的选择。现如今有很多研究致力于使用间充质干细胞促进如外伤源性、血管源性、神经源性等损伤的肌纤维增殖修复进程[29-32]。
2.3 间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的机制及方法
2.3.1 间充质干细胞促进肌纤维再生
(1)旁分泌作用:细胞间的联系和外来刺激均可促使间充质干细胞产生大量的可溶性细胞因子,用于协调机体功能变化、拮抗细胞凋亡、促进组织修复等。旁分泌机制参与机体生命活动的各个过程,同时也是间充质干细胞参与肌肉组织修复的主要机制。
研究干细胞治疗肌肉损伤的过程中发现Ⅵ型胶原纤维[33]、E-选择素[34]、促血管生成因子等细胞因子大量分泌[35],见表4,这些细胞因子可促进肌纤维再生修复、促进血管形成、抑制肌纤维凋亡,拮抗炎症细胞的毒性反应,其中最关键的细胞生长因子有肝细胞生长因子、胰岛素样生长因子1等[36],在肌纤维增殖修复过程中发挥重要作用[37]。多数信号通路可通过激活细胞分泌细胞生长因子,从而参与调控肌纤维,如腺苷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMP-activated protein kinase,AMPK)信号通路可通过磷酸化多种下游的转录因子[38],参与调控糖代谢、脂代谢、细胞增殖等,调节肌纤维再生和肥大,防止肌纤维的凋亡[39-40]。PIAO等[41-42]深入研究发现间充质干细胞通过激活AMPK-mTOR-Erk1/2信号通路来改善小鼠衰老骨骼肌的肌肉完整性。此外,在应用脐带间充质干细胞后,骨骼肌中过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ辅激活因子1α(peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor γ coactivator lalpha-1α,PGC-1α)蛋白及其mRNA水平显著增加,既往研究报道PGC-1α参与恢复肌纤维的线粒体稳态[43],提示间充质干细胞促进肌纤维增殖可能与减少氧化应激、抑制细胞凋亡以及激活AMPK/PGC-1α信号介导的线粒体生物发生有关[41]。
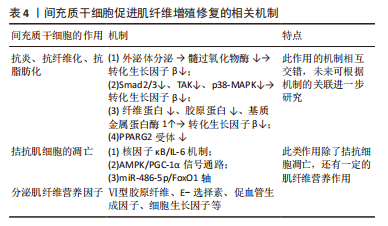
间充质干细胞还能拮抗肌肉组织向脂肪转变,辅助肌肉组织慢性损伤所致退化性病变治疗[44],钝化肌肉中脂肪积聚和萎缩的进展,下调(至少2倍)脂肪细胞分化标志物过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ 2(peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ2,PPARG2),但是文献没有明确哪种细胞因子参与了相关进程,只是推测为不明原因的旁分泌途径[45]。
目前,关于间充质干细胞的旁分泌机制研究主要集中在改善肌细胞的内环境,拮抗间质纤维化、脂肪化,以及促进肌细胞再生修复进程,虽可明显改善肌细胞的内环境稳态,但在促进肌细胞再生修复方面的效果有限。明确间充质干细胞的旁分泌机制,人为干预相关信号通路的激活均可提高间充质干细胞对肌肉损伤的治疗效果,例如通过基因修饰、蛋白修饰等方式。
(2)外泌体:外泌体是一种直径在 40-100 nm的盘状囊泡,可携带多种物质介导细胞间通讯。而间充质干细胞来源外泌体富含数百种胞外蛋白、核酸以及细胞因子等,临床上多用于组织再生治疗。
间充质干细胞分泌的低致瘤性和免疫原性的外泌体作为细胞间通讯的方式之一,可通过下调炎症细胞因子、改变 M1/M2巨噬细胞比例来促进肌纤维增殖修复和新血管生成,并抑制转化生长因子β(transforming growth factor-β,TGF-β)的下游信号来对抗纤维化[46-52],见表4。深入研究发现该机制是通过阻断Smad2/3 信号通路、非Smad依赖性转化生长因子β激活激酶 1(TAK1)以及p38丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(p38 mitogen activated protein kinase,p38 MAPK)信号通路来减弱转化生长因子β1的表达,并且通过减少纤连蛋白1、胶原蛋白1A1、胶原蛋白10A1以及增加基质金属蛋白酶1来抑制转化生长因子β1诱导的肌组织纤维化[53-54]。除了干预肌肉组织的炎症反应,间充质干细胞衍生的外泌体还可通过调节miR-486-5p/FoxO1轴等信号通路[55],促进小鼠成肌细胞(C2C12)的肌纤维分化增殖,见图4。现在间充质干细胞迁移疗法面临的其中一个问题就是:同基因间充质干细胞提取困难,但是无排异性,而异体间充质干细胞迁移存在一定的免疫炎性反应,这会明显影响干细胞的疗效[56],此时使用低免疫原性的间充质干细胞外泌体在一定程度上可以解决这个困难。目前的科学研究在间充质干细胞以及外泌体的获取方面仍然存在技术上的限制。有学者为提高间充质干细胞及外泌体的利用率,利用巨噬细胞的趋化特性,将间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞融合后,提取可以表达整联蛋白等趋化因子的外泌体[49],明显提高了干细胞疗法的精准性,提示间充质干细胞和巨噬细胞融合有望成为新的研究方向。
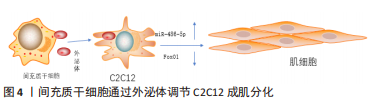
但是,不是所有的间充质干细胞外泌体都会对肌纤维再生产生促进作用,外泌体包含的蛋白质、RNA等物质不是一成不变的,它会随着间充质干细胞的生理或病理变化而变化,因此其产生的作用也会随之改变。据报道,C2C12细胞融合在各种病理条件下产生的外泌体会导致C2C12细胞增殖和分化减少[57-59],并且衰老间充质干细胞外泌体的摄取与外泌体表面的CD81受体有重要联系[60],提示衰老的间充质干细胞会产生有害的外泌体,损害肌纤维修复潜能,推测与细胞凋亡、自噬等机制产生的蛋白有关,对于衰老等退化性疾病的治疗可以考虑通过封闭CD81等位点,阻断或减少外泌体的摄入。
为保证间充质干细胞的质量,避免因其衰老产生的不良结果[61],有学者认为筛选增殖能力强和治疗潜能大的间充质干细胞具有重要意义,因为它们可以避免因长期培养导致衰老的可能,缩短获得足够数量的间充质干细胞的时间。KIM等[62]研究首次证实极光激酶 A (aurora kinase A,AURKA)和胞质分裂作用因子2 (dedicator of cytokinesis 2,DOCK2)的 mRNA 表达水平均与 Wharton’s jelly间充质干细胞的增殖能力呈正相关,这在动物模型中进一步得到证实。
(3)机械刺激:急性损伤所致炎症反应刺激可使间充质干细胞迅速进入细胞周期并通过旁分泌营养因子,支持肌肉干细胞的成肌活性[63]。机械刺激也应该存在独特的机制激活间充质干细胞,有学者发现间充质干细胞是通过Hippo激酶级联效应子YAP1/TAZ的转录激活[64-65],对机械刺激所致压力负荷做出回应,促进间充质干细胞旁分泌血小板反应蛋白1(thrombospondin 1,Thbs1)增加,激活肌肉干细胞上的CD47受体,进而调节肌纤维的增殖,即“机械负荷”激活间充质干细胞并通过YAP1/TAZ-Thbs1-CD47信号传导调节肌纤维增殖肥大。但是Thbs1不仅可以激活转化生长因子β[66],也通过结合 CD36和 CD47抑制 cGMP 信号传导,进而抑制血管生成的能力,存在过度的肌肉组织纤维化的可能[64],提示Thbs作为一个信号传导因子,与CD47结合既有调节肌纤维增殖肥大的能力,也有导致肌肉组织纤维化的可能。然而这种双重特性恰恰验证了控制机械刺激的“度”的必要性,即适度的身体锻炼。
2.3.2 诱导成肌分化 间充质干细胞虽然具有分化为各种类型组织细胞的潜能,但是其成肌分化的效率较低,特别是骨髓来源间充质干细胞,若无外物诱导,基本难以形成肌源性谱系分化。目前已经拥有相当有效的方法能够提高诱导间充质干细胞成肌分化的效率,比如药物、基因修饰、蛋白修饰、表观遗传修饰等。
(1)药物诱导:药物诱导的方式目前有效研究较少,但其易于控制和调整,例如通过糖皮质激素、DNA去甲基化药物5-氮杂胞苷等药物诱导的成骨骼肌分化[67-68],深入研究发现p38 MAPK途径在药物诱导过程中发挥重要作用[69]。
(2)细胞修饰:细胞修饰方法具有精准制导的作用,成功率相对较高。有研究利用基质细胞衍生因子1通过趋化因子受体作用于骨髓间充质干细胞[70-71],出现miR-151或 miR-5100表达上调,以及胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白2水平降低,干细胞成肌分化能力明显增强[72-76]。目前其他类似细胞修饰研究较少,可能是其效率低下的原因,局限了该方式的发展。
(3)表观遗传修饰:表观遗传修饰强调外部环境对细胞迁移的影响,现有研究尝试通过模拟细胞微环境进而调节干细胞行为,实现生物材料对细胞核基因组的可遗传调控,包括间充质干细胞的增殖、迁移、分化甚至凋亡的进程[77-79]。有研究报道了一种具有电位响应型纳米生物接口的超薄细胞培养平台[80],利用细胞间“力”的相互作用,调节间充质干细胞的黏附、迁移和分化,控制其自发分化为肌细胞。还有实验研究发现间充质干细胞在聚酰胺树枝状聚合物表面迁移过程中通过细胞和细胞核形变实现肌肉谱系转换的机制,发现核纤层蛋白A/C和核纤层蛋白b1表达降低,进一步通过对2种抑制性组蛋白修饰(H3K9me3和H3K27甲基化)和一种激活性组蛋白修饰(H3K9ac)的分析,发现H3K9me3被抑制,而H3K9ac和H3K27甲基化被上调[77]。目前,在生物材料方面应用表观遗传修饰方式干预间充质干细胞分化方向的研究较少,这可能与技术的高要求有关,但其在间充质干细胞研究方面产生了明显的促进作用。在信息技术和材料高速发展的今天,表观遗传修饰方法应用于间充质干细胞成肌分化的前景值得期待。
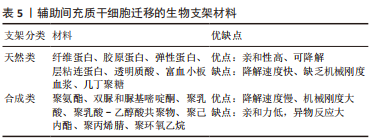
2.3.3 组织工程 目前,基于间充质干细胞治疗的主要障碍包括由于细胞凋亡、坏死或失巢导致的迁移后生存率差,以及无法维持自我更新能力。据报道移植后几天内在注射部位存活的间充质干细胞不到5% [81-82]。由此间充质干细胞联合生物材料辅助迁移的方式应运而生。相关的生物材料包括支架、细胞和生物活性分子等,辅助间充质干细胞迁移能显著提高存活率,以及促进肌源性分化和再生,见表5。
细胞外基质为周围细胞提供物理支持,为组织形态发生、分化和稳态提供关键的生物化学和生物力学信号。组织工程通过尽可能模拟细胞外基质的特性,已经开发了许多用于细胞外基质模拟的超分子聚合物,包括基于聚氨酯、双脲和脲基嘧啶酮基元的热塑性弹性体以及水凝胶等[83],广泛用于体外或体内组织细胞再生研究[83-84]。水凝胶是此类生物材料发展的热点,研究显示其可明显促进干细胞移植后存活、抗炎作用、血管生成和分化潜能,保护干细胞免受炎症细胞和细胞因子的伤害,允许氧气、营养物质和废物的扩散[83,85-87],并且可以生物降解,还可避免局部神经等组织的压迫损伤。常见的有纤维蛋白和海藻酸盐水凝胶、透明质酸光聚合水凝胶、纤维蛋白-层粘连蛋白复合水凝胶、富血小板血浆水凝胶等天然复合材料[88-91],此类水凝胶最突出的特点就是可以通过自身的成分在一定程度上刺激受损肌肉中神经纤维和毛细血管网络的形成以及间充质干细胞的成肌分化。然而此类天然材料容易降解和缺乏机械刚度。为弥补生物材料的机械性能缺陷,合成生物材料如聚乳酸[92]、聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物[93]、聚己内酯[94]、聚丙烯腈和聚环氧乙烷联合所制的复合纳米纤维支架等逐步研发,以低降解速率等优点诱导肌源性再生。但是这些合成生物材料具有较低的生物活性和细胞亲和力,体内植入后或可引起免疫或异物反应。相比之下,当前组织工程研究可能更倾向于天然材料形成的载体。
随着组织工程技术的快速发展,单一组织细胞的组织工程技术已经无法达到所要求的疗效,新研究的模拟天然细胞外基质的合成生物材料更倾向于联合细胞支架构建,CHEN等[95]设计一种“人工肌肉”作为细胞外基质模拟支架。HEIDARI MOGHADAM等[96]利用脂肪组织来源间充质干细胞和人脐静脉内皮细胞在工程化的生物支架上共培养,结合血管内皮生长因子的双重作用,形成工程化血管-肌肉组织,还有工程化神经-肌肉组织等[97]。此类生物支架材料不仅模拟细胞外基质的特性,还兼顾不同组织之间的影响,是未来组织工程研究的重点所在。

| [1] CRUZ-JENTOFT AJ, BAHAT G, BAUER J, et al. Sarcopenia: revised European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Age Ageing. 2019;48(1):16-31. [2] CHEN LK, WOO J, ASSANTACHAI P, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 Consensus Update on Sarcopenia Diagnosis and Treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2020;21(3):300-307.e2. [3] 邓苏爱, 郭雨露, 周文静,等. 肌肉损伤与修复的研究进展[J].武汉轻工大学学报,2020,39(2):27-34. [4] GARCÍA-VÁZQUEZ MD, HERRERO DE LA PARTE B, GARCÍA-ALONSO I, et al. Analysis of Biological Properties of Human Adult Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Effect on Mouse Hind Limb Ischemia. J Vasc Res. 2019;56(2):77-91. [5] GAO WH, GAO HY, LI YT, et al. Effectiveness of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in patients with critical limb ischemia. Med Clin (Barc). 2019;153(9):341-346. [6] TARK KC, HONG JW, KIM YS, et al. Effects of human cord blood mesenchymal stem cells on cutaneous wound healing in leprdb mice. Ann Plast Surg. 2010;65(6):565-572. [7] JÄRVINEN TA, JÄRVINEN TL, KääRIäINEN M, et al. Muscle injuries: biology and treatment. Am J Sports Med. 2005;3(5):745-764. [8] SICARI BM, DEARTH CL, BADYLAK SF. Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine approaches to enhance the functional response to skeletal muscle injury. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2014;297(1):51-64. [9] CHARGÉ SB, RUDNICKI MA. Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev. 2004;84(1):209-238. [10] TIDBALL JG. Inflammatory processes in muscle injury and repair. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2005;288(2):R345-R353. [11] WANG YH, WANG DR, GUO YC, et al. The application of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and biomaterials in skeletal muscle regeneration. Regen Ther. 2020;15:285-294. [12] 郭鑫,于天源,周嫱,等.肌肉疲劳及肌肉损伤机制研究综述[J].中华中医药杂志,2016,31(7):2720-2724. [13] 陈世益.外用非甾体抗炎药治疗肌肉骨骼系统疼痛的中国专家共识[J].中国医学前沿杂志(电子版),2016,8(7):24-27. [14] WANG D, TAI PWL, GAO G. Adeno-associated virus vector as a platform for gene therapy delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2019;18(5):358-378. [15] COLELLA P, RONZITTI G, MINGOZZI F. Emerging Issues in AAV-Mediated In Vivo Gene Therapy. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2018;8:87-104. [16] STILHANO RS, MARTINS L, INGHAM SJM, et al. Gene and cell therapy for muscle regeneration. Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2015;8(2):182-187. [17] LINARD C, BRACHET M, L’HOMME B, et al. Long-term effectiveness of local BM-MSCs for skeletal muscle regeneration: a proof of concept obtained on a pig model of severe radiation burn. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):299. [18] GOLPANIAN S, DIFEDE DL, KHAN A, et al. Allogeneic Human Mesenchymal Stem CellInfusions for Aging Frailty. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2017;72(11):1505-1512. [19] PEREIRA T, ARMADA-DA SILVA PA, AMORIM I, et al. Effects of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated from Wharton’s Jelly of the Umbilical Cord and Conditioned Media on Skeletal Muscle Regeneration Using a Myectomy Model. Stem Cells Int. 2014;2014:376918. [20] CASEIRO AR, PEREIRA T, IVANOVA G, et al. Neuromuscular Regeneration: Perspective on the Application of Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Their Secretion Products. Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:9756973. [21] COSTELA-RUIZ VJ, MELGUIZO-RODRÍGUEZ L, BELLOTTI C, et al. Different Sources of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tissue Regeneration: A Guide to Identifying the Most Favorable One in Orthopedics and Dentistry Applications. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6356. [22] KERN S, EICHLER H, STOEVE J, et al. Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells. 2006;24(5):1294-1301. [23] VIDAL MA, KILROY GE, LOPEZ MJ, et al. Characterization of equine adipose tissue-derived stromal cells: adipogenic and osteogenic capacity and comparison with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Vet Surg. 2007;36(7):613-622. [24] CHAMBERLAIN G, FOX J, ASHTON B, et al. Concise review: mesenchymal stem cells: their phenotype, differentiation capacity, immunological features, and potential for homing. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2739-2749. [25] ZUK PA, ZHU M, MIZUNO H, et al. Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 2001;7(2):211-228. [26] TORRE P, FLORES AI. Current Status and Future Prospects of Perinatal Stem Cells. Genes (Basel). 2020;12(1):6. [27] 彭运,陈凤,黄华鑫,等.比较两种不同来源间充质干细胞的生物学特性及多向分化潜能[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2020,42(4):566-572. [28] VIA AG, FRIZZIERO A, OLIVA F Biological properties of mesenchymal Stem Cells from different sources. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2012;2(3):154-162. [29] GOVBAKH I, KYRYK V, USTYMENKO A, et al. Stem Cell Therapy Enhances Motor Activity of Triceps Surae Muscle in Mice with Hereditary Peripheral Neuropathy. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(21):12026. [30] DEMYANENKO SV, PITINOVA MA, KALYUZHNAYA YN, et al. Human Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Enhance Neuroregeneration in a Rat Model of Sciatic Nerve Crush Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(15):8583. [31] MUKAI T, TOJO A, NAGAMURA-INOUE T. Mesenchymal stromal cells as a potential therapeutic for neurological disorders. Regen Ther. 2018;9:32-37. [32] MAHINDRAN E, LAW JX, NG MH, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Age-Related Musculoskeletal Frailty. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(19):10542. [33] HARADA A, GOTO M, KATO A, et al. Systemic Supplementation of Collagen VI by Neonatal Transplantation of iPSC-Derived MSCs Improves Histological Phenotype and Function of Col6-Deficient Model Mice. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9:790341. [34] QUIROZ HJ, VALENCIA SF, SHAO H, et al. E-Selectin-Overexpressing Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy Confers Improved Reperfusion, Repair, and Regeneration in a Murine Critical Limb Ischemia Model. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021;8:826687. [35] FEIGE P, TSAI EC, RUDNICKI MA. Analysis of human satellite cell dynamics on cultured adult skeletal muscle myofibers. Skelet Muscle. 2021;11(1):1. [36] NAGAYA N, KANGAWA K, ITOH T, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells improves cardiac function in a rat model of dilated cardiomyopathy. Circulation. 2005;112(8):1128-1135. [37] WALKER N, KAHAMBA T, WOUDBERG N, et al. Dose-dependent modulation of myogenesis by HGF: implications for c-Met expression and downstream signalling pathways. Growth Factors. 2015;33(3):229-241. [38] BALNIS J, KORPONAY TC, JAITOVICH A. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK) at the Crossroads Between CO2 Retention and Skeletal Muscle Dysfunction in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(3):955. [39] SONG YN, YUAN D, ZHANG CC, et al. Effect of saponins extracted from Panax japonicus on inhibiting cardiomyocyte apoptosis by AMPK/Sirt1/NF-κB signaling pathway in aging rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2017;42(23):4656-4660. [40] YU Y, ZHAO Y, TENG F, et al. Berberine Improves Cognitive Deficiency and Muscular Dysfunction via Activation of the AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1a Pathway in Skeletal Muscle from Naturally Aging Rats. J Nutr Health Aging. 2018;22(6):710-717. [41] PIAO L, HUANG Z, INOUE A, et al. Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stromal cells ameliorate aging-associated skeletal muscle atrophy and dysfunction by modulating apoptosis and mitochondrial damage in SAMP10 mice. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022;13(1):226. [42] TAKEGAKI J, SASE K, KONO Y, et al. Intramuscular injection of mesenchymal stem cells activates anabolic and catabolic systems in mouse skeletal muscle. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):21224. [43] JI LL, YEO D. Mitochondrial dysregulation and muscle disuse atrophy. F1000Res. 2019;8:F1000 Faculty Rev-1621. [44] SALLAI I, WEIDL M, SZATMÁRI A, et al. The change of fatty degeneration in the rotator cuff muscles after repair in patients over 65. Orv Hetil. 2019;160(14):533-539. [45] FLÜCK M, KASPER S, BENN MC, et al. Transplant of Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells Halts Fatty Atrophy of Detached Rotator Cuff Muscle After Tendon Repair: Molecular, Microscopic, and Macroscopic Results From an Ovine Model. Am J Sports Med. 2021;49(14):3970-3980. [46] FRANCK T, CEUSTERS J, GRAIDE H, et al. Muscle Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit the Activity of the Free and the Neutrophil Extracellular Trap (NET)-Bond Myeloperoxidase. Cells. 2021;10(12):3486. [47] BAEK J, RYU B, KIM J, et al. Immunomodulation of Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Rotator Cuff Tears Model. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(7):1549. [48] DAI J, SHUPP AB, BUSSARD KM, et al. Extracellular Vesicles and Bone-Associated Cancer. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2021;19(3):223-229. [49] SU G, LEI X, WANG Z, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes affect macrophage phenotype: a cell-free strategy for the treatment of skeletal muscle disorders. Curr Mol Med. 2022 May 11. doi: 10.2174/1566524022666220511123625. [50] HELAL MAM, SHAHEEN NEM, ABU ZAHRA FA. Immunomodulatory capacity of the local mesenchymal stem cells transplantation after severe skeletal muscle injury in female rats. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2016;38(6):414-422. [51] LI C, WU Q, LI Z, et al. Exosomal microRNAs in cancer-related sarcopenia: Tumor-derived exosomal microRNAs in muscle atrophy. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2021; 246(10):1156-1166. [52] MYTIDOU C, KOUTSOULIDOU A, KATSIOLOUDI A, et al. Muscle-derived exosomes encapsulate myomiRs and are involved in local skeletal muscle tissue communication. FASEB J. 2021;35(2):e21279. [53] CHOI A, PARK SE, JEONG JB, et al. Anti-Fibrotic Effect of Human Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Skeletal Muscle Cells, Mediated by Secretion of MMP-1. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(17):6269. [54] SU WH, WANG CJ, FU HC, et al. Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Extricate Bupivacaine-Impaired Skeletal Muscle Function via Mitigating Neutrophil-Mediated Acute Inflammation and Protecting against Fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(17):4312. [55] LI Z, LIU C, LI S, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomes Inhibit Dexamethasone-Induced Muscle Atrophy via the miR-486-5p/FoxO1 Axis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:681267. [56] ŚWIERCZEK-LASEK B, TOLAK L, BIJOCH L, et al. Comparison of Muscle Regeneration after BMSC-Conditioned Medium, Syngeneic, or Allogeneic BMSC Injection. Cells. 2022;11(18):2843. [57] CHE J, XU C, WU Y, et al. Early-senescent bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote C2C12 cell myogenic differentiation by preventing the nuclear translocation of FOXO3. Life Sci. 2021;277:119520. [58] KIM S, LEE MJ, CHOI JY, et al. Roles of Exosome-Like Vesicles Released from Inflammatory C2C12 Myotubes: Regulation of Myocyte Differentiation and Myokine Expression. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;48(5):1829-1842. [59] GUESCINI M, MAGGIO S, CECCAROLI P, et al. Extracellular Vesicles Released by Oxidatively Injured or Intact C2C12 Myotubes Promote Distinct Responses Converging toward Myogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(11):2488. [60] DAI H, ZHENG W, LUO J, et al. Inhibiting uptake of extracellular vesicles derived from senescent bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells by muscle satellite cells attenuates sarcopenia. J Orthop Translat. 2022;35:23-36. [61] LIU J, DING Y, LIU Z, et al. Senescence in Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Functional Alterations, Molecular Mechanisms, and Rejuvenation Strategies. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:258. [62] KIM SJ, PARK SE, JEONG JB, et al. Wharton’s Jelly-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells with High Aurora Kinase A Expression Show Improved Proliferation, Migration, and Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cells Int. 2022;2022:4711499. [63] MOLINA T, FABRE P, DUMONT NA. Fibro-adipogenic progenitors in skeletal muscle homeostasis, regeneration and diseases. Open Biol. 2021;11(12):210110. [64] KANESHIGE A, KAJI T, ZHANG L, et al. Relayed signaling between mesenchymal progenitors and muscle stem cells ensures adaptive stem cell response to increased mechanical load. Cell Stem Cell. 2022;29(2):265-280.e6. [65] SUN C, DE MELLO V, MOHAMED A, et al. Common and Distinctive Functions of the Hippo Effectors Taz and Yap in Skeletal Muscle Stem Cell Function. Stem Cells. 2017;35(8):1958-1972. [66] BELLO L, PEGORARO E. The “Usual Suspects”: Genes for Inflammation, Fibrosis, Regeneration, and Muscle Strength Modify Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J Clin Med. 2019;8(5):649. [67] SEVAK JK, GOPINATH SD. Generation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells from Human Umbilical Cord Tissue and their Differentiation into the Skeletal Muscle Lineage. J Vis Exp. 2022;(186). doi: 10.3791/63725. [68] JIA D, ZHENG W, JIANG H. Growth hormone facilitates 5’-azacytidine-induced myogenic but inhibits 5’-azacytidine-induced adipogenic commitment in C3H10T1/2 mesenchymal stem cells. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2018;40:9-16. [69] FEI W, PANG E, HOU L, et al. Synergistic Effect of Hydrogen and 5-Aza on Myogenic Differentiation through the p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway in Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Stem Cells. 2022. doi: 10.15283/ijsc21238. [70] BIANCHI ME, MEZZAPELLE R. The Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 in Cell Proliferation and Tissue Regeneration. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2109. [71] SANTAGATA S, IERANÒ C, TROTTA AM, et al. CXCR4 and CXCR7 Signaling Pathways: A Focus on the Cross-Talk Between Cancer Cells and Tumor Microenvironment. Front Oncol. 2021;11:591386. [72] KOWALSKI K, DOS SANTOS M, MAIRE P, et al. Induction of bone marrow-derived cells myogenic identity by their interactions with the satellite cell niche. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):258. [73] MIERZEJEWSKI B, MICHALSKA Z, JACKOWSKI D, et al. The miR151 and miR5100 Transfected Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Increase Myoblast Fusion in IGFBP2 Dependent Manner. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2022;18(6):2164-2178. [74] FANG XB, SONG ZB, XIE MS, et al. Synergistic effect of glucocorticoids and IGF-1 on myogenic differentiation through the Akt/GSK-3β pathway in C2C12 myoblasts. Int J Neurosci. 2020;130(11):1125-1135. [75] AHMAD SS, AHMAD K, LEE EJ, et al. Implications of Insulin-Like Growth Factor-1 in Skeletal Muscle and Various Diseases. Cells. 2020;9(8):1773. [76] WANG Z, ZHANG X, LI Z, et al. MiR-34b-5p Mediates the Proliferation and Differentiation of Myoblasts by Targeting IGFBP2. Cells. 2019;8(4):360. [77] Ayuningtyas FD, Kim MH, Kino-Oka M. Muscle lineage switching by migratory behaviour-driven epigenetic modifications of human mesenchymal stem cells on a dendrimer-immobilized surface. Acta Biomater. 2020;106:170-180. [78] YANG Y, WANG K, GU X, et al. Biophysical Regulation of Cell Behavior-Cross Talk between Substrate Stiffness and Nanotopography. Engineering (Beijing). 2017;3(1):36-54. [79] SUN Y, CHEN CS, FU J. Forcing stem cells to behave: a biophysical perspective of the cellular microenvironment. Annu Rev Biophys. 2012;41:519-542. [80] PARK R, YOON JW, LEE JH, et al. Phenotypic change of mesenchymal stem cells into smooth muscle cells regulated by dynamic cell-surface interactions on patterned arrays of ultrathin graphene oxide substrates. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022;20(1):17. [81] BURDICK JA, MAUCK RL, GERECHT S. To Serve and Protect: Hydrogels to Improve Stem Cell-Based Therapies. Cell Stem Cell. 2016;18(1):13-15. [82] LI L, CHEN X, WANG WE, et al. How to Improve the Survival of Transplanted Mesenchymal Stem Cell in Ischemic Heart? Stem Cells Int. 2016;2016:9682757. [83] GOOR O, HENDRIKSE SIS, DANKERS PYW, et al. From supramolecular polymers to multi-component biomaterials. Chem Soc Rev. 2017;46(21):6621-6637. [84] KIM H, KIM Y, FENDERESKI M, et al. Recent Advancements in Decellularized Matrix-Based Biomaterials for Musculoskeletal Tissue Regeneration. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1077:149-162. [85] 张浩.构建含有间充质干细胞和外泌体的脱细胞组织水凝胶用于修复大体积肌肉缺损的实验研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2016. [86] GENOVESE P, PATEL A, ZIEMKIEWICZ N, et al. Co-delivery of fibrin-laminin hydrogel with mesenchymal stem cell spheroids supports skeletal muscle regeneration following trauma. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;15(12):1131-1143. [87] HE J, ZHANG N, ZHU Y, et al. MSC spheroids-loaded collagen hydrogels simultaneously promote neuronal differentiation and suppress inflammatory reaction through PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Biomaterials. 2021;265:120448. [88] CHIU CH, CHANG TH, CHANG SS, et al. Application of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Muscle Healing After Contusion Injury in Mice. Am J Sports Med. 2020;48(5):1226-1235. [89] SASSOLI C, VALLONE L, TANI A, et al. Combined use of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (BM-MSCs) and platelet rich plasma (PRP) stimulates proliferation and differentiation of myoblasts in vitro: new therapeutic perspectives for skeletal muscle repair/regeneration. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;372(3):549-570. [90] LYU Y, XIE J, LIU Y, et al. Injectable Hyaluronic Acid Hydrogel Loaded with Functionalized Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Aggregates for Repairing Infarcted Myocardium. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020;6(12):6926-6937. [91] PEREZ-PUYANA V, WIERINGA P, YUSTE Y, et al. Fabrication of hybrid scaffolds obtained from combinations of PCL with gelatin or collagen via electrospinning for skeletal muscle tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2021;109(9):1600-1612. [92] LIU G, FU M, LI F, et al. Tissue-engineered PLLA/gelatine nanofibrous scaffold promoting the phenotypic expression of epithelial and smooth muscle cells for urethral reconstruction. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;111:110810. [93] LEE H, KIM W, LEE J, et al. Effect of Hierarchical Scaffold Consisting of Aligned dECM Nanofibers and Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) Struts on the Orientation and Maturation of Human Muscle Progenitor Cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11(43):39449-39458. [94] APARICIO-COLLADO JL, GARCÍA-SAN-MARTÍN N, MOLINA-MATEO J, et al. Electroactive calcium-alginate/polycaprolactone/reduced graphene oxide nanohybrid hydrogels for skeletal muscle tissue engineering. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2022;214:112455. [95] CHEN S, YANG L, LEUNG FK, et al. Photoactuating Artificial Muscles of Motor Amphiphiles as an Extracellular Matrix Mimetic Scaffold for Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Am Chem Soc. 2022;144(8):3543-3553. [96] HEIDARI MOGHADAM A, BAYATI V, ORAZIZADEH M, et al. Redesigning of 3-Dimensional Vascular-Muscle Structure Using ADSCs/HUVECs Co-Culture and VEGF on Engineered Skeletal Muscle ECM. Cell J. 2022;24(7):380-390. [97] AHUJA N, AWAD K, PEPER S, et al. Mini review: Biomaterials in repair and regeneration of nerve in a volumetric muscle loss. Neurosci Lett. 2021;762: 136145. [98] NAKAYAMA KH, SHAYAN M, HUANG NF. Engineering Biomimetic Materials for Skeletal Muscle Repair and Regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019;8(5): e1801168. |
| [1] | 韦雨柔, 田佳庆, 何宪顺, 詹芝玮, 魏腾飞, 林天烨, 何 伟, 魏秋实. 慢病毒沉默Piezo1蛋白与人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化及TAZ的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 12-19. |
| [2] | 王宪峰, 王 锟, 孙 晗, 孙晓亮, 言力韬. 脐带间充质干细胞外泌体LncRNA H19修复软骨损伤的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 20-25. |
| [3] | 张元澍, 何 旭, 薛 源, 金叶盛, 汪 凯, 施 勤, 芮永军. 鸢尾素缓解棕榈酸对骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨抑制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 26-31. |
| [4] | 何莉君, 漆小娟. 脂肪间充质干细胞过表达骨形态发生蛋白2促进骨质疏松大鼠牙槽骨缺损修复[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 32-37. |
| [5] | 郑嵘炅, 邓泽润, 韩 丹, 孙丽华. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体调节大鼠肝细胞凋亡的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 44-49. |
| [6] | 郑明魁, 薛晨晖, 关晓明, 马 迅. 人脐带间充质干细胞来源外泌体降低脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的通透性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 50-55. |
| [7] | 孙 菁, 廖 健, 孙江龄, 程 萍, 冯红超. 重组人生长激素促进人牙髓干细胞的成骨分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 56-61. |
| [8] | 陈冠廷, 张琳琪, 李清茹. 外泌体在慢性肾脏病诊疗中的研究热点与趋势[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 86-92. |
| [9] | 范永晶, 王 姝, 金武龙. 颌骨来源骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的特点、优势与应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2024, 28(1): 100-106. |
| [10] | 农复香, 蒋志雄, 李英豪, 许文聪, 施智兰, 罗 慧, 张晴朗, 钟 爽, 唐梅文. 外泌体调控铁死亡在疾病诊断治疗中的应用与作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-10. |
| [11] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李佳, 蒋海越, 刘霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [12] | 何宛俞, 程乐平. 干细胞移植修复脊髓损伤的策略与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [13] | 可雨奇, 陈长健, 吴 浩, 郑连杰. 改良直接前方入路与直接前方入路初次全髋关节置换者12个月随访结果比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1377-1382. |
| [14] | 潘钟杰, 秦志鸿, 郑铁军, 丁晓飞, 廖世杰. 股骨头坏死发病机制中非编码RNA的靶标性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1441-1447. |
| [15] | 党 祎, 杜成砚, 姚红林, 袁能华, 曹 金, 熊 山, 张顶梅, 王 信. 激素型骨坏死与氧化应激[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1469-1476. |
EWGSOP 2018年报告全球65岁老年人肌少症发病率在6%-12%[1],其中亚洲男性发病率略高于女性[2],并且随着年龄的增加而增加。从目前的治疗手段来看,相关肌肉组织疾病的治疗多以抗炎、冰敷、针灸、电疗等保守治疗较为常见,一定程度上可以缓解疾病的进展,近年来的基因疗法和细胞疗法逐渐发展,成为肌肉组织疾病治疗新的发展趋势[3]。但当前尚且没有良好的治疗手段和治疗标准,基于此,寻求一种能够可行可靠的促进肌肉组织修复的治疗方式显得十分重要。
间充质干细胞是近年来组织工程领域研究的热点,它来源于胚胎发育的中胚层,是一种具有自我更新和多向分化能力的多能干细胞,在骨髓、脂肪、脐带等多种组织中被发现并提取出来。从早期的骨髓间充质干细胞到多能性更好的脐带或胎盘来源间充质干细胞,学者们一直在寻找增殖和分化潜力更强的间充质干细胞进行细胞或动物层面的相关研究,并且有不少研究应用它来进行肌肉组织修复方面的探索,例如促进肌纤维增殖再生、促进新血管生成[4-6],颇具成效。然而,目前针对间充质干细胞治疗肌肉组织疾病的综述较少。该文章拟针对间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的相关机制、联合间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的生物材料及其优劣进行综述,推动该项技术尽早合理地投入临床应用。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 第一作者在2022年10月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 从各数据库建库至2022年10月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 中文数据库:中国知网、维普、万方;英文数据库:PubMed、Embase 及Web of Science 。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“间充质干细胞、肌肉组织、肌肉损伤、肌肉萎缩、外泌体,支架”。英文检索词为“mesenchymal stem cells,muscle tissue,muscle injury,muscle atrophy,exosomes,scaffolds”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 纳入相关研究原著、综述、荟萃分析、基础研究、国内外权威学术会议报告。
1.1.6 检索策略 以PubMed数据库为例,检索策略见图1。

1.2 入组标准
1.2.1 纳入标准 观点明确、论据充分、可信度高、创新性强、有关间充质干细胞迁移促进肌纤维增殖修复的文献。
1.2.2 排除标准 剔除重复性研究文献;题目与主题不相关的文献;研究方法不符合标准、可靠性低、质量差的文献。
1.3 质量评估和数据提取 通过上述数据库检索,并按入组标准进行人工筛选,纳入相关研究原著、综述、荟萃分析、基础研究、国内外权威学术会议报告共350篇(中国知网31篇、维普5篇、万方7篇、PubMed 297篇、Embase 3篇及Web of Science 7篇),最后筛选所得文献98篇,中文文献5篇(中国知网3篇、维普1篇、万方1篇),英文文献93篇(PubMed 93篇、Embase 0篇及Web of Science 0篇),见图2。筛选所得文献经过5人小组研究讨论提取数据,信息记录侧重于间充质干细胞促进肌纤维增殖修复方面的研究进展。
3.2 该综述的独特性和局限性 系统地对间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的相关研究进行综合述评,然后试图找出现阶段最有效的方式用于促进肌肉组织修复。但该综述以近3年的文献为主,相关文献检索可能不太全面。
3.3 综述的重要意义 间充质干细胞是当前最有潜力的干细胞来源,许多组织如神经、皮肤等已经逐渐发展基于间充质干细胞的治疗方式。现在针对间充质干细胞治疗肌肉组织疾病的研究越来越多,该综述结合近年来的相关研究,希望明确间充质干细胞促进肌肉组织修复的研究现状,并指导未来研究的方向。
3.4 课题专家组对未来的建议 间充质干细胞与肌肉组织修复的关系值得更多的科研人员去探索,拓宽间充质干细胞在不同组织疾病中应用的同时,也为肌肉组织修复寻找新的更加有效的治疗方法。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
 #br#
#br#
文题释义:
间充质干细胞:来源于胚胎发育的中胚层,具有多方向分化的潜能,在相关信号或外来因素的刺激下可分化为心肌、成骨、成脂、上皮等细胞。目前,已有大量研究证实间充质干细胞可用于治疗心血管疾病、肾病、糖尿病、肌腱损伤等。肌肉组织修复:肌肉组织结构破坏涉及肌膜的破坏、细胞骨架的损伤以及细胞内基质的异常,而肌肉组织修复包括坏死肌纤维的清除、肌纤维的再生、新生肌肉组织的重塑。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
肌肉干细胞是存在于肌纤维的基底层下,即肌纤维和细胞外间质之间的卫星细胞,骨骼肌损伤后肌纤维再生的来源主要是卫星细胞的分化。根据肌肉干细胞的生理特性,学者们曾着力于肌肉干细胞的提取、纯化和迁移,用于治疗肌营养不良,但是成效较低。相较于间充质干细胞的多方向分化能力,肌肉干细胞的“单能”特性使其分化为肌纤维的效率相对较高,但是在提取及迁移治疗的过程中,其分化进程难以控制,增殖性相对较低,严重限制了肌肉干细胞移植治疗的应用。因此间充质干细胞以其独特的优势逐渐取代了肌肉干细胞的地位,成为干细胞治疗肌肉组织疾病的主要来源。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||