[1] KLÜTER T, HASSAN R, RASCH A, et al. An Ex Vivo Bone Defect Model to Evaluate Bone Substitutes and Associated Bone Regeneration Processes. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2020;26(1):56-65.
[2] AYUB N, FARAJ M, GHATAN S, et al. The Treatment Gap in Osteoporosis. J Clin Med. 2021;10(13):3002.
[3] PENG J, CHEN L, PENG K, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Endothelial Progenitor Cells Co-Culture Enhances Large Segment Bone Defect Repair. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019;15(4):742-755.
[4] KIM HK, LEE SG, LEE SW, et al. A Subset of Paracrine Factors as Efficient Biomarkers for Predicting Vascular Regenerative Efficacy of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells. Stem Cells. 2019;37(1):77-88.
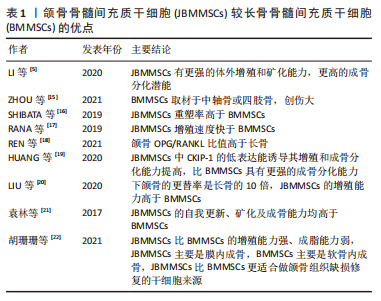
[5] LI C, WANG F, ZHANG R, et al. Comparison of Proliferation and Osteogenic Differentiation Potential of Rat Mandibular and Femoral Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells In Vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(11):728-736.
[6] ZHANG W, DONG Z, LI D, et al. Cathepsin K deficiency promotes alveolar bone regeneration by promoting jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells proliferation and differentiation via glycolysis pathway. Cell Prolif. 2021;54(7):e13058.
[7] LI L, LI J, ZOU Q, et al. Enhanced bone tissue regeneration of a biomimetic cellular scaffold with co-cultured MSCs-derived osteogenic and angiogenic cells. Cell Prolif. 2019 ;52(5):e12658.
[8] LAI K, XI Y, DU X, et al. Activation of Nell-1 in BMSC Sheet Promotes Implant Osseointegration Through Regulating Runx2/Osterix Axis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8(9):868.
[9] 程兵坤,梁建飞,秦东泽,等.高纯度大鼠下颌骨来源间充质干细胞的分离、培养及生物学特性[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(1):67-72.
[10] REDONDO LM, GARCÍA V, PERAL B, et al. Repair of maxillary cystic bone defects with mesenchymal stem cells seeded on a cross-linked serum scaffold. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2018;46(2):222-229.
[11] CHOI YH, HAN Y, JIN SW, et al. Pseudoshikonin I enhances osteoblast differentiation by stimulating Runx2 and Osterix. J Cell Biochem. 2018; 119(1):748-757.
[12] LUO J, XU J, CAI J, et al. The In Vitro and In Vivo Osteogenic Capability of the Extraction Socket-Derived Early Healing Tissue. J Periodontol. 2016; 87(9):1057-1066.
[13] NAKAJIMA R, ONO M, HARA ES, et al. Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell isolation from tooth extraction sockets. J Dent Res. 2014;93(11): 1133-1140.
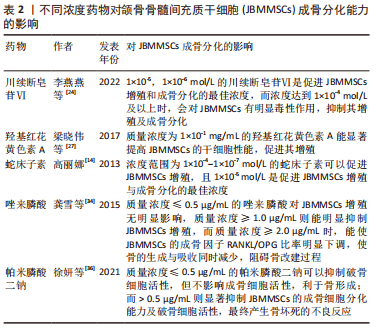
[14] 高丽娜. 蛇床子素对人牙周膜干细胞和颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞膜片形成和生物学性能的影响[D].西安:第四军医大学,2013.
[15] ZHOU B, PENG K, WANG G, et al. Polo Like Kinase 4 (PLK4) impairs human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) viability and osteogenic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2021; 549(4):221-228.
[16] SHIBATA S, TAKAHASHI M, FUJIKAWA K. Histochemical and Ultrastructural Study of Developing Gonial Bone With Reference to Initial Ossification of the Malleus and Reduction of Meckel’s Cartilage in Mice. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2019;302(11):1916-1933.
[17] RANA D, KUMAR S, WEBSTER TJ, et al. Impact of Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells in Bone Repair and Regeneration. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2019; 17(4):226-234.
[18] REN S, JIAO G, ZHANG L, et al. Bionic Tiger-Bone Powder Improves Bone Microstructure and Bone Biomechanical Strength of Ovariectomized Rats. Orthop Surg. 2021;13(3):1111-1118.
[19] HUANG X, CHENG B, SONG W, et al. Superior CKIP-1 sensitivity of orofacial bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells in proliferation and osteogenic differentiation compared to long bone-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep. 2020;22(2):1169-1178.
[20] LIU LN, ZHANG XH, LIU HH, et al. Osteogenesis Differences Around Titanium Implant and in Bone Defect Between Jaw Bones and Long Bones. J Craniofac Surg. 2020;31(8):2193-2198.
[21] 袁林,钱钧,杨征毅,等.不同来源骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力的比较[J].口腔疾病防治,2017,25(9):554-559.
[22] 胡珊珊,张为,曹炜,等.雌性健康和绝经小鼠长骨及颌骨来源骨髓间充质干细胞生物学特性的比较[J].贵州医科大学学报,2021,46(12): 1389-1395.
[23] 赵金龙,梁桂洪,韩燕鸿,等.川续断提取物续断皂苷Ⅵ防治骨质疏松症的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2020,26(5):755-759.
[24] 李燕燕,朱珠,谢雯静,等.川续断皂苷Ⅵ对人颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].口腔医学,2022,42(3):204-209.
[25] LI CY, YIN JG, ZHANG J, et al. Pharmacokinetic profiles of hydroxysafflor yellow A following intravenous administration of its pure preparations in healthy Chinese volunteers. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;162(3):225-230.
[26] ZHOU MX, FU JH, ZHANG Q, et al. Effect of hydroxy safflower yellow A on myocardial apoptosis after acute myocardial infarction in rats. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(2):3133-3141.
[27] 梁晓伟,李阳飞,李琥,等.羟基红花黄色素A对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].口腔生物医学,2017,8(2):90-94.
[28] MO Y, WU Y, LI X, et al. Osthole delays hepatocarcinogenesis in mice by suppressing AKT/FASN axis and ERK phosphorylation. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020;867(1):172788.
[29] DONG X, HE L, ZANG X, et al. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Promote Bone Coupling in Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw by TGF-β1. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;9(5):639590.
[30] KIM DS, KIM JH, OHE JY, et al. Bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw in a patient with osteoporosis following treatment of testicular cancer: a case report. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;41(6):327-331.
[31] RODRÍGUEZ-LOZANO FJ, OÑATE-SÁNCHEZ R, GONZÁLVEZ-GARCÍA M, et al. Allogeneic Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation in Tooth Extractions Sites Ameliorates the Incidence of Osteonecrotic Jaw-Like Lesions in Zoledronic Acid-Treated Rats. J Clin Med. 2020;9(6):1649.
[32] PAN B, TO LB, FARRUGIA AN, et al. The nitrogen-containing bisphosphonate, zoledronic acid, increases mineralisation of human bone-derived cells in vitro. Bone. 2004;34(1):112-123.
[33] YANG G, KIM YN, KIM H, et al. Effect of Human Umbilical Cord Matrix-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Bisphosphonate-Related Osteonecrosis of the Jaw. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2021;18(6):975-988.
[34] 龚雪,苏俭生.唑来膦酸对大鼠颌骨间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].口腔颌面外科杂志,2015,25(1):28-33.
[35] ARGENTIERO A, SOLIMANDO AG, BRUNETTI O, et al. Skeletal Metastases of Unknown Primary: Biological Landscape and Clinical Overview. Cancers (Basel). 2019;11(9):1270.
[36] 徐妍,孙晋,周海华.帕米膦酸二钠对颌骨来源间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中国口腔种植学杂志,2021,26(4):219-225.
[37] GAO SY, LIN RB, HUANG SH, et al. PDGF-BB exhibited therapeutic effects on rat model of bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaw by enhancing angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Bone. 2021;144(3):115117.
[38] ŞAHIN O, ODABAŞI O, ALIYEV T, et al. Risk factors of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: a retrospective study in a Turkish subpopulation. J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2019;45(2):108-115.
[39] GUERVILLE F, DE SOUTO BARRETO P, ADER I, et al. Revisiting the Hallmarks of Aging to Identify Markers of Biological Age. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2020; 7(1):56-64.
[40] DI MICCO R, KRIZHANOVSKY V, BAKER D, et al. Cellular senescence in ageing: from mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2):75-95.
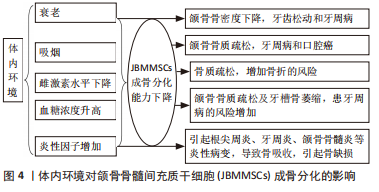
[41] 李胜丹,梁乙然,刘一涵.衰老性骨质疏松微环境对颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞生物学功能的影响[J]. 中华老年口腔医学杂志,2019,17(4):198-203,238.
[42] SHEN X, SI Y, FU Y, et al. MicroRNA-31a-5p from aging BMSCs links bone formation and resorption in the aged bone marrow microenvironment. Aging Cell. 2018;17(4):e12794.
[43] DENG P, CHANG I, WANG J, et al. Loss of KDM4B impairs osteogenic differentiation of OMSCs and promotes oral bone aging. Int J Oral Sci. 2022;14(1):24.
[44] 南京医科大学附属口腔医院. Sirtuin 1经Bmi1介导调控老年性牙槽骨丢失作用机制的研究方法:CN201810435680.8[P]. 2020-12-29.
[45] 赵喜聪.吸烟者人颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和骨向分化能力的对比研究[D].西安:第四军医大学,2012.
[46] KIM BS, KIM SJ, KIM HJ, et al. Effects of nicotine on proliferation and osteoblast differentiation in human alveolar bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Life Sci. 2012;90(3-4):109-115.
[47] BOSCO AF, BONFANTE S, DE ALMEIDA JM, et al. A histologic and histometric assessment of the influence of nicotine on alveolar bone loss in rats. J Periodontol. 2007;78(3):527-532.
[48] ROTHEM DE, ROTHEM L, SOUDRY M, et al. Nicotine modulates bone metabolism-associated gene expression in osteoblast cells. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009;27(5):555-561.
[49] PAGANI S, FINI M, GIAVARESI G, et al. The active role of osteoporosis in the interaction between osteoblasts and bone metastases. Bone. 2015;79: 176-182.
[50] 许雄程,阳雪,何梦娇,等.去卵巢对大鼠颌骨成骨细胞增殖与成骨分化能力的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(5):567-572.
[51] YU SJ, LIU HC, LING-LING E, et al. Proliferation and differentiation of osteoblasts from the mandible of osteoporotic rats. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2012;237(4):395-406.
[52] LIU XL, LI CL, LU WW, et al. Skeletal site-specific response to ovariectomy in a rat model: change in bone density and microarchitecture. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(4):392-398.
[53] DU Z, LEE RS, HAMLET S, et al. Evaluation of the first maxillary molar post-extraction socket as a model for dental implant osseointegration research. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2016;27(12):1469-1478.
[54] ABRAHAM A, COHEN A, SHANE E. Premenopausal bone health: osteoporosis in premenopausal women. Clin Obstet Gynecol. 2013;56(4):722-729.
[55] PRESSMAN AR, KINOSHITA L, KIRK S, et al. A novel telemonitoring device for improving diabetes control: protocol and results from a randomized clinical trial. Telemed J E Health. 2014;20(2):109-114.
[56] GARCÍA-HERNÁNDEZ A, ARZATE H, GIL-CHAVARRÍA I, et al. High glucose concentrations alter the biomineralization process in human osteoblastic cells. Bone. 2012;50(1):276-288.
[57] 陈杨,胡赟,杨兰,等.不同糖浓度对颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].四川大学学报(医学版),2016,47(5):679-684.
[58] YOU L, GU W, CHEN L, et al. MiR-378 overexpression attenuates high glucose-suppressed osteogenic differentiation through targeting CASP3 and activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(10): 7249-7261.
[59] KATAGIRI W, TAKEUCHI R, SAITO N, et al. Migration and phenotype switching of macrophages at early-phase of bone-formation by secretomes from bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells using rat calvaria bone defect model. J Dent Sci. 2022;17(1):421-429.
[60] 胡祥翔,胡开进,赵铱民.炎性微环境中糖原合成酶激酶-3β对颌骨来源骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化影响研究[J].中国实用口腔科杂志, 2017,10(1):40-43.
[61] 王璞,韦丽宾,倪广晓,等. TNF-α对颌骨骨髓间充质与牙周膜两种干细胞自噬水平的影响[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志,2020,34(1):14-16.
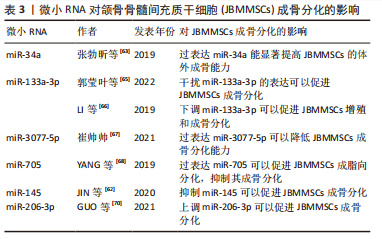
[62] JIN Y, HONG F, BAO Q, et al. MicroRNA-145 suppresses osteogenic differentiation of human jaw bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells partially via targeting semaphorin 3A. Connect Tissue Res. 2020;61(6): 577-585.
[63] 张勃昕,吉爱红,曹正垚,等. miR-34a对人颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].口腔生物医学,2019,10(1):1-5.
[64] XIAO T, FU Y, ZHU W, et al. HDAC8, A Potential Therapeutic Target, Regulates Proliferation and Differentiation of Bone Marrow Stromal Cells in Fibrous Dysplasia. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2019;8(2):148-161.
[65] 郭莹叶,高建华,郭永梅,等. miR-133a-3p靶向BMP9调控人颌骨骨髓间充质干细胞增殖、分化和凋亡的研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2022, 38(2):253-258.
[66] LI Q, XING W, GONG X, et al. RETRACTED: Astragalus polysaccharide promotes proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells by down-regulation of microRNA-152. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;115(7):108927.
[67] 崔帅帅. miRNA-3077-5p对绝经后骨质疏松小鼠颌骨BMSCs分化的影响[D].遵义:遵义医科大学,2021.
[68] YANG XH, YANG K, AN YL, et al. MicroRNA-705 regulates the differentiation of mouse mandible bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. PeerJ. 2019;7: e6279.
[69] LIAO L, YANG X, SU X, et al. Redundant miR-3077-5p and miR-705 mediate the shift of mesenchymal stem cell lineage commitment to adipocyte in osteoporosis bone marrow. Cell Death Dis. 2013;4(4):e600.
[70] GUO S, GU J, MA J, et al. GATA4-driven miR-206-3p signatures control orofacial bone development by regulating osteogenic and osteoclastic activity. Theranostics. 2021;11(17):8379-8395. |