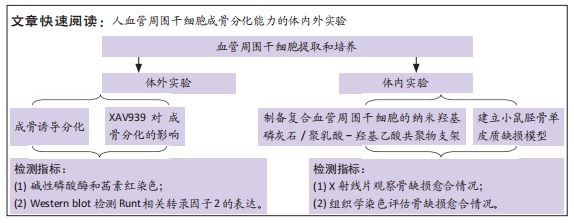
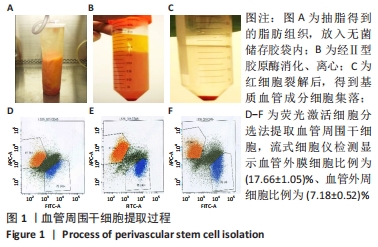
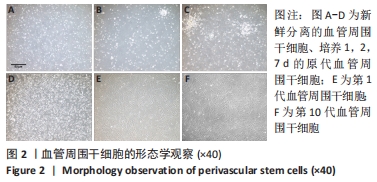
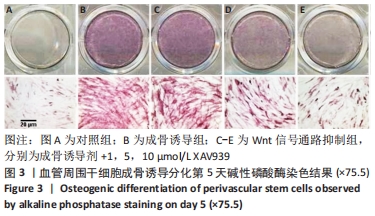
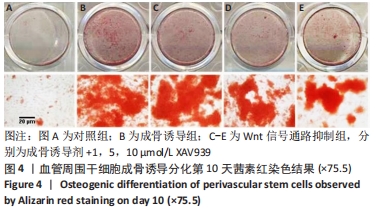
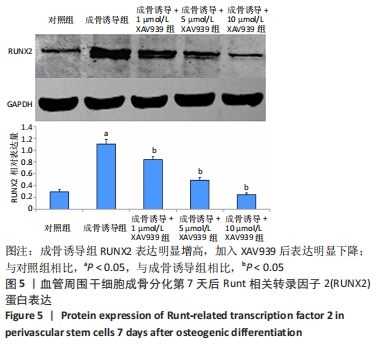
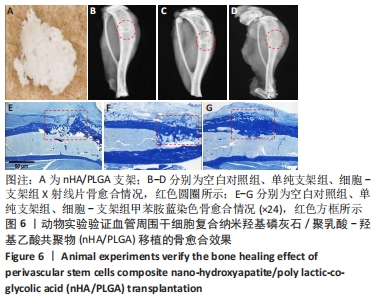
[1] GALIPEAU J, SENSÉBÉ L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):824-833.
[2] VASANTHAN J, GURUSAMY N, RAJASINGH S, et al. Role of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Regenerative Therapy. Cells. 2020;10(1):54.
[3] RODRÍGUEZ-FUENTES DE, FERNÁNDEZ-GARZA LE, SAMIA-MEZA JA, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Current Clinical Applications: A Systematic Review. Arch Med Res. 2021;52(1):93-101.
[4] SCHÄFFLER A, BÜCHLER C. Concise review: adipose tissue-derived stromal cells--basic and clinical implications for novel cell-based therapies. Stem Cells. 2007;25(4):818-827.
[5] RAPOSIO E, BONOMINI S, CALDERAZZI F. Isolation of autologous adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells for bone repair. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2016;102(7):909-912.
[6] MURATA D, FUJIMOTO R, NAKAYAMA K. Osteochondral Regeneration Using Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(10):3589.
[7] CRISAN M, YAP S, CASTEILLA L, et al. A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell. 2008;3(3):301-313.
[8] JAMES AW, ZARA JN, CORSELLI M, et al. Use of human perivascular stem cells for bone regeneration. J Vis Exp. 2012;63:e2952.
[9] XU W, SUN Y, ZHANG J, et al. Perivascular-derived stem cells with neural crest characteristics are involved in tendon repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(7):857-868.
[10] SBIERSKI-KIND J, MROZ N, MOLOFSKY AB. Perivascular stromal cells: Directors of tissue immune niches. Immunol Rev. 2021;302(1):10-31.
[11] YUAN Z, LI Q, LUO S, et al. PPARgamma and Wnt Signaling in Adipogenic and Osteogenic Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;11(3):216-225.
[12] HAN H, TIAN T, HUANG G, et al. The lncRNA H19/miR-541-3p/Wnt/beta-catenin axis plays a vital role in melatonin-mediated osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Aging (Albany NY). 2021;13(14):18257-18273.
[13] YANG F, YANG D, TU J, et al. Strontium enhances osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and in vivo bone formation by activating Wnt/catenin signaling. Stem Cells. 2011;29(6):981-991.
[14] CORSELLI M, CRISAN M, MURRAY IR, et al. Identification of perivascular mesenchymal stromal/stem cells by flow cytometry. Cytometry A. 2013;83(8):714-720.
[15] CUI Z, LI C, JIANG N, et al. Isolation and characterization of minipig perivascular stem cells for bone tissue engineering. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(4):3555-3562.
[16] LIANG CY, LUO YC, YANG GD, et al .Graphene Oxide Hybridized nHAC/PLGA Scaffolds Facilitate the Proliferation of MC3T3-E1 Cells. Nanoscale Res Lett. 2018;13(1):15.
[17] YAN J, LIU C, TU C, et al. Hydrogel-hydroxyapatite-monomeric collagen type-I scaffold with low-frequency electromagnetic field treatment enhances osteochondral repair in rabbits. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021; 12(1):572.
[18] KIM JM, HONG KS, SONG WK, et al. Perivascular Progenitor Cells Derived From Human Embryonic Stem Cells Exhibit Functional Characteristics of Pericytes and Improve the Retinal Vasculature in a Rodent Model of Diabetic Retinopathy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016; 5(9):1268-1276.
[19] XU J, WANG Y, HSU CY, et al. Human perivascular stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles mediate bone repair. Elife. 2019;8:e48191.
[20] JAMES AW, PÉAULT B. Perivascular Mesenchymal Progenitors for Bone Regeneration. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(6):1221-1228.
[21] CORSELLI M, CHEN CW, CRISAN M, et al. Perivascular ancestors of adult multipotent stem cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010;30(6): 1104-1109.
[22] CANO E, GEBALA V, GERHARDT H. Pericytes or Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Is That the Question? Cell Stem Cell. 2017;20(3):296-297.
[23] RIBEIRO AJ, TOTTEY S, TAYLOR RW, et al. Mechanical characterization of adult stem cells from bone marrow and perivascular niches. J Biomech. 2012;45(7):1280-1287.
[24] LI CS, ZHANG X, PÉAULT B, et al. Accelerated Chondrogenic Differentiation of Human Perivascular Stem Cells with NELL-1. Tissue Eng Part A. 2016;22(3-4):272-285.
[25] XU J, WANG Y, GOMEZ-SALAZAR MA, et al. Bone-forming perivascular cells: Cellular heterogeneity and use for tissue repair. Stem Cells. 2021; 39(11):1427-1434.
[26] THELEN K, AYALA-LOPEZ N, WATTS SW, et al. Expansion and Adipogenesis Induction of Adipocyte Progenitors from Perivascular Adipose Tissue Isolated by Magnetic Activated Cell Sorting. J Vis Exp. 2017;(124):55818.
[27] MEYERS CA, XU J, ZHANG L, et al. Skeletogenic Capacity of Human Perivascular Stem Cells Obtained Via Magnetic-Activated Cell Sorting. Tissue Eng Part A. 2019;25(23-24):1658-1666.
[28] DENG Q, LI P, CHE M, et al. Activation of hedgehog signaling in mesenchymal stem cells induces cartilage and bone tumor formation via Wnt/beta-Catenin. Elife. 2019;8:e50208.
[29] WANG Y, ZHANG X, SHAO J, et al. Adiponectin regulates BMSC osteogenic differentiation and osteogenesis through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3652.
[30] HUANG W, ZHENG X, YANG X, et al. Stimulation of Osteogenic Differentiation by Saikosaponin-A in Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Via WNT/β-Catenin Pathway. Calcif Tissue Int. 2017;100(4):392-401.
[31] ALMASOUD N, BINHAMDAN S, YOUNIS G, et al. Tankyrase inhibitor XAV-939 enhances osteoblastogenesis and mineralization of human skeletal (mesenchymal) stem cells. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):16746.
[32] LI M, ZHANG C, LI X, et al. Isoquercitrin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of osteoblasts and BMSCs via the RUNX2 or BMP pathway. Connect Tissue Res. 2019;60(2):189-199.
[33] CAI T, SUN D, DUAN Y, et al. WNT/beta-catenin signaling promotes VSMCs to osteogenic transdifferentiation and calcification through directly modulating Runx2 gene expression. Exp Cell Res. 2016;345(2): 206-217.
[34] SHEN J, CHEN X, JIA H, et al. Effects of WNT3A and WNT16 on the Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation of Perivascular Stem/Stromal Cells. Tissue Eng Part A. 2018;24(1-2):68-80.
[35] BACAKOVA L, ZARUBOVA J, TRAVNICKOVA M, et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells - a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(4): 1111-1126.
|