[1] JONASSON G, RYTHÉN M. Alveolar bone loss in osteoporosis: a loaded and cellular affair. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2016;8:95-103.
[2] LI X, CHEN M, LI L, et al. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy: a potential adjuvant treatment for peri-implantitis. Med Hypotheses. 2010;74(1): 120-122.
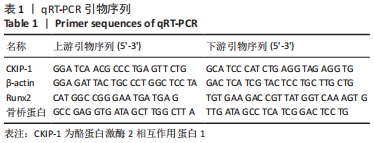
[3] BOSC DG, GRAHAM KC, SAULNIER RB, et al. Identification and characterization of CKIP-1, a novel pleckstrin homology domain-containing protein that interacts with protein kinase CK2. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(19):14295-14306.
[4] LU K, YIN X, WENG T, et al. Targeting WW domains linker of HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 for activation by CKIP-1. Nat Cell Biol. 2008; 10(8):994-1002.
[5] 龙燕鸣,谢梦生,薛文利,等.维甲酸诱导骨质疏松模型大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的特征[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(17):2637-2643.
[6] HOLLICK RJ, REID DM. Role of bisphosphonates in the management of postmenopausal osteoporosis: an update on recent safety anxieties. Menopause Int. 2011;17(2):66-72.
[7] SCHILCHER J, MICHAËLSSON K, Aspenberg P. Bisphosphonate use and atypical fractures of the femoral shaft. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(18): 1728-1737.
[8] WANG Y, NISHIDA S, BOUDIGNON BM, et al. IGF-I receptor is required for the anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(9):1329-1337.
[9] BIKLE DD, SAKATA T, LEARY C, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I is required for the anabolic actions of parathyroid hormone on mouse bone. J Bone Miner Res. 2002;17(9):1570-1578.
[10] 韩辰,谢幼专,袁君杰.小干扰RNA技术与骨质疏松症治疗[J].国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(2):86-88.
[11] HOWARD KA, PALUDAN SR, BEHLKE MA, et al. Chitosan/siRNA nanoparticle-mediated TNF-alpha knockdown in peritoneal macrophages for anti-inflammatory treatment in a murine arthritis model. Mol Ther. 2009;17(1):162-168.
[12] KRAMER PR, PURI J, BELLINGER LL. Knockdown of Fcγ receptor III in an arthritic temporomandibular joint reduces the nociceptive response in rats. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(10):3109-3118.
[13] WANG Y, GRAINGER DW. RNA therapeutics targeting osteoclast-mediated excessive bone resorption. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12): 1341-1357.
[14] BUCKBINDER L, CRAWFORD DT, QI H, et al. Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2 regulates osteoprogenitor cells and bone formation, and offers an anabolic treatment approach for osteoporosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(25):10619-10624.
[15] LIU J, LU C, WU X, et al. Targeting osteoblastic casein kinase-2 interacting protein-1 to enhance Smad-dependent BMP signaling and reverse bone formation reduction in glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41295.
[16] MCKEE MD, PEDRAZA CE, KAARTINEN MT. Osteopontin and wound healing in bone. Cells Tissues Organs. 2011;194(2-4):313-319.
[17] NIE J, LIU L, HE F, et al. CKIP-1: a scaffold protein and potential therapeutic target integrating multiple signaling pathways and physiological functions. Ageing Res Rev. 2013;12(1):276-281.
[18] ZHANG G, GUO B, WU H, et al. A delivery system targeting bone formation surfaces to facilitate RNAi-based anabolic therapy. Nat Med. 2012;18(2):307-314.
[19] ZHANG L, WU K, SONG W, et al. Chitosan/siCkip-1 biofunctionalized titanium implant for improved osseointegration in the osteoporotic condition. Sci Rep. 2015;5:10860.
[20] ZHOU ZC, CHE L, KONG L, et al. CKIP-1 silencing promotes new bone formation in rat mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2017;123(1):e1-e9.
[21] BUSILLO JM, BENOVIC JL. Regulation of CXCR4 signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1768(4):952-963.
[22] GUO B, ZHANG B, ZHENG L, et al. Therapeutic RNA interference targeting CKIP-1 with a cross-species sequence to stimulate bone formation. Bone. 2014;59:76-88.
[23] XU P, GUO X, ZHANG YG, et al. The effect of retinoic acid on induction of osteoporotic model rats and the possible mechanism. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2005;36(2):229-232.
[24] LIU Q, ZHANG X, JIAO Y, et al. In vitro cell behaviors of bone mesenchymal stem cells derived from normal and postmenopausal osteoporotic rats. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(2):669-678.
[25] PINO AM, ROSEN CJ, RODRÍGUEZ JP. In osteoporosis, differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) improves bone marrow adipogenesis. Biol Res. 2012;45(3):279-287.
|