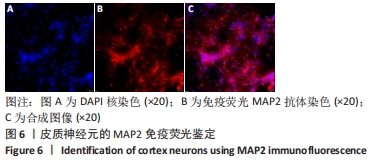
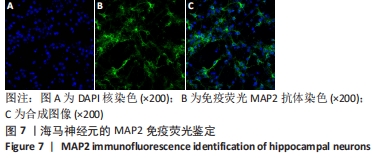
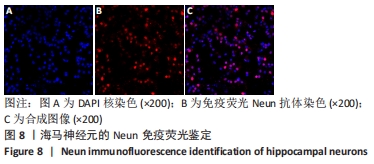
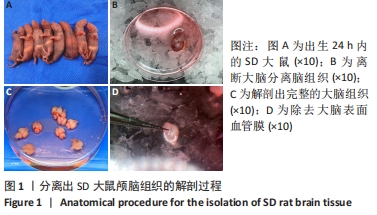
[1] WANG XJ, WANG MH, FU XT, et al. Selenocysteine antagonizes oxygen glucose deprivation-induced damage to hippocampal neurons. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(8):1433-1439.
[2] 许永劼,许雯,陈钢,等.2 种高糖诱导海马神经元模型应用及优势比较[J].中国比较医学杂志,2021,31(8):1-8.
[3] KANEKO Y, LEE JY, TAJIRI N, et al. Translating intracarotid artery transplantation of bone marrow-derived NCS-01 cells for ischemic stroke: Behavioral and histological readouts and mechanistic insights into stem cell therapy. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(2):203-220.
[4] BORLONGAN CV, NGUYEN H, LIPPERT T, et al. May the force be with you: Transfer of healthy mitochondria from stem cells to stroke cells. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019;39(2):367-370.
[5] 高超,杜贵琴,许永劼,等.海马神经元原代细胞培养方法的改良[J].贵州医科大学学报,2020,45(8):894-898.
[6] KHAN J, DAS G, GUPTA V, et al. Neurosphere Development from Hippocampal and Cortical Embryonic Mixed Primary Neuron Culture: A Potential Platform for Screening Neurochemical Modulator. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018;9(11):2870-2878.
[7] 仁德芳,付裕,王洪连,等.乳鼠海马神经元的分离和原代培养[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2017,33(5):660-663.
[8] 王平,陈秀.胎鼠海马神经细胞无血清原代培养法及鉴定[J].临床合理用药杂志,2018,11(2A):29-30,32.
[9] XU K, LEE JY, KANEKO Y, et al. Human stem cells transplanted into the rat stroke brain migrate to the spleen via lymphatic and inflammation pathways. Haematologica. 2019;104(5):1062-1073.
[10] BABENKO VA, SILACHEV DN, POPKOV VA, et al. Miro1 Enhances Mitochondria Transfer from Multipotent Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MMSC) to Neural Cells and Improves the Efficacy of Cell Recovery. Molecules. 2018;23(3):687.
[11] YOUSEFSANI BS, AKBARIZADEH N, POURAHMAD J. The antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of Zolpidem on acrylamide-induced neurotoxicity using Wistar rat primary neuronal cortical culture. Toxicol Rep. 2020;7:233-240.
[12] 冯龙,刘蔷薇,冯泽国,等.改良无血清法培养新生SD乳鼠原代海马神经元细胞[J].解放军医学院学报,2020,41(12):1222-1225.
[13] 王静欢,张志敏,邱炳勋,等. 2种原代培养方法对新生大鼠大脑皮质神经元生物学特性的影响[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,40(2):19-26.
[14] 薛建锋,魏娜,杨淳.一种同时培养原代神经元和原代星形胶质细胞的实验方法[J].临床与实验病理学杂志,2021,37(12):1479-1482.
[15] 康杨婷,王丽琨,伍国锋.胰酶稀释法提取乳鼠原代海马神经元[J].贵州医科大学学报,2019,44(1):59-63.
[16] BREWER GJ. Isolation and culture of adult rat hippocampal neurons. Neurosci Methods. 1997;71(2):143-155.
[17] XU SY, WU YM, JI Z, et al. A modified technique for culturing primary fetal rat cortical neurons. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:803930.
[18] TODD GK, BOOSALIS CA, BURZYCKI A A, et al. Towards neuronal organoids: a method for long-term culturing of high-density hippocampal neurons. PLoS One. 2013;8(4):e58996.
[19] 李兴统,汤红艳,马微,等.一种高纯度原代神经元培养和高效率转染的方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(32):5186-5190.
[20] 何伟亮,田小超,崔丽丽,等.大脑皮质神经元细胞的原代培养模型建立及鉴定[J].脑与神经疾病杂志,2020,28(7):407-409.
[21] 李一鹏,杨凯,刘英富,等.接种密度对大鼠海马神经元产出量的影响[J].生物技术通讯,2016,27(6):838-841,883.
[22] 李晓晓,陈欣月,刘丽娜,等. SD大鼠乳鼠皮层神经元细胞原代培养模型的建立及鉴定[J].现代生物医学进展,2021,21(21):4001-4005, 4050.
[23] 张余,刘英富,陈旭,等. 阿糖胞苷对大鼠海马神经元原代培养的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志 ,2016,32(3):218-220,224.
[24] 王东艳,杨金伟,程敬茹,等.一种新生SD大鼠皮质源性神经元的培养方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(51):7672 -7677.
[25] LV H, LI J, CHE Y. miR-31 from adipose stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles promotes recovery of neurological function after ischemic stroke by inhibiting TRAF6 and IRF5. Exp Neurol. 2021;342:113611.
[26] BHUIYAN MIH, KIM SY, CHO KO. Lin28 overexpression inhibits neurite outgrowth of primary cortical neuronsinvitro. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars). 2018;78(4):297-304.
[27] GADAU SD. Tubulin post-translational modifications in developing dog primary neurons obtained with methods according to the 3Rs principles. Res Vet Sci. 2019;122:56-63.
[28] 曹珂,刘检,苗露阳,等.皮质神经元B27原代培养及MAP2鉴定[J].沈阳药科大学学报,2013,30(1):40-43.
[29] SUN R, PENG M, XU P, et al. Low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) regulates NLRP3-mediated neuronal pyroptosis following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):330.
[30] MIKHAILOVA MM, BOLSHAKOV AP, CHABAN EA, et al. Primary culture of mouse embryonic spinal cord neurons: cell compositionand suitability for axonal regeneration studies. Int J Neurosci. 2019;129(8):762-769.
|