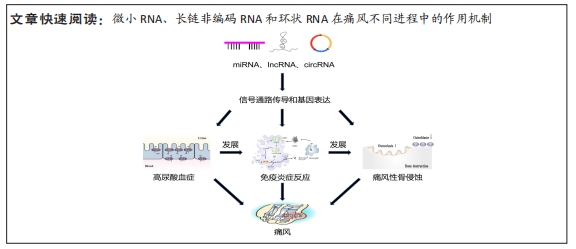
[1] DALBETH N, GOSLING AL, GAFFO A, et al. Gout. Lancet. 2021;397 (10287):1843-1855.
[2] 张超凤,刘晓莉,李雪娟,等.痛风急性发作一线药物治疗方案的系统评价及药物经济学分析[J].中国新药杂志,2021,30(16):1530-1536.
[3] DEHLIN M, JACOBSSON L, RODDY E. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(7):380-390.
[4] XU YT, LENG YR, LIU MM, et al. MicroRNA and long noncoding RNA involvement in gout and prospects for treatment. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;87:106842.
[5] DAI F, ZHANG QB, TANG YP, et al. Expression Profile and Potential Function of Circular RNAs in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells in Male Patients With Primary Gout. Front Genet. 2021;12:728091.
[6] HA M, KIM VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509-524.
[7] NI WJ, LENG XM. miRNA-Dependent Activation of mRNA Translation. Microrna. 2016;5(2):83-86.
[8] CORREIA DE SOUSA M, GJORGJIEVA M, DOLICKA D, et al. Deciphering miRNAs’ Action through miRNA Editing. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(24):6249.
[9] VISHNOI A, RANI S. MiRNA Biogenesis and Regulation of Diseases: An Overview. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1509:1-10.
[10] WANG Y, XU D, WANG B, et al. Could MicroRNAs be Regulators of Gout Pathogenesis? Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(6):2085-2092.
[11] FERRÈ F, COLANTONI A, HELMER-CITTERICH M. Revealing protein-lncRNA interaction. Brief Bioinform. 2016;17(1):106-116.
[12] STATELLO L, GUO CJ, CHEN LL, et al. Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021;22(2):96-118.
[13] ATIANAND MK, CAFFREY DR, FITZGERALD KA. Immunobiology of Long Noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017;35:177-198.
[14] SCHMITZ SU, GROTE P, HERRMANN BG. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016;73(13):2491-2509.
[15] LI X, PAN Y, LI W, et al. The Role of Noncoding RNAs in Gout. Endocrinology. 2020;161(11):bqaa165.
[16] KRISTENSEN LS, ANDERSEN MS, STAGSTED LVW, et al. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019; 20(11):675-691.
[17] PANDA AC. Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1087:67-79.
[18] GUO G, WANG H, YE L, et al. Hsa_circ_0000479 as a Novel Diagnostic Biomarker of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front Immunol. 2019; 10:2281.
[19] ICHIDA K, MATSUO H, TAKADA T, et al. Decreased extra-renal urate excretion is a common cause of hyperuricemia. Nat Commun. 2012; 3:764.
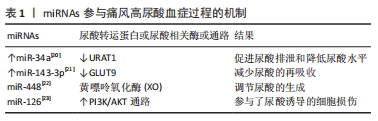
[20] SUN WF, ZHU MM, LI J, et al. Effects of Xie-Zhuo-Chu-Bi-Fang on miR-34a and URAT1 and their relationship in hyperuricemic mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015;161:163-169.
[21] RIPPERGER A, BENNDORF RA. The C421A (Q141K) polymorphism enhances the 3’-untranslated region (3’-UTR)-dependent regulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCG2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016; 104:139-147.
[22] JOSHI G, SHARMA M, KALRA S, et al. Design, synthesis, biological evaluation of 3,5-diaryl-4,5-dihydro-1H-pyrazole carbaldehydes as non-purine xanthine oxidase inhibitors: Tracing the anticancer mechanism via xanthine oxidase inhibition. Bioorg Chem. 2021;107:104620.
[23] BOHATÁ J, HORVÁTHOVÁ V, PAVLÍKOVÁ M, et al. Circulating microRNA alternations in primary hyperuricemia and gout. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):186.
[24] NARANG RK, DALBETH N. Pathophysiology of Gout. Semin Nephrol. 2020;40(6):550-563.
[25] WANG B, CHEN S, QIAN H, et al. Role of T cells in the pathogenesis and treatment of gout. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;88:106877.
[26] HANEKLAUS M, O’NEILL LA, COLL RC. Modulatory mechanisms controlling the NLRP3 inflammasome in inflammation: recent developments. Curr Opin Immunol. 2013;25(1):40-45.
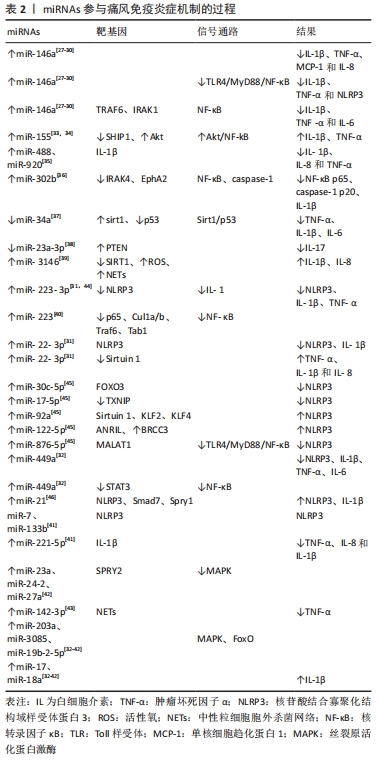
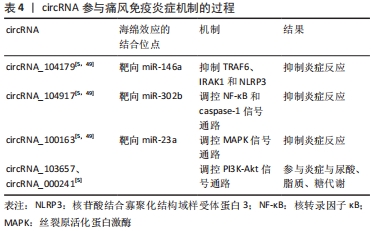
[27] ZHANG QB, QING YF, YIN CC, et al. Mice with miR-146a deficiency develop severe gouty arthritis via dysregulation of TRAF 6, IRAK 1 and NALP3 inflammasome. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):45.
[28] CHEN X, GAO Q, ZHOU L, et al. MiR-146a alleviates inflammation of acute gouty arthritis rats through TLR4/MyD88 signal transduction pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(21):9230-9237.
[29] DALBETH N, POOL B, SHAW OM, et al. Role of miR-146a in regulation of the acute inflammatory response to monosodium urate crystals. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(4):786-790.
[30] 徐阳洋,青玉凤,张全波,等.微小RNA-146a在原发性痛风性关节炎患者的变化及其临床意义[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2016,20(12): 796-800.
[31] WANG X, CHI J, DONG B, et al. MiR-223-3p and miR-22-3p inhibit monosodium urate-induced gouty inflammation by targeting NLRP3. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021;24(4):599-607.
[32] WANG Y. Tripterine ameliorates monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis by altering macrophage polarization via the miR-449a/NLRP3 axis. Inflamm Res. 2021;70(3):323-341.
[33] JIN HM, KIM TJ, CHOI JH, et al. MicroRNA-155 as a proinflammatory regulator via SHIP-1 down-regulation in acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2014;16(2):R88.
[34] YANG Q, ZHANG Q, QING Y, et al. miR-155 is dispensable in monosodium urate-induced gouty inflammation in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):144.
[35] ZHOU W, WANG Y, WU R, et al. MicroRNA-488 and -920 regulate the production of proinflammatory cytokines in acute gouty arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017;19(1):203.
[36] MA T, LIU X, CEN Z, et al. MicroRNA-302b negatively regulates IL-1β production in response to MSU crystals by targeting IRAK4 and EphA2. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018;20(1):34.
[37] 杨彬,黄俊卿,孟庆良,等.秦艽醇提物对痛风性关节炎大鼠氧化应激损伤及miR-34a/sirt1轴的影响研究[J].中药药理与临床,2019, 35(5):64-69.
[38] 孙广瀚,刘健,万磊,等. 黄芩清热除痹胶囊含药血清对痛风性关节炎CD4+T细胞与心肌细胞共培养后miR-23a-3p/PTEN表达的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报,2021,44(8):735-743.
[39] SHAN L, YANG D, FENG F, et al. miR-3146 induces neutrophil extracellular traps to aggravate gout flare. J Clin Lab Anal. 2021;35(11): e24032.
[40] YANG QB, LI LQ, ZHANG QB, et al. microRNA-223 Deficiency Exacerbates Acute Inflammatory Response to Monosodium Urate Crystals by Targeting NLRP3. J Inflamm Res. 20211;14:1845-1858.
[41] LI G, ZHANG H, MA H, et al. MiR-221-5p is involved in the regulation of inflammatory responses in acute gouty arthritis by targeting IL-1β. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021;24(3):335-340.
[42] 李玲琴,王东生,青玉凤,等. 微小RNA-23a~27a~24-2簇在原发性痛风性关节炎患者的表达及其临床意义[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志, 2015,19(2):76-80.
[43] LU Y, FANG L, XU X, et al. MicroRNA-142-3p facilitates inflammatory response by targeting ZEB2 and activating NF-κB signaling in gouty arthritis. Cell Cycle. 2022:1-15.
[44] TIAN J, ZHOU D, XIANG L, et al. MiR-223-3p inhibits inflammation and pyroptosis in monosodium urate-induced rats and fibroblast-like synoviocytes by targeting NLRP3. Clin Exp Immunol. 2021;204(3):396-410.
[45] MENG Q, MENG W, BIAN H, et al. Total glucosides of paeony protects THP-1 macrophages against monosodium urate-induced inflammation via MALAT1/miR-876-5p/NLRP3 signaling cascade in gouty arthritis. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;138:111413.
[46] 陈刚,李梦兰,彭春梅,等. 微RNA-21在原发性痛风患者中的变化及意义[J]. 中华风湿病学杂志,2019,23(3):165-169.
[47] 杨颜瑜,熊琴,谭敏,等.长链非编码RNA调节痛风炎症信号通路的研究进展[J].中华老年多器官疾病杂志,2019,18(6):473-477.
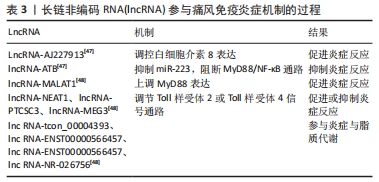
[48] QING YF, ZHENG JX, TANG YP, et al. LncRNAs Landscape in the patients of primary gout by microarray analysis. PLoS One. 2021;16(2): e0232918.
[49] 戴菲,郑建雄,唐乙萍,等.痛风患者外周血单个核细胞环状RNA的表达谱分析[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2021,25(1):26-31,c1-3,c1-4.
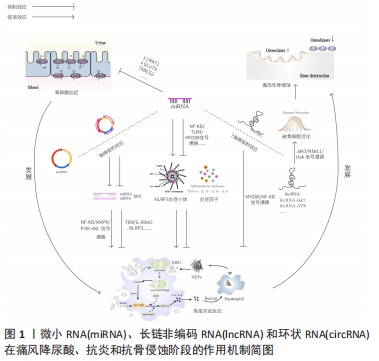
[50] SCHLESINGER N, THIELE RG. The pathogenesis of bone erosions in gouty arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(11):1907-1912.
[51] LEE CP, HUANG YN, NITHIYANANTHAM S, et al. LncRNA-Jak3:Jak3 coexpressed pattern regulates monosodium urate crystal-induced osteoclast differentiation through Nfatc1/Ctsk expression. Environ Toxicol. 2019;34(2):179-187.
[52] DALBETH N, SMITH T, NICOLSON B, et al. Enhanced osteoclastogenesis in patients with tophaceous gout: urate crystals promote osteoclast development through interactions with stromal cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(6):1854-1865.
[53] EULER M, HOFFMANN MH. The double-edged role of neutrophil extracellular traps in inflammation. Biochem Soc Trans. 2019;47(6): 1921-1930.
|