[1] CASTILLO-GALVÁN ML, MARTÍNEZ-RUIZ FM, DE LA GARZA-CASTERO O, et al. Study of peripheral nerve injury in trauma patients. Gac Med Mex. 2014;150(6):527-532.
[2] NOCERA G, JACOB C. Mechanisms of Schwann cell plasticity involved in peripheral nerve repair after injury. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2020;77(20): 3977-3989.
[3] BHANDARI PS. Management of peripheral nerve injury. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2019;10(5):862-866.
[4] KLIMOVICH P, RUBINA K, SYSOEVA V, et al. New frontiers in peripheral nerve regeneration: concerns and remedies. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(24):13380.
[5] 宋凯凯, 张锴, 贾龙. 周围神经系统损伤的微环境与修复方式[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(4):651-656.
[6] LKUMI A,GINGERY A,TOYOSHIMA Y, et al. Administration of purified exosome product in a rat sciatic serve reverse autograft model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(2):200-211.
[7] KUBIAK CA,KUNG TA,BOWN DL, et al. State-of-the-art techniques in treating peripheral nerve injury. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;141(3):702-710.
[8] RAZA C, RIAZ HA, ANJUM R, et al. Repair strategies for injured peripheral nerve: review. Life Sci. 2020;243:117308.
[9] 朱芳慧.甲钴胺联合硫辛酸治疗糖尿病周围神经病变的临床疗效[J].实用心脑肺血管病杂志,2017,25(S2):32-34.
[10] 赵华飞,王维新,崔硕,等.几丁糖对鼠坐骨神经损伤后再生的影响[J].中国临床药理学杂志,2018,34(14):1659-1661.
[11] MODRAK M, TALUKDER MAH, GURGENASHVILI K, et al. Peripheral nerve injury and myelination: Potential therapeutic strategies. J Neurosci Res. 2020;98(5):780-795.
[12] LI Y, MA Z, REN Y, et al. Tissue engineering strategies for peripheral nerve regeneration. Front Neurol. 2021;12:768267.
[13] BUSUTTIL F, RAHIM AA, PHILLIPS JB. Cand stem cell therapy for peripheral nerve tissue engineering. Stem Cells Dev. 2017;26(4):231-238.
[14] 陈渝,邓忠良,翁政,等.NGF/MAG双基因共表达腺病毒修复大鼠周围神经损伤的试验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2016,30(8):1026-1033.
[15] LI H, CHANG LJ, NEUBAUER DR, et al. Immortalization of human normal and NF1 neurofibroma Schwann cells. Laboratory Investigation. 2016; 96(10):1105-1115.
[16] CHEN J, REN S, DUSCHER D, et al. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote sciatic nerve regeneration via optimizing Schwann cell function. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(12):23097-23110.
[17] DAI J, SU Y, ZHONG S, et al. Exosomes: key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020; 5(1):145.
[18] 袁一鸣,王艳,陈程程,等.外泌体在周围神经损伤进程中的效应[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(31):5079-5084.
[19] MONK KR, FELTRI ML, TAVEGGIA C. New insights on Schwann cell development. Glia. 2015;63(8):1376-1393.
[20] JESSEN KR, MIRSKY R. The success and failure of the Schwann cell response to nerve injury. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:33.
[21] HARTY BL, MONK KR. Unwrapping the unappreciated: recent progress in remak Schwann cell biology. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2017;47:131-137.
[22] 蒋玲丽,魏在荣.周围神经损伤修复过程以及miRNA在周围神经修复中的研究进展[J].遵义医科大学学报,2020,43(6):801-806.
[23] MADISON RD, MCGEE C, RAWSON R, et al. Extracellular vesicles from a muscle cell line (C2C12) enhance cell survival and neurite outgrowth of a motor neuron cell line (NSC-34). J Extracell Vesicles. 2014;3(1): 22865.
[24] BOERBOOM A, DION V, CHARIOT A, et al. Molecular mechanisms involved in Schwann cell plasticity. Front Mol Neurosci. 2017;10:38.
[25] WONG FC, YE L, DEMIR IE, et al. Schwann cell-derived exosomes: Janus-faced mediators of regeneration and disease. Glia. 2022;70(1):20-34.
[26] IBRAHIM A, MARBÁN E. Exosomes: Fundamental biology and roles in cardiovascular physiology. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:67-83.
[27] DE GREGORIO C, DíAZ P, LÓPEZ-LEAL R, et al. Purification of exosomes from primary Schwann cells, RNA extraction, and next-generation sequencing of exosomal RNAs. Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1739:299-315.
[28] 谢欢. HUVECs分泌的外泌体通过抑制miR-21-3p减弱缺氧/复氧诱导的神经细胞凋亡[D].南昌:南昌大学,2019.
[29] KALLURI R, LEBLEU VS. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science. 2020;367(6478):6977.
[30] XIE F, ZHOU X, FANG M, et al. Extracellular vesicles in cancer immune microenvironment and cancer immunotherapy. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019; 6(24):1901779.
[31] ZHOU B, XU K, ZHENG X, et al. Application of exosomes as liquid biopsy in clinical diagnosis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020;5(1):144.
[32] 周敏,洪莉,胡鸣,等.外泌体在周围神经损伤中的研究进展[J].医学综述,2017,23(13):2497-2500.
[33] 高方园, 焦丰龙, 张养军,等.外泌体分离技术及其临床应用研究进展[J].色谱,2019,37(10):1071-1083.
[34] HYUNG S, KIM JY, YU CJ, et al. Neuroprotective effect of glial cell-derived exosomes on neurons. Immunotherapy: Open Access. 2019; 5(1):156.
[35] SOHN E J, PARK H T, SHIN YK. Exosomes derived from differentiated Schwann cells inhibit Schwann cell migration via microRNAs. Neuroreport. 2020;31(7):515-522.
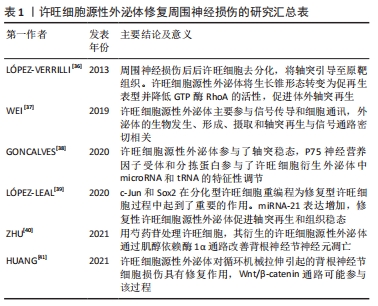
[36] LÓPEZ-VERRILLI MA, PICOU F, COURT FA. Schwann cell-derived exosomes enhance axonal regeneration in the peripheral nervous system. Glia. 2013;61(11):1795-1806.
[37] WEI Z, FAN B, DING H, et al. Proteomics analysis of Schwann cell-derived exosomes: a novel therapeutic strategy for central nervous system injury. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019;457(1-2):51-59.
[38] GONCALVES NP, YAN Y, ULRICHSEN M, et al. Modulation of small RNA signatures in Schwann-cell-derived extracellular vesicles by the p75 neurotrophin receptor and Sortilin. Biomedicines. 2020;8(11):450.
[39] LÓPEZ-LEAL R, DÍAZ-VIRAQUÉ F, CATALÁN RJ, et al. Schwann cell reprogramming into repair cells increases miRNA-21 expression in exosomes promoting axonal growth. J Cell Sci. 2020;133(12):239004.
[40] ZHU Y, HAN S, LI X, et al. Paeoniflorin effect of Schwann cell-derived exosomes ameliorates dorsal root ganglion neurons apoptosis through IRE1α pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021; 2021:6079305.
[41] HRANG G, HU M, LU D, et al. Protective effect and potential mechanism of Schwann cell-derived exosomes on mechanical damage of rat dorsal root ganglion cells. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2021;47(10):3691-3701.
[42] GONÇALVES NP, VÆGTER CB, ANDERSEN H, et al. Schwann cell interactions with axons and microvessels in diabetic neuropathy. Nat Rev Neurol. 2017;13(3):135-147.
[43] PAN D, ZHU S, ZHANG W, et al. Autophagy induced by Schwann cell-derived exosomes promotes recovery after spinal cord injury in rats. Biotechnol Lett. 2022;44(1):129-142.
[44] PAN D, LI Y, YANG F, et al. Increasing toll-like receptor 2 on astrocytes induced by Schwann cell-derived exosomes promotes recovery by inhibiting CSPGs deposition after spinal cord injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2021;18(1):172.
[45] HU M, HONG L, LIU C, et al. Electrical stimulation enhances neuronal cell activity mediated by Schwann cell derived exosomes. Sci Rep. 2019; 9(1):4206.
[46] CONG M, SHEN M, WU X, et al. Improvement of sensory neuron growth and survival via negatively regulating PTEN by miR-21-5p-contained small extracellular vesicles from skin precursor-derived Schwann cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):80.
[47] Liu D, Liang X, Zhang H. Effects of High Glucose on Cell Viability and Differentiation in Primary Cultured Schwann Cells: Potential Role of ERK Signaling Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2016;41(6):1281-1290.
[48] JIA L, CHOPP M, WANG L, et al. Exosomes derived from high-glucose-stimulated Schwann cells promote development of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. FASEB J. 2018;32(12):fj201800597R.
[49] Dong R, Liu Y, Yang Y, et al. MSC-Derived Exosomes-Based Therapy for Peripheral Nerve Injury: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy. Biomed Res Int. 2019;2019:6458237.
[50] WANG H, JIA Y, LI J, et al. Schwann cell derived exosomes induce bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells to express Schwann cell markers in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2020;21(3):1640-1646.
[51] COURT FA, ALVAREZ J. Schwann cell and axon: an interlaced unit-from action potential to phenotype expression. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2016; 949:183-201.
[52] WANG L, CHOPP M, SZALAD A, et al. Exosomes derived from schwann cells ameliorate peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetic mice. Diabetes. 2020;69(4):749-759.
|