1.1 设计 细胞学体外实验,采用单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)进行各组间比较。
1.2 时间及地点 2022年1-3月在贵阳市口腔医院进行样本收集,2022年4-11月在贵州医科大学附属医院临床研究中心完成细胞培养、相关形态学及基因检测。
1.3 材料
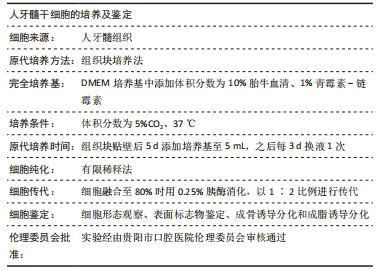
1.3.1 细胞来源 选取在贵阳市口腔医院口腔颌面外科经过患者知情同意及匿名处理后拔除的正畸牙或者第三磨牙,年龄在18-20岁之间,已签署知情同意书,此次实验在贵阳市口腔医院伦理委员会审核通过下进行,批准号:GYSKLL-20211014-01。
1.3.2 主要试剂及仪器 DMEM培养基、青霉素-链霉素、胰蛋白酶(美国,Gibco);胎牛血清(以色列,BI);rhGH (中国,长春金赛药业有限公司);PBS、地塞米松、吲哚美辛、抗坏血酸、β-甘油磷酸钠、IBMX、胰岛素、油红O染液、茜素红染液(北京,索莱宝);40 g/L多聚甲醛细胞固定液(中国,Biosharp);CCK-8试剂盒(美国,APEXBIO)、碱性磷酸酶显色试剂盒、BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(上海,碧云天);碱性磷酸酶检测试剂盒(南京,建成);RNA提取试剂盒、反转录试剂盒、SYBRgreen qPCR试剂盒(北京,聚合美);CD90-FITC、CD34-PE/CY7、CD29-PE、CD45-pacific blue、CD105-APC(Biolegend)。
1.4 方法
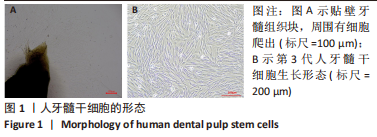
1.4.1 人牙髓干细胞的培养 收集18-20岁患者因正畸或智齿拔除的牙齿,用PBS冲洗3次,去除根尖1 mm牙体组织,高速涡轮手机沿牙颈部磨出凹槽,无菌条件下沿凹槽劈开牙齿,取出牙髓组织,在含青霉素-链霉素的PBS中浸泡30 min,剪成1.0 mm×1.0 mm×1.0 mm大小的组织块,将细胞块均匀铺于25T培养瓶底,加入含体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养液约2 mL,将培养瓶翻转向上,静置于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2细胞培养箱中,2 h后将瓶底翻转向下,5 d后将培养瓶取出观察,并将培养液加至5 mL,以后每3 d换液1次,2周后去除组织块。镜下观察,待细胞融合度达70%-80%时,用0.25%胰酶消化细胞,1 000 r/min离心5 min,按1∶2比例进行传代,扩增培养。
1.4.2 有限稀释法纯化人牙髓干细胞 取对数生长期的第1代人牙髓干细胞,用0.25%胰酶消化细胞,1 000 r/min离心5 min,用含体积分数为20%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基倍比稀释,调整细胞密度至10-15个/mL,充分吹打混匀,按100 μL/孔接种于96孔板中,37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2细胞培养箱中,培养24 h后标记单个细胞孔,3 d换液1次。当细胞数量增多时每2 d换液1次,待长满孔底后0.25%胰蛋白酶消化,1 000 r/min离心5 min,按1∶2比例进行传代,扩增培养。
1.4.3 人牙髓干细胞克隆形成能力检测 取有限稀释法克隆获得的细胞,用DMEM完全培养基重悬细胞,调整细胞密度为1个/mL或2个/mL,将细胞接种至培养皿中培养7 d进行结晶紫染色,室温下自然晾干,倒置显微镜下观察集落生长情况并拍照。
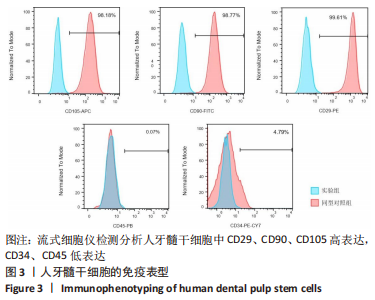
1.4.4 流式细胞术检测人牙髓干细胞免疫表型 取第3代细胞,待细胞生长至80%时用0.25%胰酶消化,1 000 r/min离心5 min,PBS重悬洗涤细胞,重复2次,调整细胞浓度为5×109 L-1。取7支流式管,分别标记空白对照组、实验组、补偿微球组(CD29、CD34、CD45、CD90、CD105)。取2份100 μL细胞悬液分别置于空白对照组和实验组流式管,按照说明书在实验组中依次加入5种抗体,补偿微球组中加入补偿微球和对应抗体,室温下避光孵育30 min,洗涤后500 μL PBS重悬,上流式细胞仪检测,FlowJo V10软件分析。
1.4.5 人牙髓干细胞多项分化能力检测
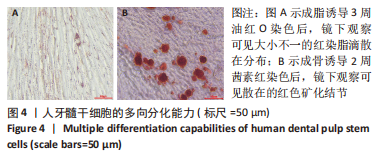
(1)成脂向分化诱导:取第3代人牙髓干细胞消化成细胞悬液,调整细胞浓度为1×108 L-1,充分混匀后接种至6孔板,每孔2 mL细胞悬液,每3 d换液1次,待细胞生长达100%时,换成脂诱导液进行成脂诱导,见表1,3周后油红O染色,光镜下观察脂滴形成情况并拍照。
(2)成骨向分化诱导:取第3代人牙髓干细胞消化成细胞悬液,调整细胞浓度为1×108 L-1,充分混匀后接种至6孔板,每孔2 mL细胞悬液,每3 d换液1次,待细胞生长达80%时,换成骨诱导液进行成骨诱导,见表1,2周后茜素红染色,光镜下观察矿化结节形成情况并拍照。

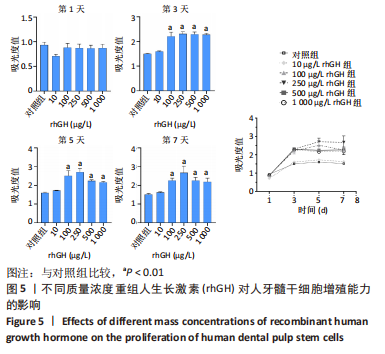
1.4.6 CCK-8检测不同浓度rhGH对人牙髓干细胞增殖的影响 取第3代人牙髓干细胞消化成细胞悬液,调整细胞浓度为2×107 L-1,充分混匀后以每孔100 μL细胞悬液接种至96孔板,分为对照组和10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH组,每组设置5个复孔,培养24 h后换成含有10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH的DMEM完全培养基,每2 d换液1次,干预后1,3,5,7 d收样,根据CCK-8试剂盒说明操作,酶标仪检测450 nm处的吸光度值。
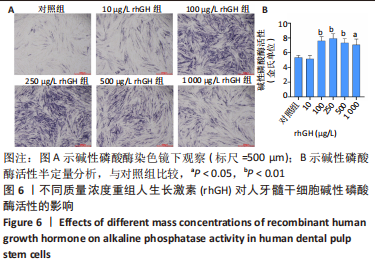
1.4.7 碱性磷酸酶染色及半定量分析 取第3代人牙髓干细胞消化成细胞悬液,调整细胞浓度为1×108 L-1,充分混匀后接种至6孔板,每孔加入2 mL细胞悬液,分为对照组和10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH组,每3 d换液1次,待细胞生长达80%时,换成含有10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH的成骨诱导液,每2 d换液1次,诱导7 d后去掉孔内成骨诱导液,PBS洗涤3次,加入40 g/L多聚甲醛固定20 min,根据碱性磷酸酶显色试剂盒说明书对细胞进行染色,显微镜下观察碱性磷酸酶染色情况并拍照。半定量检测:在诱导7 d时去掉孔内成骨诱导液,PBS洗涤3次,加入1%裂解液400 μL,冰上裂解30 min,4 000 r/min离心15 min,用BCA法测定总蛋白浓度,按照碱性磷酸酶测试盒说明书配制检测液,每组3个复孔,37 ℃孵育15 min,加入显色液,使用酶标仪检测520 nm处各孔的吸光度值,计算各组碱性磷酸酶活性(金氏单位)。
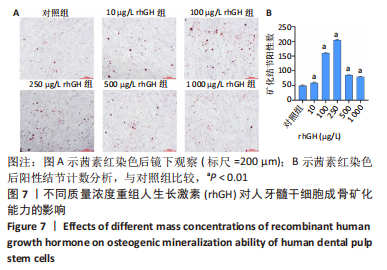
1.4.8 茜素红染色 取第3代人牙髓干细胞消化成细胞悬液,调整细胞浓度为1×108 L-1,充分混匀后接种至6孔板,每孔加入2 mL细胞悬液,分为对照组和10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH组,每3 d换液1次,待细胞生长达80%时,换成含有10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH的成骨诱导液,每2 d换液1次,矿化诱导14 d后去掉孔内的成骨诱导液,PBS洗涤3次,40 g/L多聚甲醛固定20 min,PBS洗涤2次,茜素红染色,显微镜下观察矿化结节形成情况并拍照,用Image J 软件统计矿化结节数量。
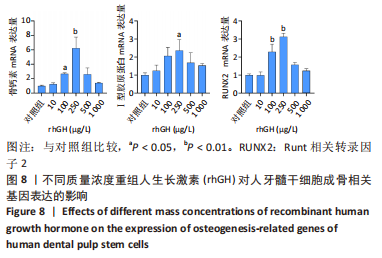
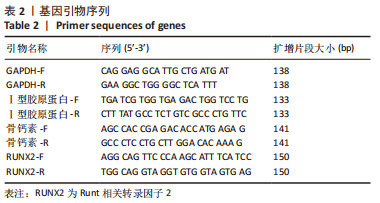
1.4.9 荧光定量RT-qPCR 取第3代人牙髓干细胞消化成细胞悬液,调整细胞浓度为1×108 L-1,充分混匀后接种至6孔板,每孔加入2 mL细胞悬液,分为对照组和10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH组,每3 d换液1次,待细胞生长达80%时,换成含有10,100,250,500,1 000 μg/L rhGH的成骨诱导液,每2 d换液1次,诱导7 d后去掉孔内的成骨诱导液,PBS洗涤3次,按RNA提取试剂盒操作说明提取细胞RNA,按照cDNA反转录试剂盒操作说明将mRNA反转录成cDNA,以95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 15 s,72 ℃ 30 s为1个循环,总共40个循环为程序,用RT-qPCR检测相关基因的表达,观察成骨分化相关因子Ⅰ型胶原蛋白、骨钙素、Runt相关转录因子2(runt-related transcription factor 2,RUNX2)的表达水平。基因引物序列,见表2。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①人牙髓干细胞的鉴定结果;②rhGH对人牙髓干细胞增殖的影响;③rhGH对人牙髓干细胞成骨分化的影响。
1.6 统计学分析 采用 GraphPad Prism 8.0 软件对各项数据进行统计分析并绘制统计图。正态分布多组间的比较采用单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA),而非正态分布多组间的比较采用非参数检验,P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。文章统计学方法已经通过贵州医科大学统计学专家审核。