[1] VINA ER, KWOH CK. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis: literature update. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2018;30(2):160-167.
[2] LOESER RF, GOLDRING SR, SCANZELLO CR, et al. Osteoarthritis: a disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(6):1697-1707.
[3] GAO SG, LI KH, ZENG KB, et al. Elevated osteopontin level of synovial fluid and articular cartilage is associated with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis patients. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2010;18(1):82-87.
[4] MELDOLESI J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr Biol. 2018;28(8):R435-R444.
[5] 王新伟,赵英杰,常艳,等.间充质干细胞治疗骨关节炎软骨损伤:作用、应用与问题[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(31):5053-5058.
[6] 王宪峰,欧昕,邓必勇.不同来源间充质干细胞外泌体治疗骨关节炎疗效的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(25):3980-3985.
[7] YAN L, WU X. Exosomes produced from 3D cultures of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in a hollow-fiber bioreactor show improved osteochondral regeneration activity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2020;36(2):165-178.
[8] YAN L, LIU G, WU X. Exosomes derived from umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells in mechanical environment show improved osteochondral activity via upregulation of LncRNA H19. J Orthop Translat. 2021;26:111.
[9] WU F, AN Y, ZHOU L, et al. Whole-transcriptome sequencing and ceRNA interaction network of temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis. Front Genet. 2022;13:962574.
[10] CHEN H, CHEN L. An integrated analysis of the competing endogenous RNA network and co-expression network revealed seven hub long non-coding RNAs in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(3):90-98.
[11] YAN L, LIU G, WU X. The umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA H19 improves osteochondral activity through miR-29b-3p/FoxO3 axis. Clin Transl Med. 2021;11(1):e255.
[12] LIU YL, YANG WH, CHEN BY, et al. miR‑29b suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma ascites H22 cells via regulating TGF‑β1 and p53 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 2021;48(2):157.
[13] GUO J, LIN Q, SHAO Y, et al. miR-29b promotes skin wound healing and reduces excessive scar formation by inhibition of the TGF-β1/Smad/CTGF signaling pathway. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2017;95(4):437-442.
[14] PRITZKER KP, GAY S, JIMENEZ SA, et al. Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: grading and staging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14(1):13-29.
[15] SACITHARAN PK. Ageing and Osteoarthritis. Subcell Biochem. 2019;91:123-159.
[16] FUJII Y, LIU L, YAGASAKI L, et al. Cartilage Homeostasis and Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(11):6316.
[17] 王琦,易诚青.膝关节骨关节炎治疗的研究进展[J].复旦学报(医学版),2022, 49(5):765-770.
[18] HUSSAIN SM, NEILLY DW, BALIGA S, et al. Knee osteoarthritis: a review of management options. Scott Med J. 2016;61(1):7-16.
[19] KAN HS, CHAN PK, CHIU KY, et al. Non-surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Hong Kong Med J. 2019;25(2):127-133.
[20] MAKRIS EA, GOMOLL AH, MALIZOS KN, et al. Repair and tissue engineering techniques for articular cartilage. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(1):21-34.
[21] LEE KB, HUI JH, SONG IC, et al. Injectable mesenchymal stem cell therapy for large cartilage defects--a porcine model. Stem Cells. 2007;25(11):2964-2971.
[22] NEJADNIK H, HUI JH, FENG CHOONG EP, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells versus autologous chondrocyte implantation: an observational cohort study. Am J Sports Med. 2010;38(6):1110-1116.
[23] BACAKOVA L, ZARUBOVA J, TRAVNICKOVA M, et al. Stem cells: their source, potency and use in regenerative therapies with focus on adipose-derived stem cells - a review. Biotechnol Adv. 2018;36(4):1111-1126.
[24] ZHANG S, CHU WC, LAI RC, et al. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(12):2135-2140.
[25] 凌华军,王其友,林伟文,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体保护软骨细胞延缓骨关节炎的发生发展[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(31):4964-4969.
[26] ZHANG Y, BI J, HUANG J, et al. Exosome: A Review of Its Classification, Isolation Techniques, Storage, Diagnostic and Targeted Therapy Applications. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:6917-6934.
[27] BATRAKOVA EV, KIM MS. Using exosomes, naturally-equipped nanocarriers, for drug delivery. J Control Release. 2015;219:396-405.
[28] DUDEK KA, LAFONT JE, MARTINEZ-SANCHEZ A, et al. Type II collagen expression is regulated by tissue-specific miR-675 in human articular chondrocytes. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(32):24381-24387.
[29] WANG CL, ZUO B, LI D, et al. The long noncoding RNA H19 attenuates force-driven cartilage degeneration via miR-483-5p/Dusp5. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(2):210-217.
[30] NING B, JIN R, WANG D, et al. The H19/let-7 feedback loop contributes to developmental dysplasia and dislocation of the hip. Physiol Res. 2019;68(2):275-284.
[31] 王伟康,刘晓冬,周长林,等.MiRNAs在骨关节炎发生发展中的调控作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(35):5709-5715.
[32] CHEN L, LI Q, WANG J, et al. MiR-29b-3p promotes chondrocyte apoptosis and facilitates the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by targeting PGRN. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(12):3347-3359.
[33] LV M, ZHONG Z, HUANG M, et al. lncRNA H19 regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of bladder cancer by miR-29b-3p as competing endogenous RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2017;1864(10):1887-1899.
[34] DING D, LI C, ZHAO T, et al. LncRNA H19/miR-29b-3p/PGRN Axis Promoted Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Acting on Wnt Signaling. Mol Cells. 2018;41(5):423-435.
[35] TIAN X, ZUO X, HOU M, et al. LncRNA-H19 regulates chemoresistance to carboplatin in epithelial ovarian cancer through microRNA-29b-3p and STAT3. J Cancer. 2021;12(19):5712-5722.
[36] CAO B, DAI X. Platelet lysate induces chondrogenic differentiation of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells by regulating the lncRNA H19/miR-29b-3p/SOX9 axis. FEBS Open Bio. 2020;10(12):2656-2665.
|

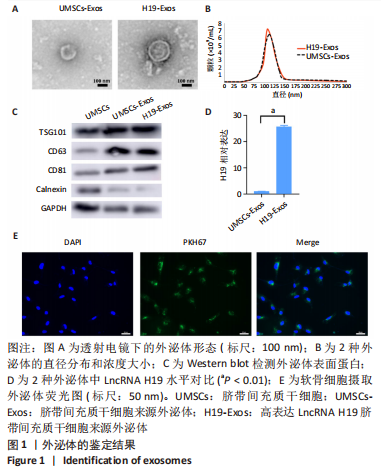
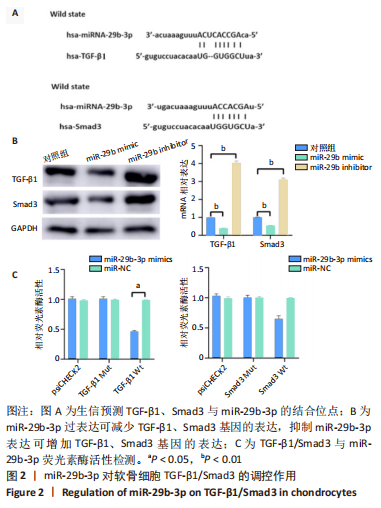
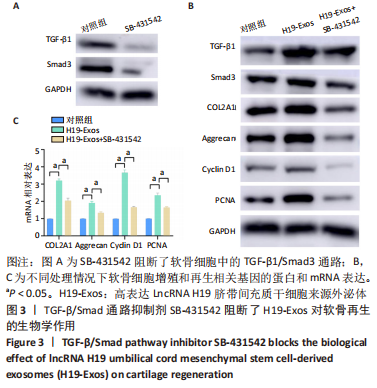

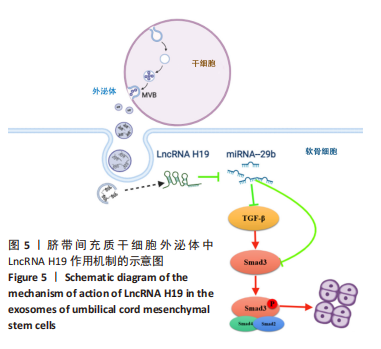 综上所述,该研究通过体内和体外实验系统论证高表达LncRNA H19的UMSCs外泌体对软骨细胞再生修复的促进作用,并详细解析LncRNA H19通过内源竞争RNA机制激活TGF-β1/Smad3通路促进软骨再生的具体分子机制。这将为发现一个新的治疗靶点提供可能的研究基础,为干细胞外泌体在软骨损伤中的运用提供可能的理论基础,对于软骨修复的基础和临床研究具有重要意义。
综上所述,该研究通过体内和体外实验系统论证高表达LncRNA H19的UMSCs外泌体对软骨细胞再生修复的促进作用,并详细解析LncRNA H19通过内源竞争RNA机制激活TGF-β1/Smad3通路促进软骨再生的具体分子机制。这将为发现一个新的治疗靶点提供可能的研究基础,为干细胞外泌体在软骨损伤中的运用提供可能的理论基础,对于软骨修复的基础和临床研究具有重要意义。