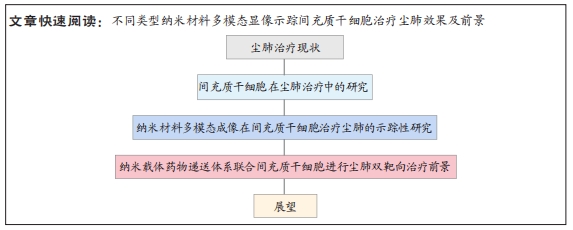
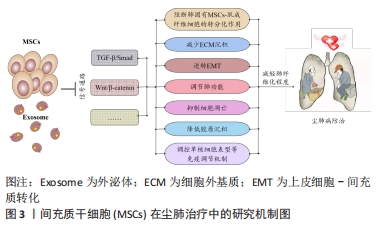
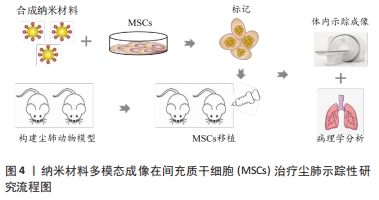
[1] QI XM, LUO Y, SONG MY, et al. Pneumoconiosis: current status and future prospects. Chin Med J (Engl). 2021;134(8):898-907.
[2] The Lancet. Improving occupational health in China. Lancet. 2019; 394(10197):443.
[3] MROZ MM, FERGUSON JH, FAINO AV, et al. Effect of inhaled corticosteroids on lung function in chronic beryllium disease. Respir Med. 2018;138S:S14-S19.
[4] ZHANG Y, LU P, QIN H, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine combined with pulmonary drug delivery system and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: rationale and therapeutic potential. Biomed Pharmacother. 2021;133:111072.
[5] WU X, HUANG J, WANG J, et al. Multi-pharmaceutical activities of chinese herbal polysaccharides in the treatment of pulmonary fibrosis: concept and future prospects. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:707491.
[6] XIAO S, YU Y, XIONG Y, et al. Chinese herbal medicines for the treatment of cough in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99(44):e22991.
[7] GUO J, LI B, WU W, et al. Chinese herbal medicines compared with n-acetylcysteine for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:5170638.
[8] ROGLIANI P, CALZETTA L, CAVALLI F, et al. Pirfenidone, nintedanib and N-acetylcysteine for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 2016;40:95-103.
[9] GUO J, YANG Z, JIA Q, et al. Pirfenidone inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and pulmonary fibrosis in the rat silicosis model. Toxicol Lett. 2019;300:59-66.
[10] WOLLIN L, DISTLER JHW, REDENTE EF, et al. Potential of nintedanib in treatment of progressive fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Eur Respir J. 2019;54(3):1900161.
[11] VALENZUELA C, TORRISI SE, KAHN N, et al. Ongoing challenges in pulmonary fibrosis and insights from the nintedanib clinical programme. Respir Res. 2020;21(1):7.
[12] EL-KASHEF DH. Nicorandil ameliorates pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis in a rat model of silicosis. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;64:289-297.
[13] HUANG H, CHEN M, LIU F, et al. N-acetylcysteine tiherapeutically protects against pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse model of silicosis. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(7):BSR20190681.
[14] DU S, LI C, LU Y, et al. Dioscin alleviates crystalline silica-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis through promoting alveolar macrophage autophagy. Theranostics. 2019;9(7):1878-1892.
[15] FENG F, CHENG P, ZHANG H, et al. The protective role of tanshinone iia in silicosis rat model via TGF-beta1/Smad signaling suppression, NOX4 inhibition and Nrf2/ARE signaling activation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019; 13:4275-4290.
[16] LI S, LI C, ZHANG Y, et al. Targeting mechanics-induced fibroblast activation through CD44-RhoA-YAP pathway ameliorates crystalline silica-induced silicosis. Theranostics. 2019;9(17):4993-5008.
[17] WEI Z, XU H, ZHANG Y, et al. Rho GDP dissociation inhibitor alpha silencing attenuates silicosis by inhibiting RhoA/Rho kinase signalling. Exp Cell Res. 2019;380(2):131-140.
[18] QIAN Q, CAO X, WANG B, et al. TNF-alpha-TNFR signal pathway inhibits autophagy and promotes apoptosis of alveolar macrophages in coal worker’s pneumoconiosis. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(5):5953-5963.
[19] ZHAO H, WANG Y, QIU T, et al. Autophagy, an important therapeutic target for pulmonary fibrosis diseases. Clin Chim Acta. 2020;502:139-147.
[20] YANG M, QIAN X, WANG N, et al. Inhibition of MARCO ameliorates silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Toxicol Lett. 2019;301:64-72.
[21] LI X, YAN X, WANG Y, et al. NLRP3 inflammasome inhibition attenuates silica-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human bronchial epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2018;362(2):489-497.
[22] WANG X, XU K, YANG XY, et al. Upregulated miR-29c suppresses silica-induced lung fibrosis through the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway in mice. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2018;37(9):944-952.
[23] PAN SC, CUI HH, QIU CG. HOTAIR promotes myocardial fibrosis through regulating URI1 expression via Wnt pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(20):6983-6990.
[24] ZHOU H, GAO L, YU ZH, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes renal interstitial fibrosis by regulating Notch1 pathway via the modulation of miR-124. Nephrology (Carlton). 2019;24(4):472-480.
[25] YU F, CHEN B, DONG P, et al. HOTAIR epigenetically modulates PTEN expression via MicroRNA-29b: a novel mechanism in regulation of liver fibrosis. Mol Ther. 2020;28(12):2703.
[26] XY T, YAN W, WU Q, et al. MiR-326 Inhibits inflammation and promotes autophagy in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis through targeting TNFSF14 and PTBP1. Chem Res Toxicol. 2019;32(11):2192-2203.
[27] ODINTSEVA OV, SEMENIKHIN VA, LEE GA. Total broncho-alveolar lavage in respiratory diseases among coal mining workers. Med Tr Prom Ekol. 2015;(5):25-29.
[28] ZHAO H, XIE Y, WANG J, et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation can improve the functional capacity and quality of life for pneumoconiosis patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;2020:6174936.
[29] ZHAO H, XIE Y, WANG J, et al. Pulmonary rehabilitation for pneumoconiosis: protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9(8):e025891.
[30] ROSENGARTEN D, FOX BD, FIREMAN E, et al. Survival following lung transplantation for artificial stone silicosis relative to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Ind Med. 2017;60(3):248-254.
[31] HOY RF, CHAMBERS DC. Silica-related diseases in the modern world. Allergy. 2020;75(11):2805-2817.
[32] ZHANG E, YANG Y, CHEN S, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells attenuate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis potentially by attenuating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):311.
[33] LI X, WANG Y, AN G, et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells attenuate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis via paracrine mechanisms. Toxicol Lett. 2017;270:96-107.
[34] MANSOURI N, WILLIS GR, FERNANDEZ-GONZALEZ A, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cell exosomes prevent and revert experimental pulmonary fibrosis through modulation of monocyte phenotypes. JCI Insight. 2019;4(21):e128060.
[35] CHEN S, CUI G, PENG C, et al. Transplantation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells attenuates pulmonary fibrosis of silicosis via anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptosis effects in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):110.
[36] Wei J, Zhao Q, Yang G, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibition of inflammation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Cell Mol Med. 2021;25(13):6417-6428.
[37] XIE L, ZENG Y. Therapeutic potential of exosomes in pulmonary fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:590972.
[38] ZHUANG WZ, LIN YH, SU LJ, et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapy: mechanism, systemic safety and biodistribution for precision clinical applications. J Biomed Sci. 2021;28(1):28.
[39] XU C, ZHAO J, LI Q, et al. Exosomes derived from three-dimensional cultured human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate pulmonary fibrosis in a mouse silicosis model. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):503.
[40] Cao H, Wang C, Chen X, et al. Inhibition of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling suppresses myofibroblast differentiation of lung resident mesenchymal stem cells and pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):13644.
[41] Li X, An G, Wang Y, et al. Targeted migration of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibits silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):335.
[42] DINH PC, PAUDEL D, BROCHU H, et al. Inhalation of lung spheroid cell secretome and exosomes promotes lung repair in pulmonary fibrosis. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):1064.
[43] ZHOU J, LIN Y, KANG X, et al. microRNA-186 in extracellular vesicles from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells alleviates idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis via interaction with SOX4 and DKK1. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021;12(1):96.
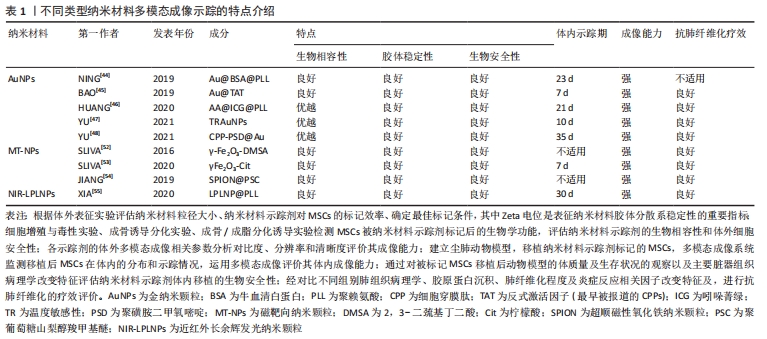
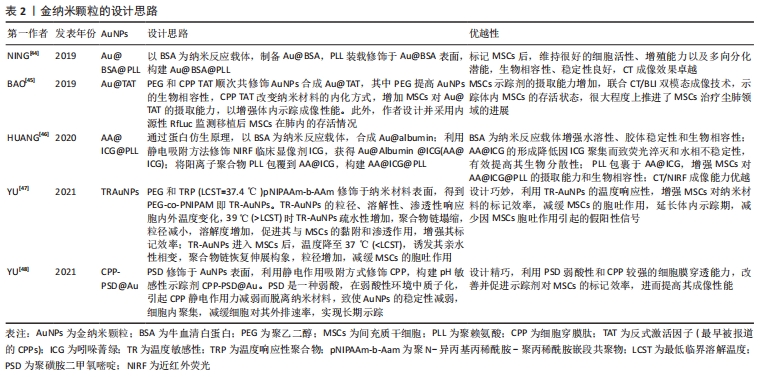
[44] NING X, BAO H, LIU X, et al. Long-term in vivo CT tracking of mesenchymal stem cells labeled with Au@BSA@PLL nanotracers. Nanoscale. 2019;11(43):20932-20941.
[45] BAO H, XIA Y, YU C, et al. CT/Bioluminescence Dual-Modal Imaging Tracking of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Small. 2019;15(46):e1904314.
[46] HUANG J, HUANG J, NING X, et al. CT/NIRF dual-modal imaging tracking and therapeutic efficacy of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells labeled with Au nanoparticles in silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(8):1713-1727.
[47] YU C, BAO H, CHEN Z, et al. Enhanced and long-term CT imaging tracking of transplanted stem cells labeled with temperature-responsive gold nanoparticles. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(12):2854-2865.
[48] YU C, CHEN Z, LI X, et al. pH-triggered aggregation of gold nanoparticles for enhanced labeling and long-term CT imaging tracking of stem cells in pulmonary fibrosis treatment. Small. 2021;17(33):e2101861.
[49] LI W, CAO Z, LIU R, et al. AuNPs as an important inorganic nanoparticle applied in drug carrier systems. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2019; 47(1):4222-4233.
[50] DAS P, FATEHBASHARZAD P, COLOMBO M, et al. Multifunctional Magnetic Gold Nanomaterials for Cancer. Trends Biotechnol. 2019; 37(9):995-1010.
[51] MA Y, HUANG J, SONG S, et al. Cancer-targeted nanotheranostics: recent advances and perspectives. Small. 2016;12(36):4936-4954.
[52] SILVA LH, DA SILVA JR, FERREIRA GA, et al. Labeling mesenchymal cells with DMSA-coated gold and iron oxide nanoparticles: assessment of biocompatibility and potential applications. J Nanobiotechnology. 2016;14(1):59.
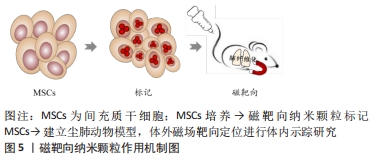
[53] SILVA LHA, SILVA MC, VIEIRA JB, et al. Magnetic targeting increases mesenchymal stromal cell retention in lungs and enhances beneficial effects on pulmonary damage in experimental silicosis. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2020;9(10):1244-1256.
[54] JIANG R, LIAO Y, YANG F, et al. SPIO nanoparticle-labeled bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit pulmonary EndoMT induced by SiO2. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(1):111492.
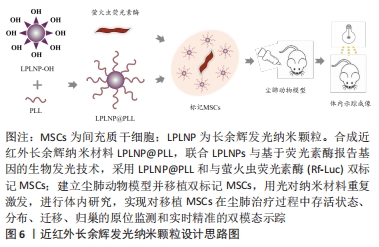
[55] XIA Y, BAO H, HUANG J, et al. Near-infrared-persistent luminescence/bioluminescence imaging tracking of transplanted mesenchymal stem cells in pulmonary fibrosis. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(11):3095-3105.
[56] TASSALI N, BIANCHI A, LUX F, et al. MR imaging, targeting and characterization of pulmonary fibrosis using intra-tracheal administration of gadolinium-based nanoparticles. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 2016;11(5):396-404.
[57] WANG J, SUN Y, TIAN X. The inhibitory effect of icariin nanoparticles on angiogenesis in pulmonary fibrosis. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2021; 21(11):5429-5435.
[58] SAGHIR SAM, AL-GABRI NA, KHAFAGA AF, et al. Thymoquinone-PLGA-PVA nanoparticles ameliorate bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats via regulation of inflammatory cytokines and iNOS signaling. Animals (Basel). 2019;9(11):951.
[59] PANDOLFI L, Frangipane V, BOCCA C, et al. Hyaluronic acid-decorated liposomes as innovative targeted delivery system for lung fibrotic cells. Molecules. 2019;24(18):3291.
[60] ABNOOS M, MOHSENI M, MOUSAVI SAJ, et al. Chitosan-alginate nano-carrier for transdermal delivery of pirfenidone in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Biol Macromol. 2018;118(Pt A):1319-1325.
|