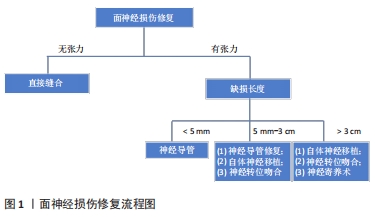
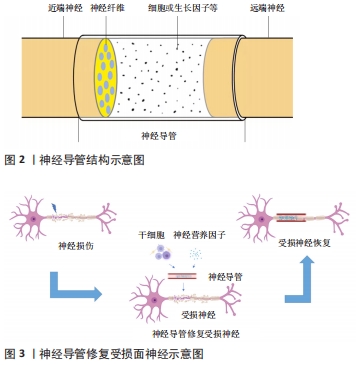
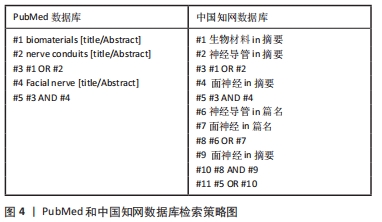
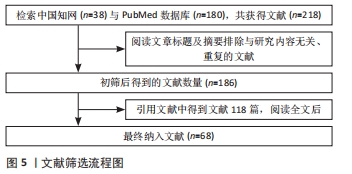
[1] GAUDIN R, KNIPFER C, HENNINGSEN A, et al. Approaches to peripheral nerve repair: generations of biomaterial conduits yielding to replacing autologous nerve grafts in craniomaxillofacial surgery. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:3856262.
[2] SUN Y, LIU L, HAN Y, et al. The role of great auricular-facial nerve neurorrhaphy in facial nerve damage. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(8): 12970-12976.
[3] CHRZASZCZ P, DERBISZ K, SUSZYNSKI K, et al. Application of peripheral nerve conduits in clinical practice: a literature review. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2018;52(4):427-435.
[4] JANDALI D, REVENAUGH PC. Facial reanimation:an update on nerve transfers in facial paralysis. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;27(4):231-236.
[5] 李煜,於子卫.神经干细胞与许旺细胞联合应用于神经损伤修复的研究进展[J].临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志,2014,28(13):1006-1009.
[6] LI X, YANG W, XIE H, et al. CNT/sericin conductive nerve guidance conduit promotes functional recovery of transected peripheral nerve injury in a rat model. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2020;12(33):36860-36872.
[7] WANG J, CHENG Y, WANG H, et al. Biomimetic and hierarchical nerve conduits from multifunctional nanofibers for guided peripheral nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;117:180-191.
[8] BENGUR FB, STOY C, BINKO MA, et al. Facial nerve repair: bioengineering approaches in preclinical models. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2022;28(2):364-378.
[9] HU A, ZUO B, ZHANG F, et al. Evaluation of electronspun silk fibroin-based transplants used for facial nerve repair. Otol Neurotol. 2013; 34(2):311-318.
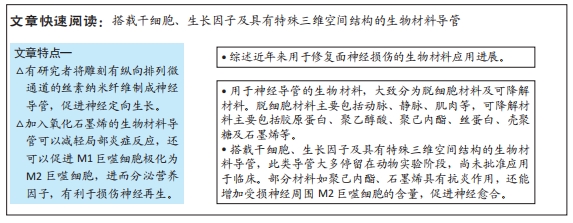
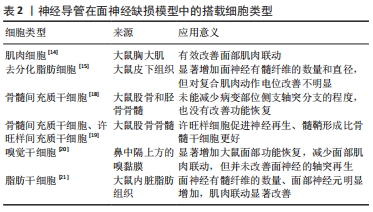
[10] LIU H, WEN W, HU M, et al. Chitosan conduits combined with nerve growth factor microspheres repair facial nerve defects. Neural Regen Res. 2013;8(33):3139-3147.
[11] KAYA Y, OZSOY U, TURHAN M, et al. Hypoglossal-facial nerve reconstruction using a Y-tube-conduit reduces aberrant synkinetic movements of the orbicularis oculi and vibrissal muscles in rats. Biomed Res Int. 2014. doi:10.1155/2014/543020.
[12] JANG CH, LEE H, KIM M, et al. Effect of polycaprolactone/collagen/hUCS microfiber nerve conduit on facial nerve regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;93(Pt B):1575-1582.
[13] MA F, XU F, LI R, et al. Sustained delivery of glial cell-derived neurotrophic factors in collagen conduits for facial nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2018;69:146-155.
[14] LIU H, HUANG H, BI W, et al. Effect of chitosan combined with hyaluronate on promoting the recovery of postoperative facial nerve regeneration and function in rabbits. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(2):739-745.
[15] FUJIMAKI H, MATSUMINE H, OSAKI H, et al. Corrigendum to “Dedifferentiated fat cells in polyglycolic acid-collagen nerve conduits promote rat facial nerve regeneration” [Regen Ther 11 (2019) 240-248]. Regen Ther. 2020;15:35-43.
[16] MANTHOU ME, GENCHEVA D, SINIS N, et al. Facial nerve repair by muscle-vein conduit in rats:functional recovery and muscle reinnervation. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(5-6):351-361.
[17] AGHAJANIAN S, TAGHI DOULABI A, AKHBARI M, et al. Facial nerve regeneration using silicone conduits filled with ammonia-functionalized graphene oxide and frankincense-embedded hydrogel. Inflamm Regen. 2021;41(1):13.
[18] GROSHEVA M, GUNTINAS-LICHIUS O, ARNHOLD S, et al. Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation does not improve quality of muscle reinnervation or recovery of motor function after facial nerve transection in rats. Biol Chem. 2008;389(7):873-888.
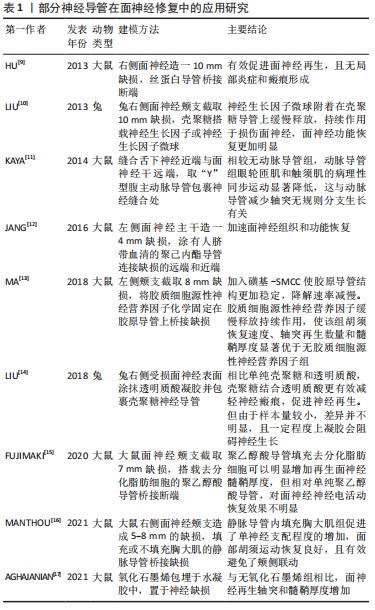
[19] COSTA HJ, BENTO RF, SALOMONE R, et al. Mesenchymal bone marrow stem cells within polyglycolic acid tube observed in vivo after six weeks enhance facial nerve regeneration. Brain Res. 2013;1510:10-21.
[20] BENSE F, MONTAVA M, DUCLOS C, et al. Syngeneic transplantation of rat olfactory stem cells in a vein conduit improves facial movements and reduces synkinesis after facial nerve injury. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2020;146(6):1295-1305.
[21] SUN F, ZHOU K, MI WJ, et al. Repair of facial nerve defects with decellularized artery allografts containing autologous adipose-derived stem cells in a rat model. Neurosci Lett. 2011;499(2):104-108.
[22] WANG P, ZHAO H, YAO Y, et al. Repair of facial nerve crush injury in rabbits using collagen plus basic fibroblast growth factor. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2020;108(6):1329-1337.
[23] CHAO X, XU L, LI J, et al. Facilitation of facial nerve regeneration using chitosan-beta-glycerophosphate-nerve growth factor hydrogel. Acta Otolaryngol. 2016;136(6):585-591.
[24] SERPE CJ, BYRAM SC, SANDERS VM, et al. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor supports facial motoneuron survival after facial nerve transection in immunodeficient mice. Brain Behav Immun. 2005;19(2):173-180.
[25] SAHIN MM, CAYONU M, DINC SK, et al. Effects of chitosan and platelet-rich plasma on facial nerve regeneration in an animal model. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2022;279(2):987-994.
[26] 杨美蓉,潘博,赵博.整形外科的脱细胞基质材料:研究进展和临床应用的有机结合[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(26):4259-4264.
[27] BENDELLA H, RINK S, MANTHOU M, et al. Effect of surgically guided axonal regrowth into a 3-way-conduit (isogeneic trifurcated aorta) on functional recovery after facial-nerve reconstruction: experimental study in rats. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2019;37(2):181-196.
[28] OZSOY U, DEMIREL BM, HIZAY A, et al. Hypoglossal-facial anastomosis (HFA) over a 10 mm gap bridged by a Y-tube-conduit enhances neurite regrowth and reduces collateral axonal branching at the lesion site. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 2011;29(4):227-242.
[29] MARCOCCIO I, VIGASIO A. Muscle-in-vein nerve guide for secondary reconstruction in digital nerve lesions. J Hand Surg Am. 2010;35(9): 1418-1426.
[30] TSENG CY, HU G, AMBRON RE, et al. Histologic analysis of Schwann cell migration and peripheral nerve regeneration in the autogenous venous nerve conduit (AVNC). J Reconstr Microsurg. 2003;19(5):331-340.
[31] WANG KK, COSTAS PD, BRYAN DJ, et al. Inside-out vein graft repair compared with nerve grafting for nerve regeneration in rats. Microsurgery. 1995;16(2):65-70.
[32] PAPROTTKA FJ, WOLF P, HARDER Y, et al. Sensory recovery outcome after digital nerve repair in relation to different reconstructive techniques:meta-analysis and systematic review. Plast Surg Int. 2013.doi:10.1155/2013/704589.
[33] CHEN P, KNOX CJ, YAO L, et al. The effects of venous ensheathment on facial nerve repair in the rat. Laryngoscope. 2017;127(7):1558-1564.
[34] SABONGI RG, FERNANDES M, DOS SANTOS JB. Peripheral nerve regeneration with conduits:use of vein tubes. Neural Regen Res. 2015; 10(4):529-533.
[35] BATIOGLU-KARAALTIN A, KARAALTIN MV, OZTEL ON, et al. Human olfactory stem cells for injured facial nerve reconstruction in a rat model. Head Neck. 2016;38 Suppl 1:E2011-E2020.
[36] Han GH, Peng J, Liu P, et al. Therapeutic strategies for peripheral nerve injury: decellularized nerve conduits and Schwann cell transplantation. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(8):1343-1351.
[37] WANG X, LUO E, LI Y. Schwann-like mesenchymal stem cells within vein graft facilitate facial nerve regeneration and remyelination. Brain Res. 2011;1383:71-80.
[38] FAWCELTT JW, KEYNES RJ. Muscle basal lamina: a new graft material for peripheral nerve repair. J Neurosurg. 1986;65(3):354-363.
[39] 周振宇,蔡锦方.构建肌肉组织床修复股神经长段缺损两例[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2020,34(10):1352-1353.
[40] 陈勇,范林,付贞,等.神经导管支架修复外周神经损伤的研究与现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(30):4901-4907.
[41] YAO L, BILLIAR KL, WINDEBANK AJ, et al. Multichanneled collagen conduits for peripheral nerve regeneration: design, fabrication, and characterization. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(6):1585-1596.
[42] KITAHARA AK, NISHIMURA Y, SHIMIZU Y, et al. Facial nerve repair accomplished by the interposition of a collagen nerve guide. J Neurosurg. 2000;93(1):113-120.
[43] MA F, WANG H, YANG X, et al. Controlled release of ciliary neurotrophic factor from bioactive nerve grafts promotes nerve regeneration in rats with facial nerve injuries. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2022;110(4):788-796.
[44] MA F, ZHU T, XU F, et al. Neural stem/progenitor cells on collagen with anchored basic fibroblast growth factor as potential natural nerve conduits for facial nerve regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2017;50:188-197.
[45] LONG Q, WU B, YANG Y, et al. Nerve guidance conduit promoted peripheral nerve regeneration in rats. Artif Organs. 2021;45(6):616-624.
[46] WATANABE Y, SASAKI R, MATSULMINE H, et al. Undifferentiated and differentiated adipose-derived stem cells improve nerve regeneration in a rat model of facial nerve defect. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2017; 11(2):362-374.
[47] NAVISSANO M, MALAN F, CARNINO R, et al. Neurotube for facial nerve repair. Microsurgery. 2005;25(4):268-271.
[48] ZUKKAWA M, OSADA R, KIMURA T. Clinical outcome and ultrasonographic evaluation of treatment using polyglycolic acid-collagen tube for chronic neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Orthop Sci. 2019;24(6):1064-1067.
[49] NAKAMURA Y, TAKANARI K, EBISAWA K, et al. Repair of temporal branch of the facial nerve with novel polyglycolic acid-collagen tube:a case report of two cases. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2020;82(1):123-128.
[50] WAITAYAWINYU T, PARISI DM, MILLER B, et al. A comparison of polyglycolic acid versus type 1 collagen bioabsorbable nerve conduits in a rat model: an alternative to autografting. J Hand Surg Am. 2007; 32(10):1521-1529.
[51] MOHAMADI F, EBRAHIMI-BAROUGH S, REZA NOURANI M, et al. Electrospun nerve guide scaffold of poly (epsilon-caprolactone)/collagen/nanobioglass:an in vitro study in peripheral nerve tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(7):1960-1972.
[52] LOPEZ J, XIN K, QUAN A, et al. Poly (epsilon-caprolactone) nanofiber wrap improves nerve regeneration and functional outcomes after delayed nerve repair. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;144(1):48e-57e.
[53] SUN B, ZHOU Z, LI D, et al. Polypyrrole-coated poly (l-lactic acid-co-epsilon-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofibrous nerve guidance conduit induced nerve regeneration in rat. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;94:190-199.
[54] ASSAF K, LEAL CV, DERAMI MS, et al. Sciatic nerve repair using poly (epsilon-caprolactone) tubular prosthesis associated with nanoparticles of carbon and graphene. Brain Behav. 2017;7(8):e00755.
[55] SARHANE KA, IBRAHIM Z, MARTIN R, et al. Macroporous nanofiber wraps promote axonal regeneration and functional recovery in nerve repair by limiting fibrosis. Acta Biomater. 2019;88:332-345.
[56] GALLA TJ, VEDECNIK SV, HALBGEWACHS J, et al. Fibrin/Schwann cell matrix in poly-epsilon-caprolactone conduits enhances guided nerve regeneration. Int J Artif Organs. 2004;27(2):127-136.
[57] KUIHUA Z, CHUNYANG W, CUNYI F, et al. Aligned SF/P(LLA-CL)-blended nanofibers encapsulating nerve growth factor for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(8):2680-2691.
[58] WANG C, JIA Y, YANG W, et al. Silk fibroin enhances peripheral nerve regeneration by improving vascularization within nerve conduits. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(7):2070-2077.
[59] LI X,ZHANG Q, LUO Z, et al. Biofunctionalized silk fibroin nanofibers for directional and long neurite outgrowth. Biointerphases. 2019; 14(6):061001.
[60] NUNE M, MANCHINEELLA S, GOVINDARAJU T, et al. Melanin incorporated electroactive and antioxidant silk fibroin nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;94:17-25.
[61] HE B, WU F, FAN L, et al. Carboxymethylated chitosan protects Schwann cells against hydrogen peroxide-induced apoptosis by inhibiting oxidative stress and mitochondria dependent pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018;825:48-56.
[62] ZHAO Y, WANG Y, GONG J, et al. Chitosan degradation products facilitate peripheral nerve regeneration by improving macrophage-constructed microenvironments. Biomaterials. 2017;134:64-77.
[63] GAUDET AD, POPOVICH PG, RAMER MS. Wallerian degeneration:gaining perspective on inflammatory events after peripheral nerve injury. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:110.
[64] MANOUKIAN OS, RUDRAIAH S, ARUL MR, et al. Biopolymer-nanotube nerve guidance conduit drug delivery for peripheral nerve regeneration: in vivo structural and functional assessment. Bioact Mater. 2021;6(9):2881-2893.
[65] SOLANKI A, CHUENG ST, YIN PT, et al. Axonal alignment and enhanced neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells on graphene-nanoparticle hybrid structures. Adv Mater. 2013;25(38):5477-5482.
[66] FANG X, GUO H, ZHANG W, et al. Reduced graphene oxide-GelMA-PCL hybrid nanofibers for peripheral nerve regeneration. J Mater Chem B. 2020;8(46):10593-10601.
[67] HAN J, KIM YS, LIM MY, et al. Dual roles of graphene oxide to attenuate inflammation and elicit timely polarization of macrophage phenotypes for cardiac repair. ACS Nano. 2018;12(2):1959-1977.
[68] MOKARRAM N,DYMANUS K, SRINIVASAN A, et al. Immunoengineering nerve repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(26):E5077-E5084.
|