中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (1): 72-75.doi: 10.12307/2022.989
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
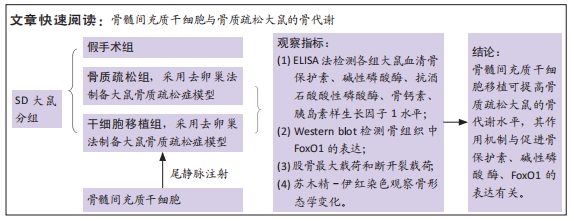
骨髓间充质干细胞移植可提高骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢水平
冯 皓1,张 斌2,王建平1
- 1鹰潭市人民医院,江西省鹰潭市 335000;2南昌大学第一附属医院,江西省南昌市 330000
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell transplantation can improve bone metabolism in osteoporotic rats
Feng Hao1, Zhang Bin2, Wang Jianping1
- 1Yingtan City People’s Hospital, Yingtan 335000, Jiangxi Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Nanchang University, Nanchang 330000, Jiangxi Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
骨髓间充质干细胞:是在动物的骨髓基质中发现的一种具有分化形成骨、软骨、脂肪、神经及成肌细胞多种分化潜能的细胞亚群,对骨髓中的造血干细胞具有机械支持作用,还可分泌多种生长因子来支持造血,骨髓间充质干细胞还具有修复骨、软骨、关节损伤、心脏损伤、肝脏损伤、脊髓损伤和神经系统疾病的作用。
骨代谢:人体正常的骨代谢过程是骨组织不断进行改建活动的一个复杂过程,包括骨吸收和骨形成2个方面。在骨代谢过程中,每天都有一定量的骨组织被吸收,又有相当数量的骨组织合成,两者保持着动态的平衡,当骨吸收大于骨形成时,可出现骨丢失,发生骨质疏松、骨软化等;当骨形成而无相应的骨吸收时,则可出现骨质硬化。
背景:研究证实骨髓间充质干细胞具有增加骨保护素水平、促进骨代谢的作用。
目的:探讨骨髓间充质干细胞对骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢的影响。
方法:实验所用健康SD大鼠42只,随机分为假手术组、骨质疏松组、干细胞移植组,每组14只,后2组采用去卵巢法制备大鼠骨质疏松症模型,造模成功后干细胞移植组经尾静脉移植骨髓间充质干细胞,移植28 d后采用ELISA法检测各组大鼠血清骨保护素、碱性磷酸酶、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、骨钙素、胰岛素样生长因子1水平;Western blot检测各组大鼠骨组织中FoxO1的表达;AG-IX生物力学万能试验机检测股骨最大载荷和断开裂载荷;苏木精-伊红染色观察大鼠骨形态学改变。
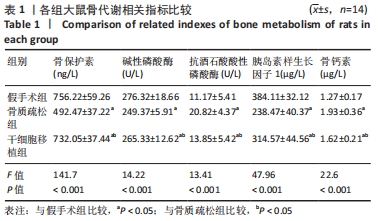
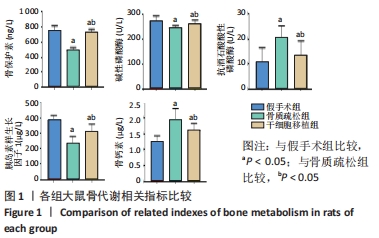
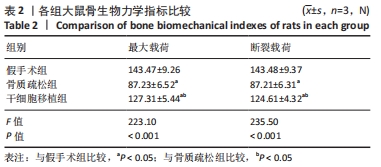
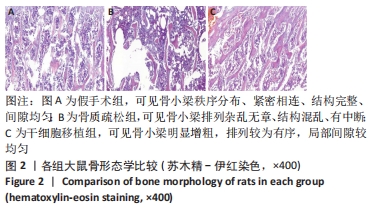
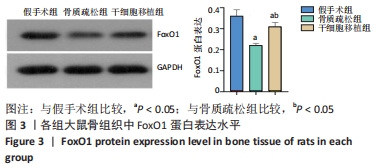
结果与结论:①骨质疏松组骨保护素、碱性磷酸酶、胰岛素样生长因子1水平低于假手术组(P < 0.05),抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、骨钙素水平高于假手术组(P < 0.05);干细胞移植组骨保护素、碱性磷酸酶、胰岛素样生长因子1水平高于骨质疏松组(P < 0.05),抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶、骨钙素的表达水平低于骨质疏松组(P < 0.05);②骨质疏松组最大载荷、断裂载荷值均低于假手术组(P < 0.05);干细胞移植组最大载荷、断裂载荷值高于骨质疏松组(P < 0.05);③干细胞移植组骨小梁明显增粗,排列较为有序,局部间隙较均匀,较骨质疏松组明显改善;④骨质疏松组大鼠骨髓组织中FoxO1蛋白表达水平低于假手术组(P < 0.05);干细胞移植组大鼠骨髓组织中FoxO1蛋白表达水平高于骨质疏松组(P < 0.05);⑤结果表明,骨髓间充质干细胞移植可提高骨质疏松大鼠骨代谢水平,其作用机制与促进骨保护素、碱性磷酸酶、FoxO1的表达有关。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8571-1183 (冯皓)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
中图分类号: