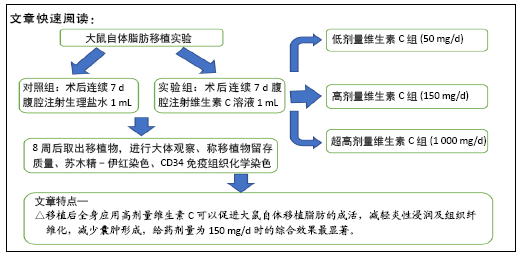
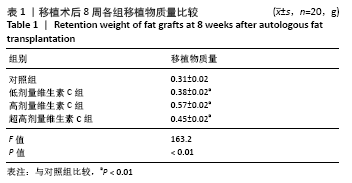
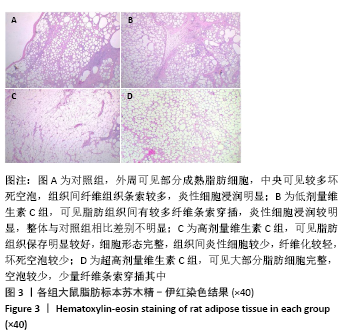
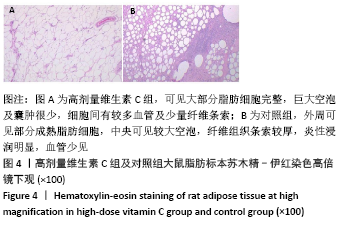
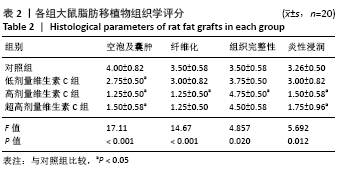
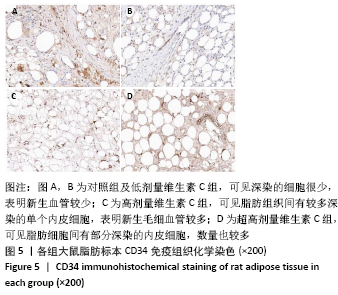
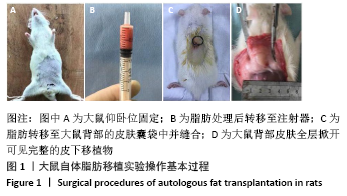
[1] LEE SS, HUANG YH, LIN TY, et al. Long-Term Outcome of Microautologous Fat Transplantation to Correct Temporal Depression. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(3):629-634.
[2] LINDENBLATT N, VAN HULLE A, VERPAELE AM, et al. The Role of Microfat Grafting in Facial Contouring. Aesthet Surg J. 2015;35(7):763-771.
[3] 吴亮亮,马莉,蒋思静,等.还原型谷胱甘肽对兔自体脂肪移植存活的影响[J].中华整形外科杂志,2019,35(9):928-933.
[4] CARITÁ AC, FONSECA-SANTOS B, SHULTZ JD, et al. Vitamin C: One compound, several uses. Advances for delivery, efficiency and stability. Nanomedicine. 2020;24:102117.
[5] WANG K, JIANG H, LI W, et al. Role of Vitamin C in Skin Diseases. Front Physiol. 2018;9:819.
[6] SPOELSTRA-DE MAN AME, ELBERS PWG, OUDEMANS-VAN STRAATEN HM. Making sense of early high-dose intravenous vitamin C in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Crit Care. 2018;22(1):70.
[7] YI CG, XIA W, ZHANG LX, et al. VEGF gene therapy for the survival of transplanted fat tissue in nude mice. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007;60(3):272-278.
[8] DEL VECCHIO D, WALL S JR. Expansion Vibration Lipofilling: A New Technique in Large-Volume Fat Transplantation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;141(5):639e-649e.
[9] IMPIERI D, TØNSETH KA, HIDE Ø, et al. Autologous fat transplantation to the velopharynx for treating mild velopharyngeal insufficiency: A 10-year experience. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2019;72(8):1403-1410.
[10] STROUMZA N, FUZCO G, LAPORTE J, et al. Surgical treatment of trans-sphincteric anal fistulas with the Fat GRAFT technique: a minimally invasive procedure. Colorectal Dis. 2017;19(8):e316-e319.
[11] NEUBER G. Fat transplantation. Verh Dtsch Ges Chi. 1893;22:66.
[12] ZHANG Y, CAI J, ZHOU T, et al. Improved Long-Term Volume Retention of Stromal Vascular Fraction Gel Grafting with Enhanced Angiogenesis and Adipogenesis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018;141(5):676e-686e.
[13] KRASTEV TK, BEUGELS J, HOMMES J, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Autologous Fat Transfer in Facial Reconstructive Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Facial Plast Surg. 2018;20(5):351-360.
[14] XU X, LAI L, ZHANG X, et al. Autologous chyle fat grafting for the treatment of hypertrophic scars and scar-related conditions. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):64.
[15] FUKUBA M, UOZAKI H, KOMURO Y. Effectiveness of the combination of fat grafting and injection on radiation ulcer healing. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2020;54(1):24-28.
[16] CERNY MK, MOOG P, BAUER AT, et al. Lipofilling of Fingertips for Volume Defects after Fingertip Injuries. Ann Plast Surg. 2018;81(6):653-656.
[17] SMITH P, ADAMS WP JR, LIPSCHITZ AH, et al. Autologous human fat grafting: effect of harvesting and preparation techniques on adipocyte graft survival. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;117(6):1836-1844.
[18] KAUFMAN MR, BRADLEY JP, DICKINSON B, et al. Autologous fat transfer national consensus survey: trends in techniques for harvest, preparation, and application, and perception of short- and long-term results. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007;119(1):323-331.
[19] ROSE JG JR, LUCARELLI MJ, LEMKE BN, et al. Histologic comparison of autologous fat processing methods. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006;22(3):195-200.
[20] YANG M, ZHANG F, SAILES FC, et al. Role of anti-TNF-α therapy in fat graft preservation. Ann Plast Surg. 2012;68(5):531-535.
[21] ETO H, KATO H, SUGA H, et al. The fate of adipocytes after nonvascularized fat grafting: evidence of early death and replacement of adipocytes. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012;129(5):1081-1092.
[22] GILLIS J, GEBREMESKEL S, PHIPPS KD, et al. Effect of N-Acetylcysteine on Adipose-Derived Stem Cell and Autologous Fat Graft Survival in a Mouse Model. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2015;136(2):179e-188e.
[23] BODANNES RS, CHAN PC. Ascorbic acid as a scavenger of singlet oxygen. FEBS Lett. 1979;105(2):195-196.
[24] BIELSKI BH, RICHTER HW, CHAN PC. Some properties of the ascorbate free radical. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975;258:231-237.
[25] NISHIKIMI M. Oxidation of ascorbic acid with superoxide anion generated by the xanthine-xanthine oxidase system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975;63(2): 463-468.
[26] MAY JM, HARRISON FE. Role of vitamin C in the function of the vascular endothelium. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2013;19(17):2068-2083.
[27] SRIRAM S, YUAN C, CHAKRABORTY S, et al. Oxidative stress mediates depot-specific functional differences of human adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):141.
[28] 庄合林,林亚秋.维生素C通过调控脂肪形成相关基因的转录促进猪前体脂肪细胞的增殖与分化[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2007,23(6):499-517.
[29] KAHN SA, BEERS RJ, LENTZ CW. Resuscitation after severe burn injury using high-dose ascorbic acid: a retrospective review. J Burn Care Res. 2011;32(1):110-117.
[30] WANG Y, LIN H, LIN BW, et al. Effects of different ascorbic acid doses on the mortality of critically ill patients: a meta-analysis. Ann Intensive Care. 2019;9(1):58.
[31] OUDEMANS-VAN STRAATEN HM, SPOELSTRA-DE MAN AM, de Waard MC. Vitamin C revisited. Crit Care. 2014;18(4):460. |