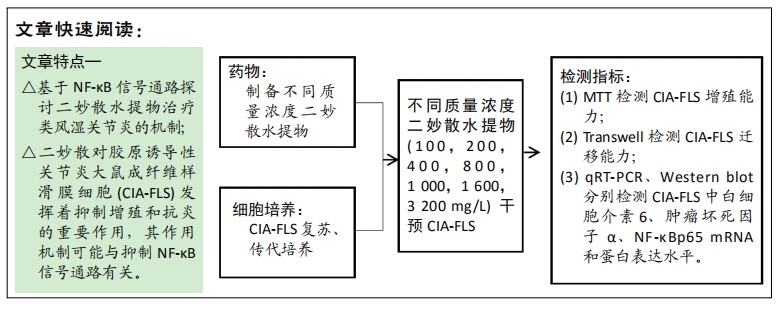
1.1 设计 细胞学体外实验,单因素方差分析。
1.2 时间及地点 实验于2020 年4至11月在山西中医药大学中西医结合基础细胞实验室完成。
1.3 材料
1.3.1 化学品与试剂 胎牛血清(Hyclone,Cat. No. SV30087.02);DMEM高糖培养基(Gibco,Cat. No. C11995500BT);噻唑蓝(Amresco,Cat. No. 0793);双抗(青霉素/链霉素,Hyclone,Cat. No. SV30010);0.25%胰蛋白酶(Hyclone,Cat. No. SH30042.01);RNAiso Plus(TakaRa,Cat. No. 9108Q);One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuPerMix (北京全式金,Cat. No. AT311);ToP Green qPCR SuPerMix (北京全式金,Cat. No. AQ131);Rabbit-Anti-NFκBp65 Polyclonal Antibody(Bioss,Cat. No. bs-0465R);Anti-β-Actin Monoclonal antibody(Solarbio,Cat. No. K200058M);Goat Anti-rabbit IgG/HRP antibody(Solarbio,Cat. No. SE134);RIPA裂解液(碧云天,Cat. No. P0013B);PMSF(碧云天,Cat. No. ST506);BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(Solarbio,Cat. No. PC0020);ECL Plus超敏发光液(Solarbio,Cat. No. PE0010)。
1.3.2 实验细胞和药物 CIA-FLS系由山西中医药大学中西医结合基础实验室提供。苍术(Cat. No. 171201 )、黄柏(Cat. No. 170901)购自安徽谓博与精诚中药饮片公司。
1.4 实验方法
1.4.1 二妙散水提物制备 准确称取中药苍术、黄柏各 100 g,以2 000 mL蒸馏水煎煮1 h,纱布过滤去除沉渣,加入1 000 mL蒸馏水再煎 20 min,浓缩成1 g/mL的母液, 0.22 µm微孔滤膜过滤灭菌,-20 ℃保存备用。配置二妙散水提物终质量浓度分别为 100,200,400,800,1 000, 1 600,3 200 mg/L的DMEM完全培养基。
1.4.2 实验分组 实验CIA-FLS分为空白对照组(只含细胞和不含二妙散水提物的DMEM完全培养基)和不同质量浓度二妙散水提物干预组(分别加入终质量浓度为100,200,400,800,1 000,1 600, 3 200 mg/L二妙散水提物的DMEM完全培养基)。
1.4.3 CIA-FLS 复苏及传代培养 15 mL离心管中加入5 mL DMEM完全培养基(含1%双抗,青霉素、链霉素各100 U/mL
及体积分数为10%胎牛血清的DMEM培养基),37 ℃水浴
5 min,取出冻存的CIA-FLS细胞系,待细胞完全融化后,放入含DMEM完全培养基的离心管中,1 500 r/min离心1 min,弃上清,加入DMEM完全培养基重悬,离心去除冻存保护剂二甲基亚砜,重复离心2次,加入DMEM完全培养基,放入 37 ℃体积分数为5%CO2培养箱培养,两三天换液1次,待细胞80%-90%融合时,加入0.25%胰酶消化一两分钟,当细胞边缘缩小、贴壁松动时去除胰酶,加3.0-4.0 mL DMEM完全培养基,以1∶3比例接种于新的培养瓶中,待细胞密度达到80%-90%以后重复上述步骤进行操作,传至4-8代用于后续实验。
1.4.4 MTT法检测不同质量浓度二妙散水提物对CIA-FLS活力的影响 当第5代CIA-FLS密度达到80%-90%融合后,进行消化、计数,按1×104个/孔细胞铺在96孔板中,放入 37 ℃体积分数为5%CO2培养箱培养12 h,加入含终质量浓度分别为 100,200,400,800,1 000,1 600,3 200 mg/L二妙散水提物的DMEM完全培养基,设CIA-FLS空白对照组,每组3个重复。培养 48 h 后,每孔加入 5 g/L MTT溶液10 μL,培养4 h,去除培养基,每孔加入100 μL二甲基亚砜,振荡 10 min,酶标仪测定490 nm波长各孔吸光度值,按以下公式计算相对增殖率。相对增殖率(%)= ×100% (A为实验组吸光度值、A0为空白对照组吸光度值)。
1.4.5 Transwell小室检测不同质量浓度二妙散水提物对 CIA-FLS迁移的影响 当第5代CIA-FLS密度达到80%-90%融合后,进行消化、计数,按 1×104个/孔细胞接种至6孔板,放入37 ℃体积分数为5%CO2培养箱培养24 h,加入含终质量浓度分别为 200,400,800,1 600,3 200 mg/L二妙散水提物的DMEM完全培养基,干预48 h。将600 μL含体积分数为15%胎牛血清的DMEM完全培养基添加到24孔培养板,将transwell小室置于孔中,吸取6孔板中的CIA-FLS悬液,加入至小室上层,在37 ℃体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中培养 48 h,用棉签轻轻在小室上层转动,擦掉小室上层的细胞,把小室转移到另外一块24孔板,加入40 g/L多聚甲醛,室温固定15 min,PBS洗涤3次,0.1%结晶紫染色transwell小室下层细胞10 min,自来水洗涤,去除浮色,显微镜下拍照。
1.4.6 不同质量浓度二妙散水提物干预组CIA-FLS总RNA提取及cDNA合成 当第5代CIA-FLS密度达到80%-90%融合后,进行消化、计数,按1×104个/孔接种至6孔板,在 37 ℃体积分数为5%CO2培养箱中培养24 h后添加含终质量浓度为200,400,800,1 600,3 200 mg/L二妙散水提物的DMEM完全培养基,继续培养48 h,收集细胞。按照RNAiso Plus操作说明,提取各组细胞总RNA,核酸蛋白测定仪测定总RNA浓度和纯度,RNA浓度调至1.0 g/L,-80 ℃保存。按照反转录试剂盒合成cDNA,反转录体系(20 μL):RNA 7.0 μL、Random Primer 1.0 μL、2×TS Reactin Mix 10.0 μL、RT/RI Enzyme Mix 1.0 μL、gDNA Remover 1.0 μL,42 ℃ 60 min,85 ℃ 5 s,反转录产物-20 ℃保存。
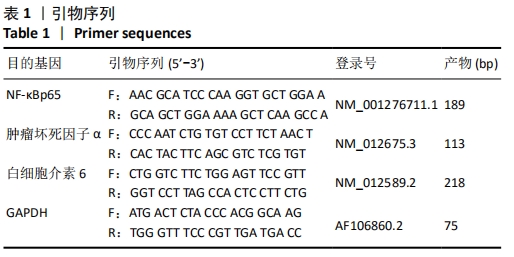
1.4.7 引物设计、合成与PCR检测 GenBank查阅大鼠白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、NF-κBp65和GAPDH cDNA序列,利用Primer 5.0软件分别设计4对特异性引物,由上海生工生物有限公司合成引物序列,见表1。15 μL PCR反应体系:正反向引物各0.6 μL、cDNA模板0.8 μL、ddH2O 5.5 μL、2×M5 HiPerTaq PCR mix 7.5 μL。反应条件:94 ℃ 3 min,94 ℃ 30 s、60 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 30 s,30个循环;72 ℃ 5 min,2.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测,割胶回收,测序。
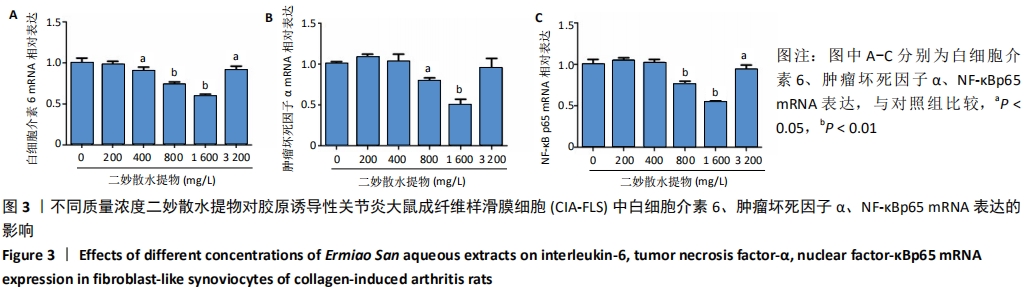
1.4.8 qRT-PCR 检测CIA-FLS中白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、NF-κBp65 mRNA水平 反应体系为:Nuclease-free Water
7.0 μL、SybrGreen qPCR Master Mix 10.0 μL、Forward Primer(10 μmol/L)0.5 μL、Reverse Primer(10 μmol/L) 0.5 μL、cDNA TemPlate 2.0 μL,总体积为20 μL,充分混匀。反应程序为:95 ℃ 30 s;95 ℃ 5 s,60 ℃ 35 s,40个循环;97 ℃ 30 s, 65 ℃ 1 min,97 ℃ 10 s,1个循环。实时荧光定量 PCR仪自动分析结果,每个样本重复3次,2-ΔΔCT 法计算相对表达量。
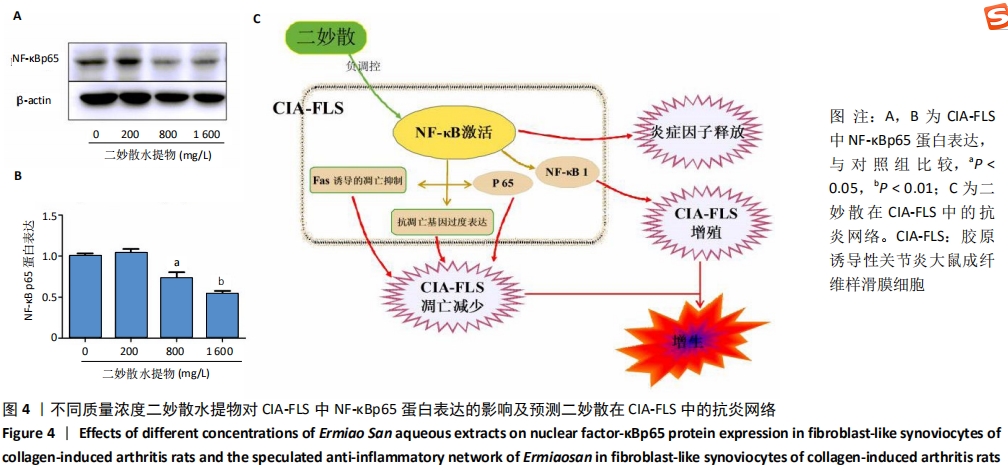
1.4.9 Western blot 检测不同质量浓度二妙散水提物干预下CIA-FLS中NF-κBp65 蛋白表达 根据组织蛋白抽提剂说明书提取蛋白,BCA 蛋白浓度测定试剂盒进行蛋白浓度检测,调平蛋白样品至合适的浓度,100 ℃加热10 min进行蛋白变性,冰上放置5-10 min,-20 ℃储藏。采用4.0%的浓缩胶和11%的分离胶十二烷基硫酸钠-聚丙烯酰胺凝胶(SDS-PAGE)电泳,80 V 30 min,120 V 70 min,蛋白上样量为 20 μg;半干法转移到醋酸纤维素膜上,稳流300 mA 30 min,5%脱脂奶粉封闭
2 h,分别加入Rabbit-NF-κBp65-antibody(1∶500)和Rabbit-β-Actin-antibody(1∶300),4 ℃孵育过夜(12-16 h),二抗 Goat-anti-rabbit-IgG-HRP(1∶3 000)孵育1 h,将配好的化学发光液加到醋酸纤维素膜上,暗室显定影。
1.5 主要观察指标 ①CIA-FLS形态以及增殖、迁移能力;②CIA-FLS 中白细胞介素6、肿瘤坏死因子α、NF-κBp65 mRNA和蛋白表达水平。
1.6 统计学分析 数据以x±s表示,并进行3次独立分析。对照组和治疗组之间的差异使用单因素方差分析(ANOVA), P < 0.05为差异有显著性意义。用SPSS 24.0分析数据,Image J分析灰度值,GraPhPad Prism 5 绘图。