[1] CHAUHAN K, JANDU JS, GOYAL A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis. 2021 Jun 29. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing. 2021.
[2] YICHENG K, BAO LG, WEIDE VC, et al. High prevalence of comorbid autoimmune diseases in adults with type 1 diabetes from the HealthFacts database. J Diabetes. 2019;11(4):273-279.
[3] TUNCER T, GILGIL E, KACAR C, et al. Prevalence of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Spondyloarthritis in Turkey: a nationwide study. Arch Rheumatol. 2017;33(2):128-136.
[4] 陶庆文,王金平,徐愿,等.类风湿关节炎中西医结合医疗质量控制指标专家共识(2021年版)[J].中日友好医院学报,2021,35(1):12-15.
[5] HAMMER HB, MICHELSEN B, SEXTON J, et al. Swollen, but not tender joints, are independently associated with ultrasound synovitis: results from a longitudinal observational study of patients with established rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(9):1179-1185.
[6] BABAEI M, JAVADIAN Y, NARIMANI H, et al. Correlation between systemic markers of inflammation and local synovitis in knee osteoarthritis. Caspian J Intern Med. 2019;10(4):383-387.
[7] LI GS, CUI L, WANG GD. miR-155-5p regulates macrophage M1 polarization and apoptosis in the synovial fluid of patients with knee osteoarthritis. Exp Ther Med. 2021;21(1):68.
[8] WOODELL-MAY JE, SOMMERFELD SD. Role of Inflammation and the Immune System in the Progression of Osteoarthritis. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(2):253-257.
[9] SHI J, LIANG Q, ZUSCIK M, et al. Distribution and alteration of lymphatic vessels in knee joints of normal and osteoarthritic mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(3):657-666.
[10] JALKANEN S, SALMI M. Lymphatic endothelial cells of the lymph node. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020;20(9):566-578.
[11] ZEDDOU M. Osteoarthritis Is a Low-grade inflammatory disease: obesity’s involvement and herbal treatment. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:2037484.
[12] HUBER-LANG M, KOVTUN A, LGNATIUS A. The role of complement in trauma and fracture healing. Semin Immunol. 2013;25(1):73-78.
[13] BALUK P, FUXE J, HASHIZUME H, et al. Functionally specialized junctions between endothelial cells of lymphatic vessels. J Exp Med. 2007;204 (10):2349-2362.
[14] VONDERWEID PY. Lymphatic Vessel Pumping. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019; 1124:357-377.
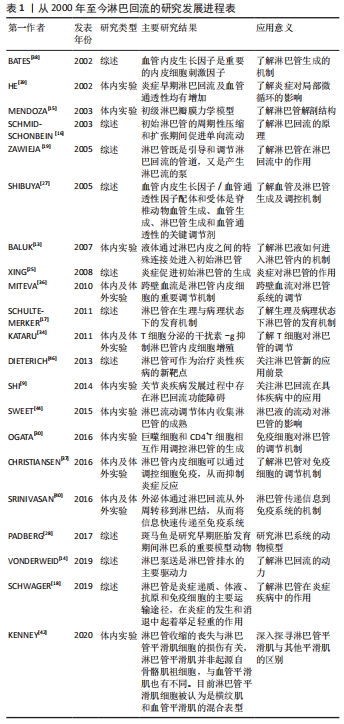
[15] MENDOZA E, SCHMID-SCHONBEIN GW. A model for mechanics of primary lymphatic valves. J Biomech Eng. 2003;125(3):407-414.
[16] SCHMID-SCHONBEIN GW. The second valve system in lymphatics. Lymphat Res Biol. 2003;1(1):25-31.
[17] SCHULTE-MERKER S, SABINE A, PETROVA TV. Lymphatic vascular morphogenesis in development, physiology, and disease. J Cell Biol. 2011;193(4):607-618.
[18] SCHWAGER S, DETMAR M. Inflammation and lymphatic function. Front Immunol. 2019;10:308.
[19] ZAWIEJA D. Lymphatic biology and the microcirculation: past, present and future. Microcirculation. 2005;12(1):141-150.
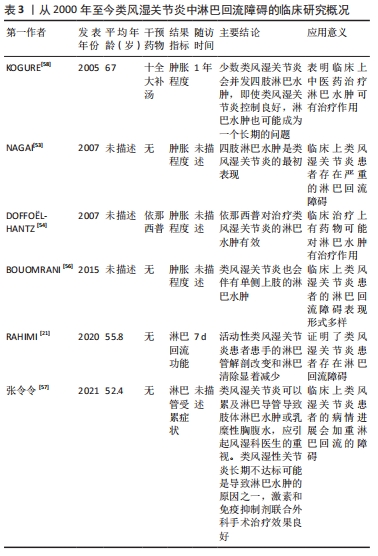
[20] RAHIMI H, BELL R, BOUTA EM, et al. Lymphatic imaging to assess rheumatoid flare: mechanistic insights and biomarker potential. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:194.
[21] RAHIMI H, BELL R, BOUTA EM, et al. Altered lymphatic vessel anatomy and markedly diminished lymph clearance in affected hands of patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72(9):1447-1455.
[22] ZHOU Q, WOOD R, SCHWARZ EM, et al. Near-infrared lymphatic imaging demonstrates the dynamics of lymph flow and lymphangiogenesis during the acute versus chronic phases of arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(7):1881-1889.
[23] LI J, ZHOU Q, WOOD RW, et al. CD23(+)/CD21(hi) B-cell translocation and ipsilateral lymph node collapse is associated with asymmetric arthritic flare in TNF-Tg mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(4):R138.
[24] MOUTA C, HEROULT M. Inflammatory triggers of lymphangiogenesis. Lymphat Res Biol. 2003;1(3):201-218.
[25] XING L, JI RC. Lymphangiogenesis myeloid cells and inflammation. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2008;4(5):599-613.
[26] BISOENDIAL R, TABET F, TAK PP, et al. Apolipoprotein A-I limits the negative effect of tumor necrosis factor on lymphangiogenesis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2015;35(11):2443-2450.
[27] SHIBUYA M, CLAESSON-WELSH L. Signal transduction by VEGF receptors in regulation of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Exp Cell Res. 2006;312(5):549-560.
[28] PADBERG Y, SCHULTE-MERKER S, VANLMPEL A. The lymphatic vasculature revisited-new developments in the zebrafish. Methods Cell Biol. 2017;138:221-238.
[29] ZHOU Q, GUO R, WOOD R, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C attenuates joint damage in chronic inflammatory arthritis by accelerating local lymphatic drainage in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2011; 63(8):2318-2328.
[30] OGATA F, FUJIU K, MATSUMOTO S, et al. Excess lymphangiogenesis cooperatively induced by macrophages and CD4(+) T cells drives the pathogenesis of lymphedema. J Invest Dermatol. 2016;136(3):706-714.
[31] LIANG Q, JU Y, CHEN Y, et al. Lymphatic endothelial cells efferent to inflamed joints produce iNOS and inhibit lymphatic vessel contraction and drainage in TNF-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016;18:62.
[32] VARMA TK, LIN CY, TOLIVER-KINSKY TE, et al. Endotoxin-induced gamma interferon production: contributing cell types and key regulatory factors. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. 2002;9(3):530-543.
[33] FATHALLAH-SHAYKH HM, ZHAO LJ, KAFROUNI AI, et al. Gene transfer of IFN-gamma into established brain tumors represses growth by antiangiogenesis. J Immunol. 2000;164(1):217-222.
[34] KATARU RP, KIM H, JANG C, et al. T lymphocytes negatively regulate lymph node lymphatic vessel formation. Immunity. 2011;34(1):96-107.
[35] LBE S, QIN Z, SCHULER T et al. Tumor rejection by disturbing tumor stroma cell interactions. J Exp Med. 2001;194(11):1549-1559.
[36] MITEVA DO, RUTKOWSKI JM, DIXON JB, et al. Transmural flow modulates cell and fluid transport functions of lymphatic endothelium. Circ Res. 2010;106(5):920-931.
[37] CHRISTIANSEN AJ, DIETERICH LC, OHS L, et al. Lymphatic endothelial cells attenuate inflammation via suppression of dendritic cell maturation. Oncotarget. 2016;7(26):39421-39435.
[38] BATES DO, HILLMAN NJ, WILLIAMS B, et al. Regulation of microvascular permeability by vascular endothelial growth factors. J Anat. 2002; 200(6):581-597.
[39] HE C, YOUNG AJ, WEST CA, et al. Stimulation of regional lymphatic and blood flow by epicutaneous oxazolone. J Appl Physiol. 2002;93(3):966-973.
[40] SRINIVASAN S, VANNBERG FO, DIXON JB. Lymphatic transport of exosomes as a rapid route of information dissemination to the lymph node. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24436.
[41] 张武强,石继祥.骨性关节炎中淋巴管的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(66):106-107.
[42] KENNEY HM, BELL RD, MASTERS EA. et al. Lineage tracing reveals evidence of a popliteal lymphatic muscle progenitor cell that is distinct from skeletal and vascular muscle progenitors. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):18088.
[43] LIANG Q, ZHANG L, XU H, et al. Lymphatic muscle cells contribute to dysfunction of the synovial lymphatic system in inflammatory arthritis in mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 2021;23(1):58.
[44] SWEET DT, JIMENEZ JM, CHANG J, et al. Lymph flow regulates collecting lymphatic vessel maturation in vivo. J Clin Invest. 2015;125(8):2995-3007.
[45] BELL RD, SLATTERY PN, WU EK, et al. iNOS dependent and independent phases of lymph node expansion in mice with TNF-induced inflammatory-erosive arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):240.
[46] DIETERICH LC, SEIDEL CD, DETMAR M. Lymphatic vessels: new targets for the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(2):359-371.
[47] BOUTA EM, BELL RD, RAHIMI H, et al. Targeting lymphatic function as a novel therapeutic intervention for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2018;14(2):94-106.
[48] WANG W, LIN X, XU H, et al. Attenuated joint tissue damage associated with improved synovial lymphatic function following treatment with bortezomib in a mouse model of experimental posttraumatic osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019;71(2):244-257.
[49] PENG L, DONG Y, FAN H, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine regulating lymphangiogenesis: a literature review. Front Pharmacol. 2020;11:1259.
[50] HAN H, MA Y, WANG X, et al. Fang-Ji-Huang-Qi-Tang attenuates degeneration of early-stage KOA mice related to promoting joint lymphatic drainage function. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020;2020:3471681.
[51] CHEN Y, LI J, LI Q, et al. Du-Huo-Ji-Sheng-Tang attenuates inflammation of TNF-Tg mice related to promoting lymphatic drainage function. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:7067691.
[52] HOU T, LIU Y, WANG X, et al. Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes lymphatic drainage and improves chronic inflammatory arthritis. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2020;20(4):526-534.
[53] NAGAI Y, AOYAMA K, ENDO Y, et al. Lymphedema of the extremities developed as the initial manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17(2):175-176.
[54] DOFFOEL-HANTZ V, SPARSA A, VERBEKE S, et al. Lymphoedema: a rare complication of inflammatory rheumatism. Successful treatment with etanercept. Eur J Dermatol. 2007;17(4):337-338.
[55] LIANG Q, SHI Q, WOOD RW, et al. Peri-articular lymphatic system and “Bi” theory of Chinese medicine in the pathogenesis and treatment of arthritis. Chin J Integr Med. 2015;21(9):648-655.
[56] BOUOMRANI S, NOUMA H, SLAMA A, et al. Unilateral lymphedema of the upper limb in a rheumatoid arthritis. Pan Afr Med J. 2015;21:214.
[57] 张令令,高兰,张国华,等.类风湿关节炎合并淋巴管受累的临床特征[J].中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志,2021,15(1):33-38.
[58] KOGURE T, HOSHINO A, LTO K, et al. Beneficial effect of complementary alternative medicine on lymphedema with rheumatoid arthritis. Mod Rheumatol. 2005;15(6):445-449.
[59] 边焱焱,程开源,常晓,等.2011至2019年中国人工髋膝关节置换手术量的初步统计与分析[J].中华骨科杂志,2020,40(21):1453-1460.
[60] 靳松,孙自强,金星,等.继发性淋巴水肿的诊治进展[J].中国血管外科杂志,2017,9(4):316-320.
[61] JONES RE, RUSSELL RD, HUO MH. Wound healing in total joint replacement. Bone Joint J. 2013;95-B(11 Suppl A):144-147.
[62] 彭志平,林云.彩超对人工关节置换术后下肢肿胀原因的诊断价值[J].中国超声医学杂志,2017,33(1):57-59.
[63] PICHONNAZ C, BASSIN JP, LECUREUX E, et al. Effect of manual lymphatic drainage after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016;97(5):674-682.
[64] VORAVITVET TY, CHEN C, LIN CY, et al. Lymphedema microsurgery reduces the rate of implant removal for patients who have pre-existing lymphedema and total knee arthroplasty for knee osteoarthritis. J Surg Oncol. 2020;121(1):57-66.
[65] KOLZ JM, RAINER WG, WYLES CC, et al. Lymphedema: a significant risk factor for infection and implant failure after total knee arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2020;28(23):996-1002.
[66] SAITO Y, NAKAGAMI H, KANEDA Y, et al. Lymphedema and therapeutic lymphangiogenesis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:804675.
[67] YOSHIDA S, HAMUY R, HAMADA Y, et al. Adipose-derived stem cell transplantation for therapeutic lymphangiogenesis in a mouse secondary lymphedema model. Regen Med. 2015;10(5):549-562.
|
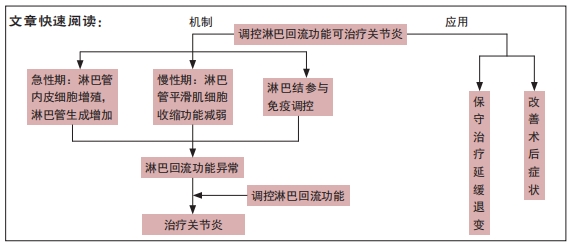
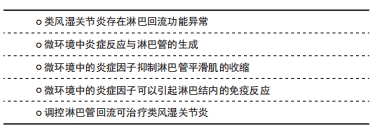



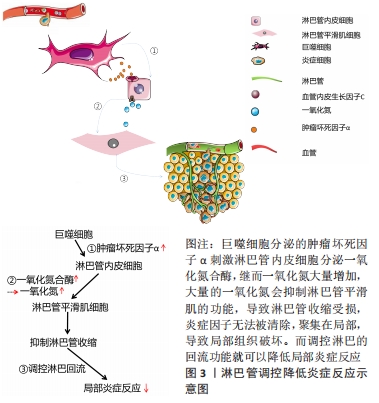 针对于淋巴管内皮细胞而言,关节炎的炎症期招募的巨噬细胞,其分泌的肿瘤坏死因子α会促使淋巴管内皮细胞产生内皮生长因子C,而内皮生长因子C作用于淋巴管内皮细胞使其增殖,淋巴管数量增加,淋巴回流增强,关节内微环境中的炎症因子被清除,关节内各组织得到保护。
针对于淋巴管内皮细胞而言,关节炎的炎症期招募的巨噬细胞,其分泌的肿瘤坏死因子α会促使淋巴管内皮细胞产生内皮生长因子C,而内皮生长因子C作用于淋巴管内皮细胞使其增殖,淋巴管数量增加,淋巴回流增强,关节内微环境中的炎症因子被清除,关节内各组织得到保护。