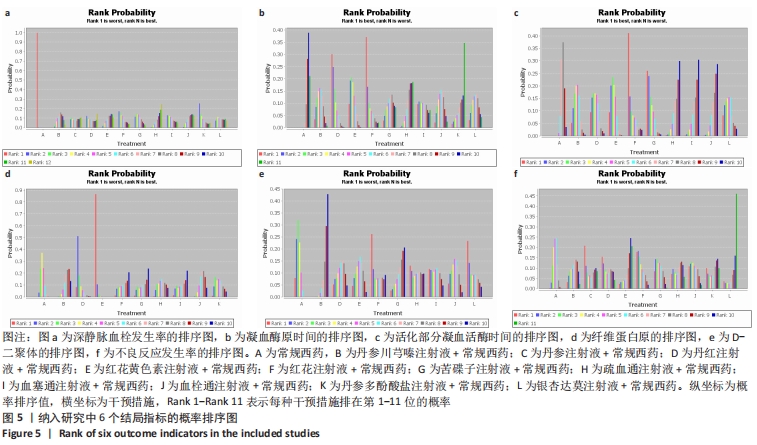
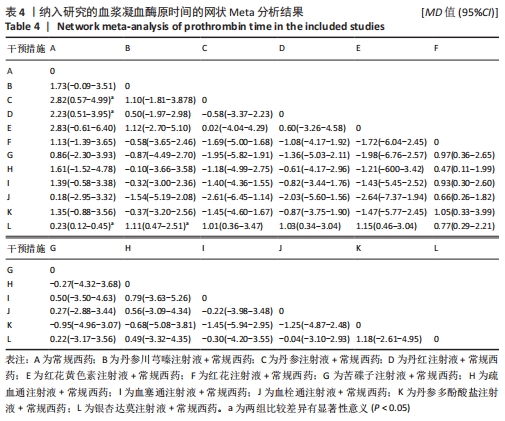
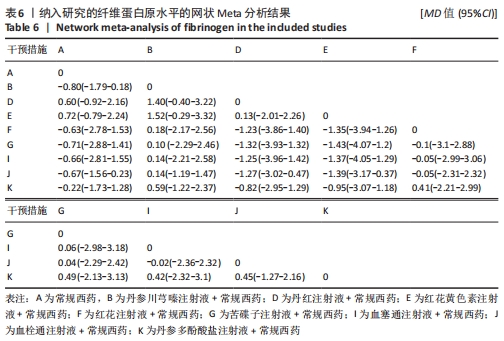
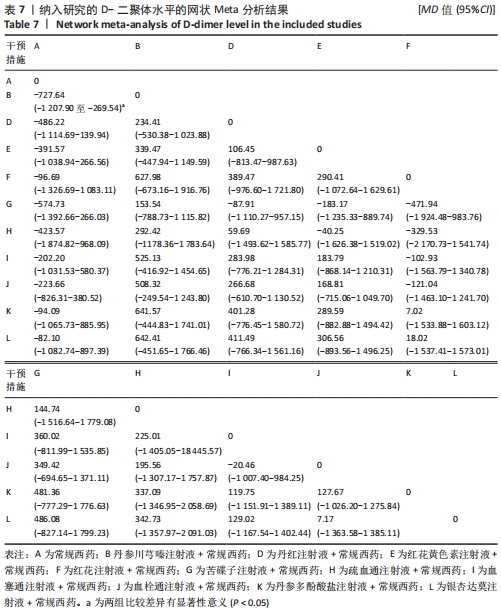
[1] THOMAS O, LYBECK E, STRANDBERG K, et al. Monitoring low molecular weight heparins at therapeutic levels: dose-responses of and correlations and differences between aPTT anti-factor Xa and thrombin generation assays. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0116835.
[2] KYRLE PA, EICHINGER S. Deep vein thrombosis. Lancet. 2005;365(9465):1163-1174.
[3] CHUNG AS, LUK W, LO AX, et al. Duplex sonography for detection of deep vein thrombosis of upper extremities: a 13-year experience. Hong Kong Med J. 2015;21(2):107-113.
[4] BUESING KL, MULLAPUDI B, FLOWERS KA. Deep Venous thrombosis and venous thromboembolism prophylaxis. Surg Clin North Am. 2015;95(2):285-300.
[5] 田伟.中国骨科大手术静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南[J].中华骨科杂志,2016,36(2): 65-71.
[6] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组.创伤骨科患者深静脉血栓形成筛查与治疗的专家共识[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2013, 15(12):1013-1017.
[7] DI NISIO M, VAN ES N, BULLER HR. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 2016;388(10063):3060-3073.
[8] 林庆荣,杨明辉,侯志勇.中国创伤骨科患者围手术期静脉血栓栓塞症预防指南(2021)[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2021,23(3):185-192.
[9] HUTTON B, SALANTI G, CALDWELL DM, et al. The PRSI-MA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews in corporating network Meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations.Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(11): 777.
[10] Cochrane Collaboration. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. [2020-12-30]. https://training.cochrane.org/cochrane-handbook-systematic-reviews-interventions.
[11] 孙元隆,阮小芬,李益萍,等.辨证论治应用芪苈强心胶囊对缺血性心力衰竭疗效影响的Meta分析比较[J].中国中药杂志,2019,44(22):4975-4984.
[12] JADAD AR, MOORE RA, CARROLL D, et al. Assessing the quality og reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials. 1996;17(1):1-12.
[13] 曾宪涛,张超,杜亮.应用ADDIS软件实现网状Meta分析[J].中国循证医学杂志, 2013, 13(12):1508-1515.
[14] 谭通,刘国恩,农北孔.丹参川芎嗪联合低分子肝素钙预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓的效果[J].北方药学,2020,17(2):83-84.
[15] 程华斌.丹参川芎嗪联合低分子肝素预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓形成的临床疗效[J].中国社区医师,2016,32(7):99-100.
[16] 杨媛媛,郭蕊,孟丽娟.丹参川芎嗪联合低分子肝素预防老年髋关节周围骨折下肢深静脉血栓形成的价值研究[J].药品评价,2019,16(6):
16-19.
[17] 冯建宏,刘文操.丹参川芎嗪联合低分子肝素预防老年髋关节周围骨折下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床研究[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2014, 9(8):867-869.
[18] 钟洪波.丹参川芎嗪与低分子肝素预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓形成疗效观察[J].医学美学美容,2019,28(5):101.
[19] 郑勇,马木提江,秦承东,等.丹参川芎嗪与低分子肝素预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓形成疗效观察[J].世界中西医结合杂志,2014,9(9):967-969.
[20] 刘腾鸿.丹参川芎嗪注射液对预防人工膝关节置换后深静脉血栓的临床研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2013.
[21] 罗琳,伍光辉,杨杰翔,等.丹参川芎嗪注射液结合低分子肝素钙对脊柱骨折后下肢深静脉血栓的预防效果观察[J].世界中医药,2019, 14(8):2073-2076, 2082.
[22] 解朋涛,江渟.丹参川芎嗪注射液联合低分子肝素钙预防髋部骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志, 2016, 32(11):1093-1094.
[23] 梁翠霞,黄定根.丹参川芎嗪注射液用于骨折围术期治疗的安全性和有效性评价[J].中国药业,2017,26(2):67-69.
[24] 彭宗生,许超,魏芳,等.丹参川芎嗪注射液预防股骨近端骨折患者术后DVT效果观察[J].山东医药,2016,56(16): 70-72.
[25] 田玉军.低分子肝素联合丹参川芎嗪预防髋部骨折术后深静脉血栓形成临床观察[J].实用中医药杂志,2017,33(9):1065-1066.
[26] 程绍君.低分子肝素联合丹参川芎嗪注射液对脊柱外科术后下肢深静脉血栓的预防效果[J].中国药物经济学,2020,15(4):59-62.
[27] 覃晓峰.髋关节置换后联合丹参川芎嗪治疗对老年患者认知功能、凝血功能及下肢深静脉血栓的影响[J].临床医学,2019,39(1):42-45.
[28] 黄绍贤,李洪韬,谭勇明,等.丹参注射液与低分子肝素联合使用对髋关节置换后出血量的影响[J].微创医学,2010,5(5):450-451.
[29] 杨建平.预防骨科手术后下肢深静脉栓塞应用丹参注射液联合低分子肝素的价值分析[J].中国医药指南,2015,13(22):143-144.
[30] 张付友,陈宝国,侯宁.中西医结合预防和治疗下肢深静脉血栓形成[J].临床医学, 2009,29(8): 111-112.
[31] 陈刚.丹红注射液对全髋关节置换患者血小板及血流变状态的影响[J].海南医学院学报, 2014,20(11):1554-1556, 1559.
[32] 田志强,杨晓艳,杨光州.丹红注射液联合达比加群酯预防下肢骨折术后下肢静脉血栓的疗效观察[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2019, 19(3):309-311.
[33] 肖伟宏.丹红注射液联合低分子肝素钙围手术期预防下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床观察[J].当代医学,2009,15(7):134.
[34] 甘茗昊.丹红注射液联合利伐沙班预防老年股骨颈骨折THA术后下肢DVT的临床研究[D].南宁:广西中医药大学,2019.
[35] 刘中岳.丹红注射液在全膝关节置换后预防下肢深静脉血栓的临床观察[D].长沙:湖南中医药大学,2014.
[36] 郭真,汤志刚.丹红注射液在下肢骨折术后的应用效果观察[J].中国中医药科技, 2018,25(3): 408-409.
[37] 史少华,吕书军,李立东.低分子肝素联合红花黄色素对下肢骨折患者围术期血小板和内皮细胞功能的影响[J].中国药业,2015,24(24):82-83.
[38] 刁丽,李宏,赵敏,等.红花黄色素对缓解骨科术后患者肢体肿胀的临床疗效观察[J].临床合理用药杂志,2016,9(30):88-89.
[39] 刘勇,李杨,关敬之.红花黄色素联合低分子肝素钙预防骨科术后下肢深静脉血栓形成分析[J].北方药学,2015,12(1):161-162.
[40] 陶永清.红花黄色素联合低分子肝素预防骨折术后卧床患者深静脉血栓的临床观察[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2017,4(95):18751-18752.
[41] 陈诚,顾臻禹.红花黄色素联合低分子肝素预防骨折术后卧床患者深静脉血栓的效果[J].交通医学,2018,32(3):222-223.
[42] 余昕.红花黄色素联合低分子量肝素钠预防全膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的疗效观察[D].福州:福建中医药大学, 2017.
[43] 黄会芳,林郁宵.红花黄色素联合低相对分子质量肝素在髋部骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成中的预防效果[J].血栓与止血学,2018,24(1):
31-33.
[44] 王志,杨卫新,张秀花,等.红花黄色素氯化钠注射液对髋关节置换患者血液流变学和凝血功能的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2016,22(15):1684-1687.
[45] 张国玲,张秀丽,张鑫.红花黄色素预防下肢深静脉血栓形成40例疗效分析[J].武警后勤学院学报(医学版),2016,25(2):149-150.
[46] 黄彦,郭广波,江恒,等.红花黄色素注射液对卧床患者凝血象及D-二聚体的影响[J].中医药导报,2015,21(11):23-25.
[47] 张坚强.红花黄色素注射液合低分子肝素钙预防髋关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成临床观察[J].湖南中医杂志,2014,30(5):71-72, 84.
[48] 赵磊.红花黄色素注射液联合低分子肝素钙预防髋关节置换后深静脉血栓的效果[J].实用临床医药杂志,2020,24(2):97-100.
[49] 彭凤,杨敏,杨红胜,等.低分子肝素钠联合红花注射液预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓形成的临床效果[J].西部医学, 2017,29(8):1085-1087,1091.
[50] 杨亚勇,牟静,金辉.红花注射液预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓形成的临床效果及其对患者血液流变学的影响[J].中国生化药物杂志, 2015,35(12):64-66,69.
[51] 高辉.中西医综合疗法对骨科大手术后DVT的预防研究[D].郑州:河南中医药大学,2013.
[52] 白文斌,王凯,韩生寿,等.苦碟子加利伐沙班预防TKA术后下肢深静脉血栓形成及对血液流变学和炎性因子的影响[J].实用骨科杂志, 2016,22(1):25-27.
[53] 焦甲勋,朱小丽,索娜,等.苦碟子注射液联合低分子肝素预防髋关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的疗效观察[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2020,20(11):1321-1323,1328.
[54] 焦甲勋,朱小丽,索娜,等.苦碟子注射液联合低分子肝素预防全膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床研究[J].中国新药与临床杂志,2020,39(7):421-424.
[55] 郑陈平,林世湾,游伟军,等.苦碟子联合低分子肝素预防人工关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓形成的效果观察[J].广东医科大学学报, 2019,37(3):328-331.
[56] 彭征程,李娟.利伐沙班与疏血通对下肢骨折患者术后预防深静脉血栓形成及其对血液流变学及炎症因子水平的影响[J].抗感染药学, 2018,15(2):357-359.
[57] 刘建涛,高丽艳.疏血通联合低分子肝素钙在老年髋部术后早期下肢深静脉血栓形成防治中的应用效果[J].中国农村卫生, 2017,10(6):38-39.
[58] 解俊杰,杨雷刚,任军龙.疏血通注射液联合利伐沙班预防髋部手术后下肢深静脉血栓形成疗效观察[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2016, 25(28):3111-3114.
[59] 万丽,肖静,蔡炜.低分子肝素钙联合血塞通用于老年髋部骨折围术期预防下肢静脉血栓的临床观察[J].基层医学论坛,2018,22(35):4942-4943.
[60] 杜开亮.低分子肝素钙联合血塞通用于老年髋部骨折围术期预防下肢静脉血栓的临床探讨[J].双足与保健,2019,28(4):103-104.
[61] 郑琪娈,沈琪,余金聪,等.利伐沙班与血塞通注射液联合使用抑制脊柱术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的效果及血液指标的影响[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学,2018,23(3):337-341.
[62] 白冰,金宝城,刘大伟.利伐沙班与血塞通注射液联合应用对脊柱术后下肢深静脉血栓的作用[J].中国生化药物杂志,2015,35(10):88-89, 92.
[63] 杨格.血塞通注射液联合低分子肝素预防老年髋部骨折患者术后DVT的临床研究[D].武汉:湖北中医药大学,2018.
[64] 赵新峰.中药血栓通注射液预防胫骨平台骨折术后深静脉血栓形成的临床观察[D].西安:陕西中医药大学,2017.
[65] 张燕文,戴勇,张威莲.低分子肝素钙联合血栓通注射液对髋关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓的临床效果[J].中医临床研究,2018,10(29):80-82.
[66] 王首贵,段涛秀,刘丽芳,等.血栓通对股骨颈骨质疏松性骨折患者置换后血液高凝状态、骨代谢和康复进程的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志, 2019,25(9):1312-1316,1326.
[67] 曾晓波,刘示,黄敬云,等.血栓通联合低分子肝素钙在预防髋部骨折术后深静脉血栓形成中的效果[J].临床医学工程, 2018,25(11):1461-1462.
[68] 镇万源.血栓通注射液对老年髋部围手术期相关血流变学影响的观察[D].昆明:云南中医学院,2012.
[69] 刘林松,岳建彪,李庆龙.血栓通注射液联合利伐沙班预防老年骨质疏松压缩性骨折经椎体后凸成形术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床应用[J].实用医院临床杂志,2019,16(6):186-189.
[70] 张敏华,金尧,汪苏英.血栓通注射液联合利伐沙班预防膝关节置换后下肢深静脉血栓临床研究[J].新中医,2021,53(2): 63-65.
[71] 何源亮,曹丹.用血栓通联合低分子肝素钠对行老年髋部骨折手术患者进行抗凝治疗的效果研究[J].当代医药论丛,2019,17(2):9-11.
[72] 黎惠金,肖智青,谢延华,等.丹参多酚酸盐联合低分子肝素在预防全髋关节置换后深静脉血栓形成中的作用[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2012, 20(7):27-29.
[73] 叶科.低分子肝素联合丹参多酚酸盐预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓形成临床效果观察[J].吉林医学,2015,36(6):1060-1062.
[74] 周红霞,王兴元,杨善进,等.低分子肝素联合丹参预防下肢骨折术后深静脉血栓效果观察[J].人民军医,2015,58(11):1308-1309.
[75] 闫桦,叶志强,岳珂,等.低分子肝素钙联合银杏达莫注射液应用于股骨粗隆间骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的疗效观察[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(28):5557-5560, 5568.
[76] 孙强,彭德付,郑加法.低分子肝素钙联合银杏达莫注射液预防股骨粗隆间骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成临床观察[J].中国中西医结合杂志, 2011,31(11):1463-1465.
[77] 王照平,吴立明,么红英,等.银杏达莫联合低分子肝素钙预防骨科术后下肢深静脉血栓形成分析[J].中国误诊学杂志,2011,11(7):1547.
[78] 沈金明,邢进峰,李飞.银杏达莫注射液预防骨盆骨折术后下肢深静脉血栓形成的临床研究[J].浙江创伤外科,2012,17(4):442-445.
[79] 李江伟,叶川,刘日光.银杏达莫注射液预防髋、膝关节置换后深静脉血栓形成的临床研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2010,19(36):4657-4659,4662.
[80] 曾庆.银杏达莫注射液预防膝关节置换后深静脉血栓形成[J].长春中医药大学学报,2016,32(5): 1019-1021.
[81] 黄彭,孟祥奇,吴晨熙,等.中医药预防骨科大手术后深静脉血栓形成的研究进展[J].中国中医急症,2020,29(11):2062-2065,2068.
[82] 吕悦,郑士林,郑英,等.我院骨科活血化瘀中药注射剂使用情况分析[J].中医药管理杂志, 2021,29(6):49-51.
[83] 王蔚,杜渊,白雪,等.蛭龙活血通瘀胶囊治疗脑血管疾病的研究现状分析[J].泸州医学院学报,2016,39(1):91-93.
[84] 陈艳明,夏珂,何杨,等.疏血通注射液体外抗栓及抗凝作用研究[J].中国全科医学,2018, 21(36):4502-4505.
[85] 陈培栋,房利勤.红花注射液和注射用红花黄色素药理作用研究[J].世界中医药, 2016,11(2): 308-310.
[86] 李瑛,邵鑫,李春燕,等.基于代谢组学的苦碟子注射液抗心肌缺血作用机制研究[J].中草药, 2021,52(3):789-798.
[87] 王云龙,房岐,郑超.丹参化学成分、药理作用及质量控制研究进展[J].中国药业, 2020, 29(15):6-10.
[88] MOHRE D, HOPEWELL S, SCHULZ KF, et al. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int J Surg. 2012;10(1):28-55.
|