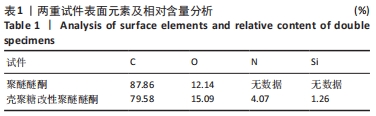
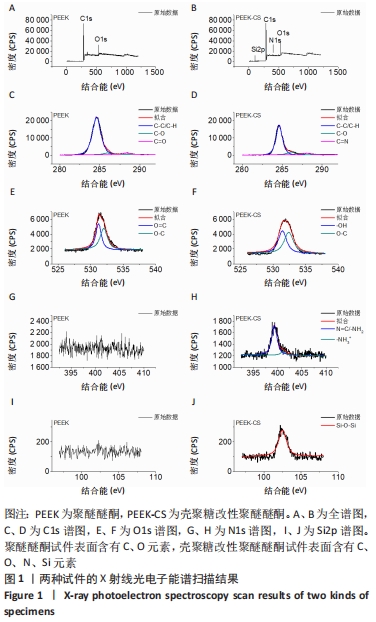
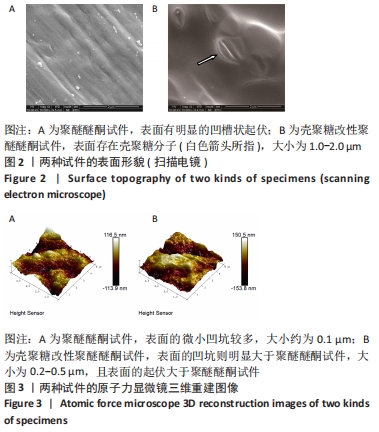
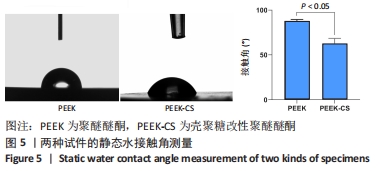
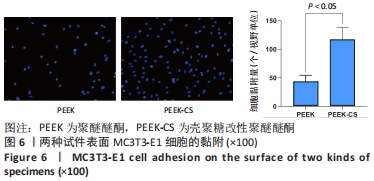
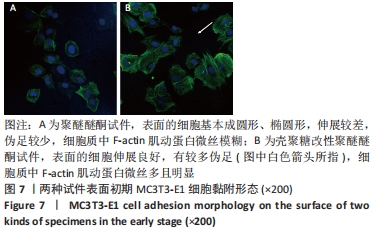
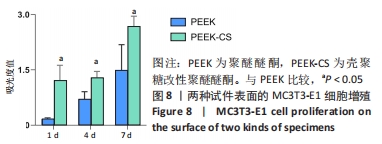
[1] 陈贤明,周王峰.聚醚醚酮在口腔医学领域的应用[J].中国标准化,2020 (S01):354-358.
[2] PANAYOTOV IV, ORTI V, CUISINIER F, et al. Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) for medical applications. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2016;27(7):118.
[3] TSUNEO S, MIYUKI H. Radiation deterioration of several aromatic polymers under oxidative conditions. Elsevier. 1987;28(11):694-699.
[4] LI HM, FOURACRE RA, GIVEN MJ, et al. The effects on polyetheretherketone and polyethersulfone of electron and /spl gamma/irradiation. IEEE T DIELECT EL IN. 1999;6(3):295-303.
[5] 陈井春雨,蓝菁.聚醚醚酮材料表面形态和骨结合原理研究进展[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2021,37(2):259-262.
[6] ABDULLAH MR, GOHARIAN A, ABDUL KADIR MR, et al. Biomechanical and bioactivity concepts of polyetheretherketone composites for use in orthopedic implants-a review. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015;103(11):3689-3702.
[7] 刘吕花,熊成东,张丽芳,等.聚醚醚酮表面接枝聚丙烯酸及其成骨细胞相容性[J].塑料工业,2021,49(7):1591-1563.
[8] SAROT JR, CONTAR CM, CRUZ AC, et al. Evaluation of the stress distribution in CFR-PEEK dental implants by the three-dimensional finite element method. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(7):2079-2085.
[9] FEERICK EM, KENNEDY J, MULLETT H, et al. Investigation of metallic and carbon fibre PEEK fracture fixation devices for three-part proximal humeral fractures. Med Eng Phys. 2013;35(6):712-722.
[10] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, GITTENS RA, SCHNEIDER JM, et al. Osteoblasts exhibit a more differentiated phenotype and increased bone morphogenetic protein production on titanium alloy substrates than on poly-ether-ether-ketone. Spine J. 2012;12(3):265-272.
[11] OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, SLOSAR PJ, et al. Implant materials generate different peri-implant inflammatory factors: poly-ether-ether-ketone promotes fibrosis and microtextured titanium promotes osteogenic factors. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2015;40(6):399-404.
[12] MUXIKA A, ETXABIDE A, URANGA J, et al. Chitosan as a bioactive polymer: Processing, properties and applications. Int J Biol Macromol. 2017;105(Pt 2): 1358-1368.
[13] PATRULEA V, OSTAFE V, BORCHARD G, et al. Chitosan as a starting material for wound healing applications. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2015;97(Pt B):417-426.
[14] 毛誉蓉,孙佳敏,周雄,等.医用特种高分子聚醚醚酮植入体及其表面界面工程[J].功能高分子学报,2021,34(2):144-160.
[15] MA R, TANG T. Current strategies to improve the bioactivity of PEEK. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):5426-5445.
[16] ABDULKAREEM MH, ABDALSALAM AH, BOHAN AJ. Influence of chitosan on the antibacterial activity of composite coating (PEEK /HAp) fabricated by electrophoretic deposition. Prog Org Coat. 2019;130:251-259.
[17] 陈睿超,孙辉,许国志.PEEK的表面改性和表征[J].中国塑料,2011,25(5): 17-23.
[18] 刘焕萍,孙辉,高艺菡.聚醚醚酮表面壳聚糖的固定[J].中国塑料,2014, 28(6):52-56.
[19] XU A, ZHOU L, DENG Y, et al. A carboxymethyl chitosan and peptide-decorated polyetheretherketone ternary biocomposite with enhanced antibacterial activity and osseointegration as orthopedic/dental implants. J Mater Chem B. 2016;4(10):1878-1890.
[20] BOLYEN E, RIDEOUT JR, DILLON MR, et al. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nat Biotechnol. 2019;37(8):852-857.
[21] AZZAWI ZGM, HAMAD TI, KADHIM SA, et al. Osseointegration evaluation of laser-deposited titanium dioxide nanoparticles on commercially pure titanium dental implants. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2018;29(7):96.
[22] GUADARRAMA BELLO D, FOUILLEN A, BADIA A, et al. A nanoporous titanium surface promotes the maturation of focal adhesions and formation of filopodia with distinctive nanoscale protrusions by osteogenic cells. Acta Biomater. 2017;60:339-349.
[23] FARAWATI FA, NAKAPARKSIN P. What is the Optimal Material for Implant Prosthesis? Dent Clin North Am. 2019;63(3):515-530.
[24] 鲁晨,陶璐,项闫颜,等.聚醚醚酮改性及在口腔种植领域的应用研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2020,36(5):819-824.
[25] 潘硕,郭晓恒.聚醚醚酮在口腔种植体及义齿修复领域的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2019,19(84):40-42+44.
[26] MASSIA SP, STARK J. Immobilized RGD peptides on surface-grafted dextran promote biospecific cell attachment. J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;56(3):390-309.
[27] 陈兰花,盛道鹏.X射线光电子能谱分析(XPS)表征技术研究及其应用[J].教育现代化,2018,5(1):180-182+92.
[28] LIEDER R, DARAI M, THOR MB, et al. In vitro bioactivity of different degree of deacetylation chitosan, a potential coating material for titanium implants. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(12):3392-3399.
[29] GALLI C, PIEMONTESE M, LUMETTI S, et al. The importance of WNT pathways for bone metabolism and their regulation by implant topography. Eur Cell Mater. 2012;24:46-59.
[30] LV L, LIU Y, ZHANG P, et al. The nanoscale geometry of TiO2 nanotubes influences the osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells by modulating H3K4 trimethylation. Biomaterials. 2015;39:193-205.
[31] BAN S, IWAYA Y, KONO H, et al. Surface modification of titanium by etching in concentrated sulfuric acid. Dent Mater. 2006;22(12):1115-1120.
[32] DE SOUZA FERREIRA SB, DE ASSIS DIAS BR, OBREGON CS, et al. Microparticles containing propolis and metronidazole: in vitro characterization, release study and antimicrobial activity against periodontal pathogens. Pharm Dev Technol. 2014;19(2):173-180.
[33] MAMALIS AA, MARKOPOULOU C, VROTSOS I, et al. Chemical modification of an implant surface increases osteogenesis and simultaneously reduces osteoclastogenesis: an in vitro study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011;22(6): 619-626.
[34] BANG SM, MOON HJ, KWON YD, et al. Osteoblastic and osteoclastic differentiation on SLA and hydrophilic modified SLA titanium surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(7):831-837.
[35] 李雪菁,邱小亥,赵宝红.亲水种植体促进骨整合机制研究进展[J].中国实用口腔科杂志,2020,13(8):501-505.
[36] CONTI M, DONATI G, CIANCIOLO G, et al. Force spectroscopy study of the adhesion of plasma proteins to the surface of a dialysis membrane: role of the nanoscale surface hydrophobicity and topography. J Biomed Mater Res. 2002;61(3):370-379.
[37] AMARAL IF, LAMGHARI M, SOUSA SR, et al. Rat bone marrow stromal cell osteogenic differentiation and fibronectin adsorption on chitosan membranes: the effect of the degree of acetylation. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;75(2):387-397.
[38] MOURSI AM, GLOBUS RK, DAMSKY CH. Interactions between integrin receptors and fibronectin are required for calvarial osteoblast differentiation in vitro. J Cell Sci. 1997;110(Pt 18):2187-2196.
[39] SAENGDEE P, CHAISRIRATANAKUL W, BUNJONGPRU W, et al. Surface modification of silicon dioxide, silicon nitride and titanium oxynitride for lactate dehydrogenase immobilization. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;67:134-138.
[40] ZHU X, CHEN J, SCHEIDELER L, et al. Effects of topography and composition of titanium surface oxides on osteoblast responses. Biomaterials. 2004; 25(18):4087-4103.
[41] ANSELME K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2000;21(7): 667-681.
[42] MARTIN HJ, SCHULZ KH, BUMGARDNER JD, et al. XPS study on the use of 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane to bond chitosan to a titanium surface. Langmuir. 2007;23(12):6645-6651.
[43] HSIAO SW, THIEN DV, HO MH, et al. Interactions between chitosan and cells measured by AFM. Biomed Mater. 2010;5(5):054117.
[44] CAI K, FRANT M, BOSSERT J, et al. Surface functionalized titanium thin films: zeta-potential, protein adsorption and cell proliferation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2006;50(1):1-8.
[45] 俞娟,徐俊华,范一民.壳聚糖抗菌性能研究进展[J].林业工程学报, 2018,3(5):20-27.
|