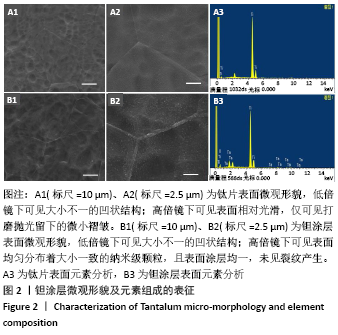
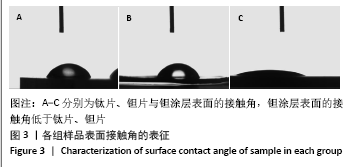
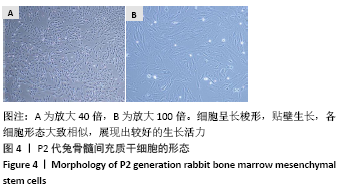
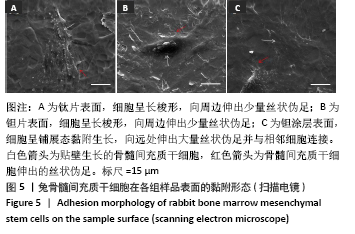
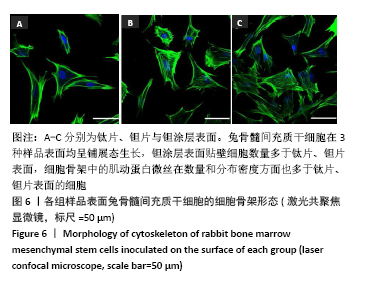
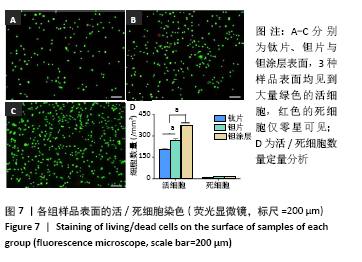
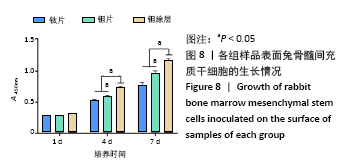
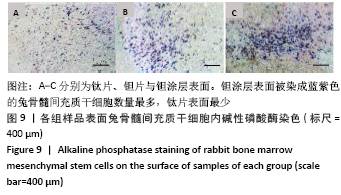
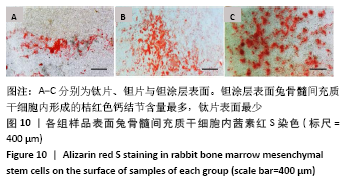
[1] KAUR M, SINGH K. Review on titanium and titanium based alloys as biomaterials for orthopaedic applications. Mater Sci Eng C. 2019;102: 844-862.
[2] KHORASANI AM, GOLDBERG M, DOEVEN EH, et al. Titanium in Biomedical Applications—Properties and Fabrication: A Review. J Biomater Tissue Eng. 2015;5(8):593-619.
[3] 李兴平,肖东琴,赵桥,等.钛表面载铜抗菌功能膜的制备及性能[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(4):553-557.
[4] ALBREKTSSON T, WENNERBERG A. On osseointegration in relation to implant surfaces. Clin. Implant Dent Relat Res. 2019;21(S1):4-7.
[5] PELLEGRINI G, FRANCETTI L, BARBARO B, et al. Novel surfaces and osseointegration in implant dentistry. J Invest Clin Dent. 2018;9(4): e12349.
[6] 李儒军,陶可,寇伯龙,等.人工髋关节置换术后翻修的原因分析及处理[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2018,26(19):1729-1734.
[7] STIEHLER M, LIND M, MYGIND T, et al. Morphology, proliferation, and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells cultured on titanium, tantalum, and chromium surfaces. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2008;86(2):448-458.
[8] LIU Y, BAO C, WISMEIJER D, et al. The physicochemical/biological properties of porous tantalum and the potential surface modification techniques to improve its clinical application in dental implantology. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2015;49:323-329.
[9] SHI L, WANG A, ZANG F, et al. Tantalum-coated pedicle screws enhance implant integration. Colloids Surf B. 2017;160:22-32.
[10] SHI J, ZHANG X, QIAO S, et al. Enhanced osteointegration of tantalum-modified titanium implants with micro/nano-topography. RSC Adv. 2017;7(73):46472-46479.
[11] ZHOU X, HU X, LIN Y. Coating of Sandblasted and Acid-Etched Dental Implants With Tantalum Using Vacuum Plasma Spraying. Implant Dent. 2018;27(2):202-208.
[12] HANAWA T. Surface treatment and modification of metals to add biofunction. Dent Mater J. 2017;36(5):533-538.
[13] LIU Y, RATH B, TINGART M, et al. Role of implants surface modification in osseointegration: A systematic review. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2020;108(3):470-484.
[14] ABRAMOVA AV, ABRAMOV VO, BAYAZITOV VM, et al. A sol-gel method for applying nanosized antibacterial particles to the surface of textile materials in an ultrasonic field. Ultrason Sonochem. 2020;60:104788.
[15] NEGRILA C, PREDOI M, ICONARU S, et al. Development of Zinc-Doped Hydroxyapatite by Sol-Gel Method for Medical Applications. Molecules. 2018;23(11):2986.
[16] MENDONÇA G, MENDONÇA DBS, ARAGÃO FJL, et al. Advancing dental implant surface technology – From micron- to nanotopography. Biomaterials. 2008;29(28):3822-3835.
[17] JEMAT A, GHAZALI MJ, RAZALI M, et al. Surface Modifications and Their Effects on Titanium Dental Implants. BioMed Res Int. 2015;2015:1-11.
[18] GÜNAY-BULUTSUZ A, BERRAK Ö, YEPREM HA, et al. Biological responses of ultrafine grained pure titanium and their sand blasted surfaces. Mater Sci Eng C. 2018;91:382-388.
[19] LU M, ZHUANG X, TANG K, et al. Intrinsic Surface Effects of Tantalum and Titanium on Integrin α5β1/ ERK1/2 Pathway-Mediated Osteogenic Differentiation in Rat Bone Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;51(2):589-609.
[20] SAGOMONYANTS KB, HAKIM-ZARGAR M, JHAVERI A, et al. Porous tantalum stimulates the proliferation and osteogenesis of osteoblasts from elderly female patients. J Orthop Res. 2011;29(4):609-616.
[21] 于晓明,谭丽丽,杨柯.医用金属表面的钽涂层制备及其临床应用趋势[J].中国骨科临床与基础研究杂志,2013(2):115-119.
[22] NUNE C, MISRA RD, SOMANI MC, et al. Dependence of cellular activity at protein adsorbed biointerfaces with nano- to microscale dimensionality. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014;102(6):1663-1676.
[23] ELIAS C, OSHIDA Y, LIMA J, et al. Relationship between surface properties (roughness, wettability and morphology) of titanium and dental implant removal torque. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2008;1(3):234-242.
[24] XU G, SHEN X, HU Y, et al. Fabrication of tantalum oxide layers onto titanium substrates for improved corrosion resistance and cytocompatibility. Surf Coat Technol. 2015;272:58-65.
[25] ESTRIN Y, IVANOVA EP, MICHALSKA A, et al. Accelerated stem cell attachment to ultrafine grained titanium. Acta Biomater. 2011;7(2): 900-906.
[26] DOU X, WEI X, LIU G, et al. Effect of porous tantalum on promoting the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in vitro through the MAPK/ERK signal pathway. J Orthop Translat. 2019;19:81-93.
[27] GITTENS RA, OLIVARES-NAVARRETE R, HYZY SL, et al. Superposition of nanostructures on microrough titanium-aluminum-vanadium alloy surfaces results in an altered integrin expression profile in osteoblasts. Connect Tissue Res. 2014;55(sup1):164-168. |