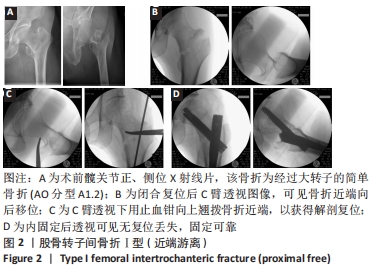
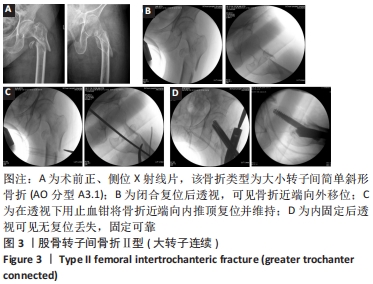
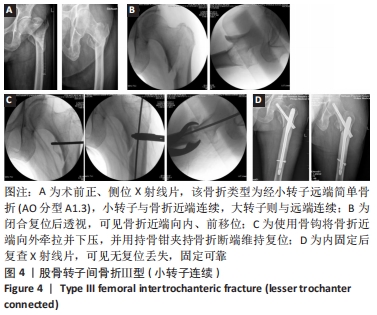
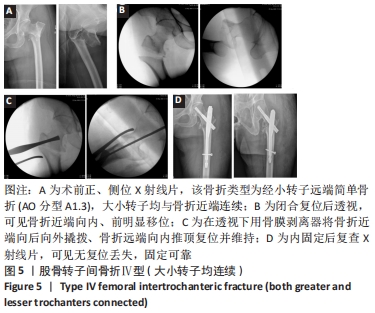
[1] NIE B, DOU W, YANG Z, et al. Comparison of intramedullary fixation and arthroplasty for the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures in the elderly. Medicine. 2017;96(27):e7446.
[2] MA KL, WANG X, LUAN FJ, et al. Proximal femoral nails antirotation, Gamma nails, and dynamic hip screws for fixation of intertrochanteric fractures of femur: A meta-analysis. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2014; 100(8):859-866.
[3] 马坤龙,王绚,栾富均,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉、动力髋螺钉、伽马钉治疗股骨转子间骨折的系统评价[J].华西医学,2013,28(3): 345-351.
[4] 王跃挺,张琳袁,龚伟华,等.老年转子间骨折股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定术后骨折断端阳性支撑与阴性支撑短期疗效比较[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2021,14(3):205-209.
[5] JIAMTON C, BOERNERT K, BABST R, et al. The nail–shaft-axis of the of proximal femoral nail antirotation (PFNA) is an important prognostic factor in the operative treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2018;138(3):339-349.
[6] MOEHRING HD, NOWINSKI GP, CHAPMAN MW, et al. Irreducible intertrochanteric fractures of the femur. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1997; (339):197-199.
[7] SHARMA G, GN KK, YADAV S, et al. Pertrochanteric fractures (AO/OTA 31-A1 and A2) not amenable to closed reduction: Causes of irreducibility. Injury. 2014;45(12):1950-1957.
[8] 殷婷,王珺琛.有限切开辅助复位治疗难复性股骨转子间骨折[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2016,10(10):1409-1413.
[9] 康亦锋,徐勇强,冯嗣寅,等.侧卧位牵引复位股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗难复性股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(19): 2988-2993.
[10] 华长城,张琪琪,张卫华,等.联动复位法治疗难复性股骨转子间骨折[J].临床骨科杂志,2019,22(2):227-228.
[11] 黄淑明,兰树华,吴泉州,等.枪式钳辅助复位髓内固定治疗内外向难复性股骨转子间骨折[J].中国基层医药,2019,26(9):1037-1041.
[12] 郑占乐,刘欢,于贤,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉专用球头改锥复位难性股骨转子间骨折临床研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019, 33(10):1250-1253.
[13] 张世民,胡孙君,杜守超,等.小转子二分型的难复位股骨转子间骨折手术技巧及疗效分析[J].同济大学学报(医学版),2020,41(6): 772-778.
[14] 汪祥,周业金,李业奎,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉近端滑动加压正性支撑复位治疗老年股骨转子间骨折[J].中国组织工程研究,2021, 25(27):4361-4367.
[15] FUTAMURA K, BABA T, HOMMA Y, et al. New classification focusing on the relationship between the attachment of the iliofemoral ligament and the course of the fracture line for intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. 2016;47(8):1685-1691.
[16] 佟大可,丁文彬,王光超,等.难复性股骨转子间骨折的临床分型与治疗[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(2):109-114.
[17] IKUTA Y, NAGATA Y, IWASAKI Y. Preoperative radiographic features of trochanteric fractures irreducible by closed reduction. Injury. 2019; 50(11):2014-2021.
[18] KIM Y, DHEEP K, LEE J, et al. Hook leverage technique for reduction of intertrochanteric fracture. Injury. 2014;45(6):1006-1010.
[19] HARRIS WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures:treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.
[20] 庞国防,胡才友,杨泽.中国人口老龄化趋势与对策[J].中国老年保健医学,2021,19(1):3-5.
[21] REN Y, HU J, LU B, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of hip fracture in a middle-aged and older Chinese population. Bone. 2019;122:143-149.
[22] 崔爽爽,赵丽坤,马信龙.中国老年髋部骨折流行病学和疾病经济负担研究现状[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2020,26(3):567-570.
[23] 贾伞伞,张颖,李海婷,等.老年股骨转子间骨折患者临床特征及血液指标分析[J].江苏医药,2021,47(2):164-167.
[24] SOO CY, HYUNSUP O, JE CY, et al. Technique and Early Results of Percutaneous Reduction of Sagittally Unstable Intertrochateric Fractures. Clin Orthop Surg. 2011;3(3):217-224.
[25] MÉNDEZ-GIL A, FERNÁNDEZ-VALENCIA LABORDE JÁ, ESTRADA-MASLLORENS JM, et al. MMinimally invasive dynamic hip screw technique: Shorter surgical time with similar post-surgical results compared to conventional DHS technique. A retrospective cohort study. Rev Esp Cir Ortop Traumatol. 2014;58(6):351-356.
[26] 华筠毅,黄伟杰,戴明华,等.切开复位髓内钉内固定对于老年性复杂股骨转子间骨折治疗的疗效分析[J].贵州医药,2021,45(2):251-252.
[27] 徐昭宁,陈方毅,李德芳,等.股骨转子间骨折患者围手术期输血的影响因素分析[J].中国临床医学,2020,27(5):822-826.
[28] 程真真,田晓瑜,唐洪涛,等.前方入路切开复位股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗复杂股骨转子间骨折[J].中医正骨,2021,33(3):58-60.
[29] 胡金玺,贺常仁,刘芳,等.微创钢丝导入器引导下的钢丝复位技术在难复性股骨转子间骨折治疗中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(10):1245-1249.
[30] HAO YL, ZHANG ZS, ZHOU F, et al. Predictors and reduction techniques for irreducible reverse intertrochanteric fractures. Chin Med J (Engl). 2019;132(21): 2534-2542.
[31] 赵益峰,姜振,李涛,等.前入路微创钳夹复位技术治疗难复性股骨转子间骨折[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(5): 544-549.
[32] 姚双全,张英泽,赵昌平,等.小切口辅助复位微创髓内钉固定治疗股骨粗隆间骨折12例[J].中国微创外科杂志,2013,13(12):1134-1136.
[33] HAIDUKEWYCH GJ. Intertrochanteric fractures: ten tips to improve results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2009;91:712-719.
[34] 石淇允,李无阴,张颖,等.股骨近端防旋髓内钉治疗转子间骨折术后内固定失败因素的研究进展[J].骨科,2020,11(3):262-266.
|