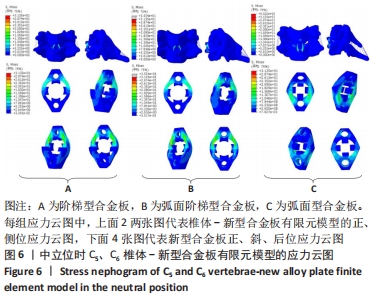
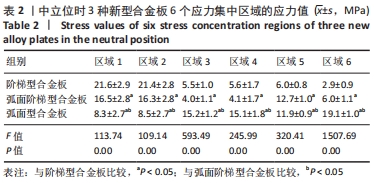
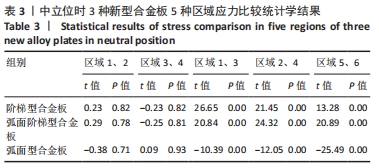
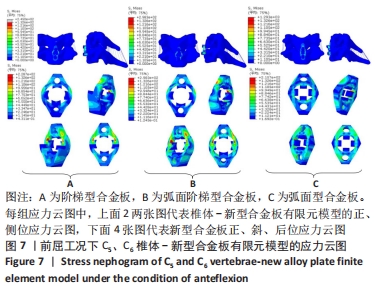
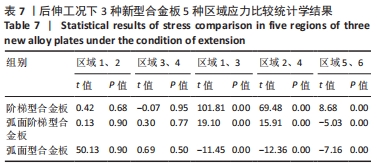
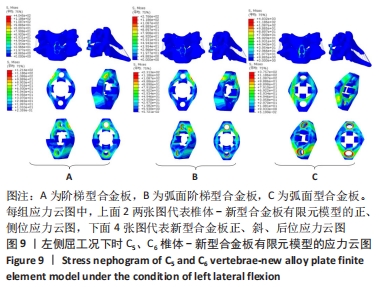
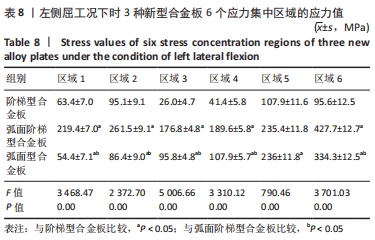
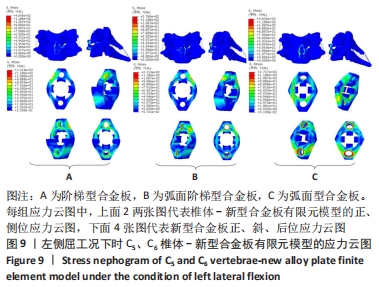
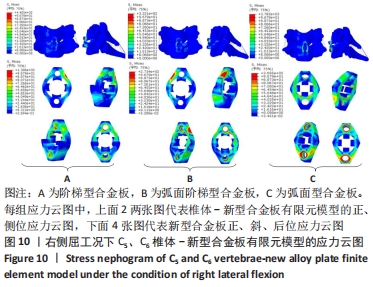
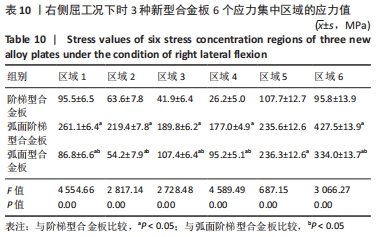
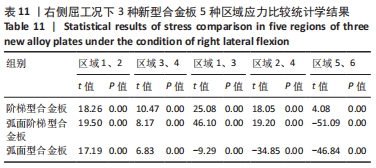
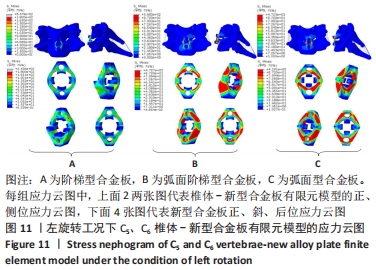
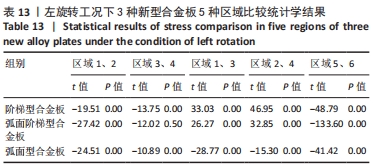
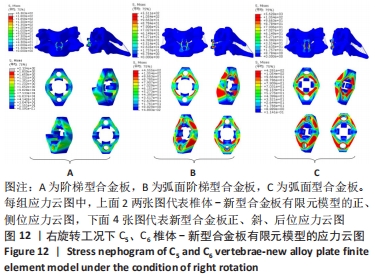
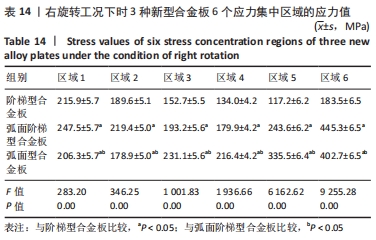
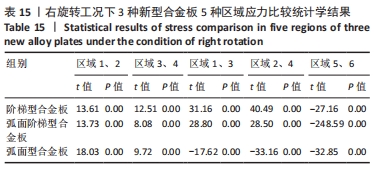
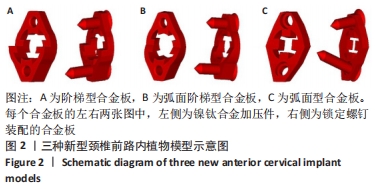
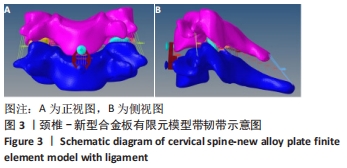
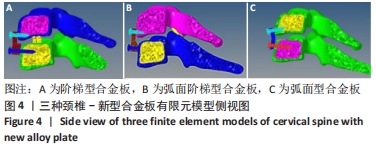
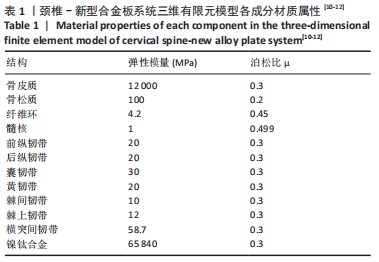
[1] RAO RD, CURRIER BL, ALBERT TJ, et al. Degenerative cervical spondylosis: clinical syndromes, pathogenesis, and management. Instr Course Lect, 2008;57(6):447-469.
[2] 翟明玉.颈椎病治疗方式的合理选择[J].中医正骨,2014,26(6):6-9.
[3] SMITH GW, ROBINSON RA. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958;40-A(3):607-624.
[4] LEE MJ, BAZAZ R, FUREY CG, et al. Influence of anterior cervical plate design on Dysphagia: a 2-year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(5):406-409.
[5] 宋奇,郭卫春,黄文俊,等.颈椎前路术后吞咽困难的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2017,14(10):60-63.
[6] NANDA A, SHARMA M, SONIG A, et al. Surgical complications of anterior cervical diskectomy and fusion for cervical degenerative disk disease: A single surgeon’s experience of 1576 patients. World Neurosurg. 2014;82(6):1380-1387.
[7] PANJABI MM, WHITE AA 3RD, JOHNSON RM. Cervical spine mechanics as a function of transection of components. J Biomech. 1975;8(5):327-336.
[8] YOGANANDAN N, KUMARESAN S, PINTAR FA. Biomechanics of the cervical spine part 2. Cervical spine soft tissue responses and biomechanical modeling. Clin Biomech. 2001;16(1):1-27.
[9] ANDERSON DG, ALBERT TJ. Bone grafting, implants, and plating options for anterior cervical fusions. Orthop Clin N Am. 2002;33(2):317-328.
[10] LEE SH, IM YJ, KIM KT, et al. Comparison of cervical spine biomechanics after fixed- and mobile-core artificial dsc replacement: A finite element analysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(9):700.
[11] NG HW, TEO EC, LEE VS. Statistical factorial analysis on the material property sensitivity of the mechanical responses of the C4-C6 under compression, anterior and posterior shear. J Biomech. 2004;37(5):771-777.
[12] 李川,徐永清,颜翼,等.镍合金记忆合金腕骨三角融合器有限元分析[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(6):678-682.
[13] 王成焘.人体生物摩擦学[M].北京:科学出版社,2008:428-432.
[14] PANJABI MM, CRISCO JJ, VASAVADA A, et al. Mechanical properties of the human cervical spine as shown by three-dimensional load–displacement curves. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(24):2692-2700.
[15] PHILIPP S, BULENT OM, FRANK H, et al. The C2-Pars interarticularis screw as an alternative in atlanto-axial stabilization. A biomechanical comparison of established techniques. Turk Neurosurg. 2018;28(6): 995-1004.
[16] ZHANG QH, TEO EC, NG HW, et al. Finite element analysis of moment-rotation relationships for human cervical spine. J Biomech. 2006;39(1):189-193.
[17] 李光淳.颈前路椎间盘切除植骨融合术治疗颈椎病疗效观察[J].中国继续医学教育,2020,12(4):109-111.
[18] 吴东荣,郭涛.颈前路减压术后植骨融合方式的研究现状与进展[J].安徽医药,2019,23(9):1701-1705.
[19] LOPEZ-ESPINA CG, AMIROUCHE F, HAVALAD V. Multilevel cervical fusion and its effect on disc degeneration and osteophyte formation. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(9):972-978.
[20] FABIO G, FRANCESCO C, ROBERTO A, et al. Anterior cervical fusion: a biomechanical comparison of 4 techniques. Laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;9(5):444-449.
[21] NOH SH, ZHANG HY. Comparison among perpect-C®, zero-p®, and plates with a cage in single-level cervical degenerative disc disease. BMC Musculoskel Dis. 2018;19(1):33.
[22] 马迅,陈辉,曹凯,等.不同影像学特点的脊髓型颈椎病的手术治疗[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(10):983-991.
[23] 陈朦村,杨述华,杨操,等.可吸收固定板在脊髓型颈椎病前路减压融合术中的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2015,35(6):602-609.
[24] 王新伟,袁文,吴晓东.颈椎手术并发症现状与新动向[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(2):97-99.
[25] GOK B, SCIUBBA DM, MCLOUGHLIN GS, et al. Surgical treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy with anterior compression: a review oF 67 cases. J Neurosurg Spine. 2008;9(2):152-157.
[26] SON DK, SON DW, KIM HS, et al. Comparative study of clinical and radiological outcomes of a zero-profile device concerning reduced postoperative Dysphagia after single level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2014;56(2):103-107.
[27] NJOKU I, ALIMIi M, LENG LZ, et al. Anterior cervical discectomy and fusion with a zero-profile integrated plate and spacer device: a clinical and radiological study: Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 2014;21(4): 529-537.
[28] 常步青,冯虎,于朝将,等.颈前路零切迹融合系统和传统钉板系统治疗脊髓型颈椎病的临床比较[J].中国骨伤,2017,30(5):411-416.
[29] HE SH, FENG HL, LAN ZM, et al. A Randomized Trial Comparing Clinical Outcomes Between Zero-Profile and Traditional Multi-Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion Surgery for Cervical Myelopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2018;43(5):E259-E266.
[30] 戎玉罗,罗勇骏,刘蔚,等.零切迹自稳型颈椎融合器在前路颈椎椎间盘切除融合术中的应用及其对吞咽困难和邻近节段骨化的影响[J].脊柱外科杂志,2019,17(2):73-78.
[31] ZHU D, ZHANG D, LIU BG, et al. Can Self-Locking Cages Offer the Same Clinical Outcomes as Anterior Cage-with-Plate Fixation for 3-Level Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF) in Mid-Term Follow-Up? Med Sci Mon Int Med J Exp Clin Res. 2019;25(1):547-557.
[32] 赵连城,郑玉峰.形状记忆与超弹性镍钛合金的发展和应用[J].中国有色金属学报,2004,14(S1):323-326.
[33] 熊洋,俞兴.腰椎棘突间撑开装置生物力学及有限元分析的研究与进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(39):5919-5928.
[34] HOH DJ, HOH BL, AMARR AP, et al. Shape memory alloys: metallurgy, biocompatibility, and biomechanics for neurosurgical applications. Neurosurgery. 2009;64(5 Suppl 2):199-214.
[35] ZHONG ZC, CHEN SH, HUNG CH. Load- and displacement-controlled finite element analyses on fusion and non-fusion spinal implants. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2009;223(2):143-157.
[36] 童杰.上颈椎后路柔性动态固定与下颈椎经关节螺钉的生物力学研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2015.
[37] LIU Y, HOU Y, YANG L, et al. Comparison of 3 reconstructive techniques in the surgical management of multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(23):E1450-1458.
[38] MO ZJ, ZHAO YB, WANG LZ, et al. Biomechanical effects of cervical arthroplasty with U-shaped disc implant on segmental range of motion and loading of surrounding soft tissue. Eur Spine J. 2014;23(3):613-621.
[39] 王晨曦,赵改平,柏磊磊,等.动态稳定器植入术后颈椎生物力学的有限元分析[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2016,33(4):645-651.
[40] LIU JT, WANG RQ, WANG HB, et al. Biomechanical comparison of a new memory compression alloy plate versus traditional titanium plate for anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: A finite element analysis. Biomed Res Int. 2020;(2020):1-10.
|