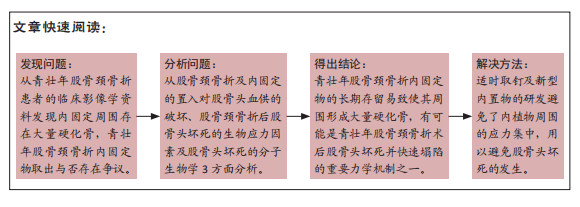
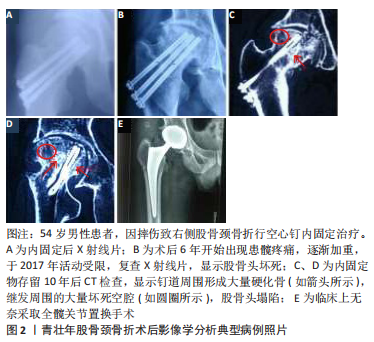
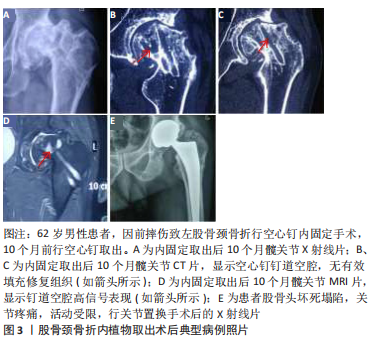
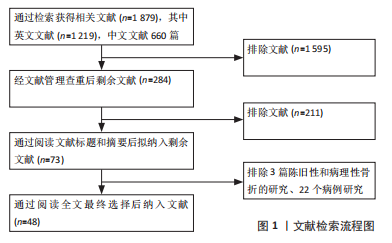
[1] BRODERICK JM, BRUCE-BRAND R, STANLEY E, et al. Osteoporotic hip fractures:the burden of fifixation failure. Sci World J. 2013;2013:515197
[2] TIAN FM, ZHANG L, ZHAO HY, et al. An increase in the incidence of hip fractures in Tangshan,China. Osteoporos Int. 2014;25:1321-1325.
[3] 中华医学会骨科学分会创伤骨科学组,中国医师协会骨科医师分会创伤专家工作委员会.成人股骨颈骨折诊治指南[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2018,20(11):921-928.
[4] 徐凯航,纪方.青壮年股骨颈骨折的治疗进展[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2020,22(6):549-552.
[5] SLOBOGEAN GP, SPRAGUE SA, SCOTT T, et al. Complications following young femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2015;46(3):484-491.
[6] STOCKTON DJ, O’HARA LM, O’HARA NN, et al. High rate of reoperation and conversion to total hip arthroplasty after internal fixation of young femoral neck fractures: a population-based study of 796 patients. Acta Orthop. 2019;90(1):21-25.
[7] PATTERSON JT, ISHII K, TORNETTA P 3RD, et al. Open reduction is associated with greater hazard of early reoperation after internal fixation of displaced femoral neck fractures in adults 18-65 Years. J Orthop Trauma. 2020;34(6):294-301.
[8] SLOBOGEAN GP, STOCKTON DJ, ZENG B. Femoral neck fractures in adults treated with internal fixation:a prospective multicenter Chinese cohort. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2017;25:297-303.
[9] SHAH SN, KAPOOR CS, JHAVERI MR, et al. Analysis of outcome of avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by core decompression and bone grafting. Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6(3):160-166.
[10] LI MN, COLE PA. Anatomical considerations in adult femoral neck fractures:how anatomy influences the treatment issues. Injury. 2015; 46:453-458.
[11] LARGE TM, ADAMS MR, LOEFFLER BJ, et al. Posttraumatic Avascular Necrosis After Proximal Femur, Proximal Humerus,Talar Neck,and Scaphoid Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2019;27(21):794-805.
[12] PAPAPIETRO N, DIMARTINO A, NICCOLI G, et al. Trabecular metal screw implanted for avascular necrosis of the femoral head may complicate subsequent arthroplasty surgery. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2014; 24(6):931-938.
[13] ZHAO D, QIU X, WANG B, et al. Epiphyseal Arterial Network and Inferior Retinacular Artery Seem Critical to Femoral Head Perfusion in Adults With Femoral Neck Fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(8): 2011-2023.
[14] LAMBERS FM, KOCH K, KUHN G, et al. Trabecular bone adapts to long-term cyclic loading by increasing stiffness and normalization of dynamic morphometric rates. Bone. 2013;55(2):325-334.
[15] ZWAHLEN A, CHRISTEN D, RUFFONI D, et al. Image -guided failure as-sessment of human trabecular bone - inverse finite element mod-elling for characterization of elastic properties. Biomed Tech (Berl). 2013;Suppl 1:/j/bmte.2013.58.issue-s1-D/bmt-2013-4114/bmt-2013-4114.xml.
[16] DUFFIN M, PILSON HT. Technologies for Young Femoral Neck Fracture Fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33Suppl1:S20-S26.
[17] SHAH SN, KAPOOR CS, JHAVERI MR, et al. Analysis of outcome of avascular necrosis of femoral head treated by core decompression and bone grafting. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2015;6(3):160-166.
[18] WANG H, JI B, LIU XS, et al. Analysis of microstructural and me-chanical alterations of trabecular bone in a simulated three-dimen-sional remodeling process. J Biomech. 2012;45(14):2417-2425.
[19] GODA I, ASSIDI M, GANGHOFFER JF. Cosserat 3D anisotropic models of trabecular bone from the homogenisation of the trabecular structure. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin. 2012;15(1):288-290.
[20] MARTELLI S, PERILLI E. Time-elapsed synchrotron-light microstructural imaging of femoral neck fracture. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2018; 84:265-272.
[21] TING BL, HENG M, VRAHAS MS, et al. Is disuse osteopenia a favorable prognostic sign after femoral neck fracture? J Orthop Trauma. 2016; 30(9):496-502.
[22] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Optimum Configuration of Cannulated Compression Screws for the Fixation of Unstable Femoral Neck Fractures: Finite Element Analysis Evaluation. Biomed Res Int. 2018; 2018:1271762.
[23] LI J, WANG M, ZHOU J, et al. Finite element analysis of different screw constructs in the treatment of unstable femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2020;51(4):995-1003.
[24] BLIVEN E, SANDRIESSER S, AUGAT P, et al. Biomechanical evaluation of locked plating fixation for unstable femoral neck fractures. Bone Joint Res. 2020;9(6):314-321.
[25] LI J, ZHAO Z, YIN P, et al. Comparison of three different internal fixation implants in treatment of femoral neck fracture-a finite element analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;12;14(1):76.
[26] LINDE F, ANDERSEN E, HVASS I, et al. Avascular femoral head necrosis following fracture fixation. injury. 1986;17(3):159-164.
[27] SHEN JZ, YAO JF, LIN DS, et al. Hollow-bone-graft dynamic hip screw can fix and promote bone union after femoral neck fracture: an experimental research. Int J Med Sci. 2012;9(10):916-22.
[28] HUANG S, WANG B, ZHANG X, et al. High-purity weight-bearing magnesium screw: Translational application in the healing of femoral neck fracture. Biomaterials. 2020;238:119829.
[29] NODA M, NAKAMURA Y, ADACHI K, et al. Dynamic finite element analysis of implants for femoral neck fractures simulating walking. J Orthop Surg(Hong Kong). 2018;26(2):2309499018777899.
[30] WU F, HUANG W, YANG Y, et al. miR-155-5p regulates mesenchymal stem cell osteogenesis and proliferation by targeting GSK3B in steroid-associated osteonecrosis. Cell Biol Int. 2021;45(1):83-91.
[31] CHEN N, XIAO B, WANG S. Bioinformatics analysis of microRNA linked to ubiquitin proteasome system in traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Medicine. 2020;99(33):e21706.
[32] HENN D, ABU-HALIMA M, KAHRAMAN M, et al. A multivariable miRNA signature delineates the systemic hemodynamic impact of arteriovenous shunt placement in a pilot study. Sci Rep.2020;10(1):21809.
[33] CUI S, ZHOU Z, LIU X, et al. Identification and Characterization of Serum microRNAs as Biomarkers for Human Disc Degeneration: An RNA Sequencing Analysis. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020;10(12):E1063.
[34] MEYER A, HERKT S, KUNZE-SCHUMACHER H, et al. The transcription factor TAL1 and miR-17-92 create a regulatory loop in hematopoiesis. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1):21438.
[35] UMEZU T, TSUNEYAMA K, KANEKURA K, et al. Comprehensive analysis of liver and blood miRNA in precancerous conditions. Sci Rep. 2020; 10(1):21766.
[36] HAO C, YANG S, XU W, et al. MiR-708 promotes steroid-induced osteonecrosis of femoral head, sup-presses osteogenic differentiation by targeting SMAD3. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22599.
[37] GU C, XU Y, ZHANG S, et al. miR-27a attenuates adipo-genesis and promotes osteogenesis in steroid-induced rat BMSCs by targeting PPARgamma and GREM1. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38491.
[38] WANG Z, WANG Z, LIU J, et al. Long non-coding RNA SNHG5 sponges miR-26a to promote the tumorigen-esis of osteosarcoma by targeting ROCK1. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;107:598-605.
[39] LIU J, MI B, WANG Y, et al. miR-26a suppresses osteo-sarcoma migration and invasion by directly targeting HMGA1. Oncol Lett. 2018;15(6): 8303-8310.
[40] LI Z, NI J. Role of microRNA-26a in the diagnosis of lower extremity deep vein thrombosis in patients with bone trauma. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(5):5069-5074.
[41] ZHAO Z, DAI XS, WANG ZY, et al. MicroRNA-26a reduces synovial inflammation and cartilage injury in osteoarthritis of knee joints through impairing the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 2019; 39:4.
[42] 张颖,张蕾蕾,柴玉娜,等.创伤性股骨头坏死中差异miRNA的筛选与验证[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2017,19(11):978-985.
[43] HAN N, LI Z. Non-coding RNA Identification in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head Using Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Analysis. Orthop Surg. 2021;21. doi: 10.1111/os.12834.
[44] NAIK AA, NARAYANAN A, KHANCHANDANI P, et al. Systems analysis of avascular necrosis of femoral head using integrative data analysis and literature mining delineates pathways associated with disease. Sci Rep. 2020;22;10(1):18099.
[45] HUANG G, ZHAO G, XIA J, et al. FGF2 and FAM201A affect the development of osteonecrosis of the femoral head after femoral neck fracture. Gene. 2018;652:39-47.
[46] LEE SW, LEE KJ, KIM BS, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Mitochondrial DNA Copy Number in Osteonecrosis of the Femoral Head. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020;56(5):239.
[47] LI T, XIAO K, XU Y, et al. Identification of long non coding RNAs expressed during the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells obtained from patients with ONFH. Int J Mol Med. 2020;46(5):1721-1732.
[48] 刘光波,梅玉倩,马海洋,等.股骨头坏死骨吸收区对股骨头内应力分布及疾病进展的影响[J].中华骨科志,2020,40(7):408-416.
|