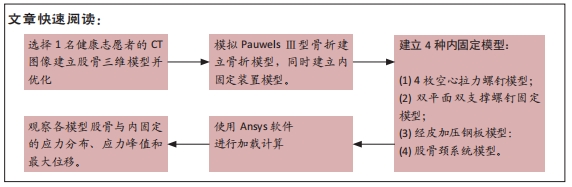
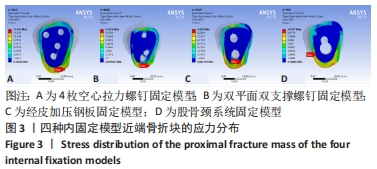
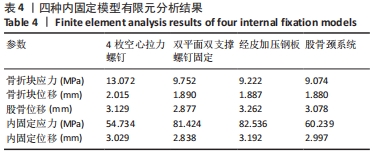
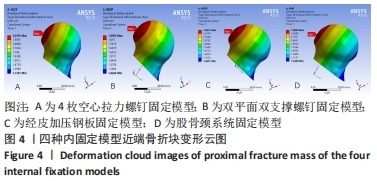
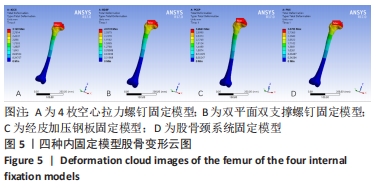
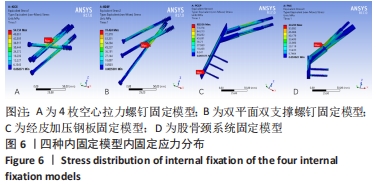
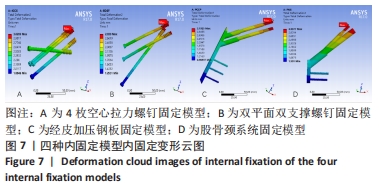
[1] KANNUS P, PARKKARI J, SIEVANEN H, et al. Epidemiology of hip fractures. Bone.1996;18(1 Suppl): 57S-63S.
[2] FLORSCHUTZ AV, LANGFORD JR, HAIDUKEWYCH GJ, et al. Femoral neck fractures: current management.J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(3):121-129.
[3] PUTNAM SM, COLLINGE CA, GARDNER MJ, et al. Vascular Anatomy of the Medial Femoral Neck and Implications for Surface Plate Fixation.J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33(3):111-115.
[4] SHEN M, WANG C, CHEN H, et al. An update on the Pauwels classification. J Orthop Surg Res. 2016;11(1):161.
[5] KALSBEEK JH, VAN WALSUM ADP, VROEMEN JPAM, et al. Displaced femoral neck fractures in patients 60 years of age or younger: results of internal fixation with the dynamic locking blade plate. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(4):443-449.
[6] NAUTH A, CREEK AT, ZELLAR A, et al. Fracture fixation in the operative management of hip fractures (FAITH): an international, multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10078):1519-1527.
[7] SLOBOGEAN G P, SPRAGUE S A, SCOTT T, et al. Complications following young femoral neck fractures. Injury.2015;46(3): 484-491.
[8] PAUYO T, DRAGER J, ALBERS A, et al. Management of femoral neck fractures in the young patient: A critical analysis review. World J Orthop. 2014;5(3):204-217.
[9] MA JX, KUANG MJ, XING F, et al. Sliding hip screw versus cannulated cancellous screws for fixation of femoral neck fracture in adults: A systematic review.Int J Surg. 2018;52:89-97.
[10] TIANYE L, PENG Y, JINGLI X, et al. Finite element analysis of different internal fixation methods for the treatment of Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108658.
[11] XIA Y, ZHANG W, ZHANG Z, et al. Treatment of femoral neck fractures: sliding hip screw or cannulated screws? A meta-analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):54.
[12] TANG Y, ZHANG Z, WANG L, et al. Femoral neck system versus inverted cannulated cancellous screw for the treatment of femoral neck fractures in adults: a preliminary coMParative study. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):504.
[13] 殷浩, 周恩昌, 潘政军,等.4枚空心钉与3枚空心钉结合支持钢板内固定治疗PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折的有限元分析 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2019,23(32):5133-5137.
[14] 王建, 冉建, 刘修信, 等.空心钉“F”技术与倒三角形方式布钉治疗股骨颈骨折的疗效比较 [J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2016,24(24):2242-2246.
[15] 胡清勇. 经皮加压钢板与空心钉内固定治疗股骨颈骨折的比较[J]. 东方药膳,2021(10): 91.
[16] WIRTZ D, PANDORF T, PORTHEINE F, et al. Concept and development of an orthotropic FE model of the proximal femur.J Biomech. 2003; 36(2):289-293.
[17] 张晟, 胡岩君, 余斌. 不同内固定方式固定PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折模型的有限元分析[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志,2017,25(2):163-169.
[18] LI J, ZHAO Z, YIN P, et al. CoMParison of three different internal fixation implants in treatment of femoral neck fracture-a finite element analysis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):76.
[19] SOWMIANARAYANAN S, CHANDRASEKARAN A, KUMAR RK. Finite element analysis of a subtrochanteric fractured femur with dynamic hip screw, dynamic condylar screw, and proximal femur nail implants--a coMParative study. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2008;222(1):117-127.
[20] HALVORSON J. Reduction Techniques for Young Femoral Neck Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 1:S12-S19.
[21] JONES CB, WALKER JB. Diagnosis and Management of Ipsilateral Femoral Neck and Shaft Fractures. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2018;26(21): e448-e454.
[22] XU DF, BI FG, MA CY, et al. A systematic review of undisplaced femoral neck fracture treatments for patients over 65 years of age, with a focus on union rates and avascular necrosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):28.
[23] CHAN DS. Femoral Neck Fractures in Young Patients: State of the Art. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 1:S7-S11.
[24] DUFFIN M, PILSON HT. Technologies for Young Femoral Neck Fracture Fixation. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 1:S20-S26.
[25] MEDDA S, SNOAP T, CARROLL EA. Treatment of Young Femoral Neck Fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2019;33 Suppl 1:S1-S6.
[26] LIPORACE F, GAINES R, COLLINGE C, et al. Results of internal fixation of Pauwels type-3 vertical femoral neck fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(8):1654-1659.
[27] CHA YH, YOO JI, HWANG SY, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of Internal Fixation of Pauwels Type III Femoral Neck Fractures: A Systematic Review of Various Fixation Methods. Clin Orthop Surg. 2019;11(1):1-14.
[28] PANTELI M, RODHAM P, GIANNOUDIS PV. Biomechanical rationale for implant choices in femoral neck fracture fixation in the non-elderly. Injury. 2015;46(3):445-452.
[29] PENG MJ, XU H, CHEN HY, et al. Biomechanical analysis for five fixation techniques of Pauwels-III fracture by finite element modeling. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;193:105491.
[30] ZENG W, LIU Y, HOU X. Biomechanical evaluation of internal fixation implants for femoral neck fractures: A coMParative finite element analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2020;196:105714.
[31] LI L, ZHAO X, YANG X, et al. Dynamic hip screws versus cannulated screws for femoral neck fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2020;15(1):352.
[32] GüMüŞTAŞ S, TOSUN H, AĞıR İ, et al. Influence of number and orientation of screws on stability in the internal fixation of unstable femoral neck fractures. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc. 2014;48(6):673-678.
[33] KUNAPULI S, SCHRAMSKI M, LEE A, et al. Biomechanical analysis of augmented plate fixation for the treatment of vertical shear femoral neck fractures. J Orthop Trauma. 2015;29(3):144-150.
[34] 位锋, 周业金, 姚涛,等 .空心钉联合支撑钢板治疗中青年PauwelsⅢ型股骨颈骨折 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(18):2869-2874.
[35] SU Z, LIANG L, HAO Y. Medial femoral plate with cannulated screw for Pauwels type III femoral neck fracture: A meta-analysis. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2021;34(2):169-177.
[36] FILIPOV O. Biplane double-supported screw fixation (F-technique): a method of screw fixation at osteoporotic fractures of the femoral neck. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2011;21(7):539-543.
[37] ZHU F, LIU G, SHAO H G, et al. Treatment of femoral neck fracture with percutaneous compression plate: preliminary results in 74 patients. Orthop Surg. 2015;7(2):132-137.
[38] 范智荣, 苏海涛, 周霖,等.新型股骨颈内固定系统治疗不稳定性股骨颈骨折的有限元分析 [J]. 中国组织工程研究,2021,25(15): 2321-2328.
[39] STOFFEL K, ZDERIC I, GRAS F, et al. Biomechanical Evaluation of the Femoral Neck System in Unstable Pauwels III Femoral Neck Fractures: A CoMParison with the Dynamic Hip Screw and Cannulated Screws.J Orthop Trauma. 2017;31(3):131-137.
[40] 杨亚军, 马涛, 张小钰, 等.股骨颈动力交叉钉系统治疗股骨颈骨折近期疗效 [J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志,2021,35(5):539-543.
[41] BOLZONI L, RUIZ-NAVAS E M, GORDO E. Evaluation of the mechanical properties of powder metallurgy Ti-6Al-7Nb alloy. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017;67:110-116.
[42] RYBALCHENKO OV, ANISIMOVA NY, KISELEVSKY MV, et al. The influence of ultrafine-grained structure on the mechanical properties and biocoMPatibility of austenitic stainless steels. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(4):1460-1468.
|