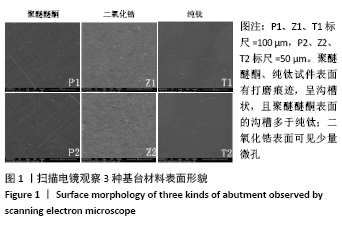
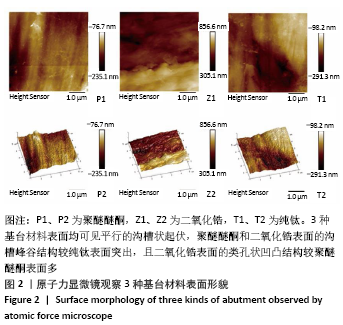
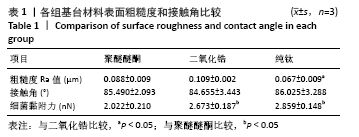
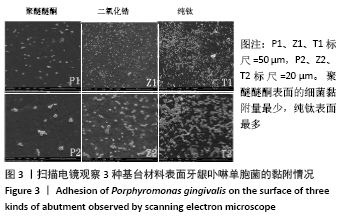
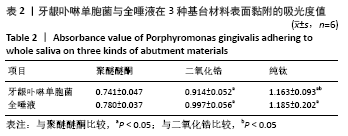
[1] SALA L, BASCONES-MARTÍNEZ A, CARRILLO-DE-ALBORNOZ A. Impact of abutment material on peri-implant soft tissue color. An in vitro study. Clin Oral Investig. 2017;21(7):2221-2233.
[2] PITTA J, ZARAUZ C, PJETURSSON B, et al. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Influence of Abutment Material on Peri-implant Soft Tissue Color Measured Using Spectrophotometry. Int J Prosthodont. 2020;33(1):39-47.
[3] THOMA D, IOANNIDIS A, CATHOMEN E, et al. Discoloration of the Peri-implant Mucosa Caused by Zirconia and Titanium Implants. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 2016;36(1):39-45.
[4] ROSKIES M, JORDAN J, FANG D, et al. Improving PEEK bioactivity for craniofacial reconstruction using a 3D printed scaffold embedded with mesenchymal stem cells. J Biomater Appl. 2016;31(1):132-139.
[5] 陈曦,于海洋.聚醚醚酮在口腔种植与修复领域的研究进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2018,45(6):657-665.
[6] HAN C, LEE E, KIM H, et al. The electron beam deposition of titanium on polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and the resulting enhanced biological properties. Biomaterials. 2010;31(13):3465-3470.
[7] TANNOUS F, STEINER M, SHAHIN R, et al. Retentive forces and fatigue resistance of thermoplastic resin clasps. Dent Mater. 2012;28(3):273-278.
[8] 秦胜男,贾慧,李英.聚醚醚酮在口腔临床中的应用现状[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2018,45(6):652-656.
[9] 宋应亮,张思佳.对种植体周围炎的认识与预防[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2020,38(5):479-483.
[10] 郑桂婷,徐燕,吴明月.种植体周围疾病治疗的专家共识及治疗方法的进展[J].国际口腔医学杂志,2020,47(6):725-731.
[11] TONETTI M, CHAPPLE I, JEPSEN S, et al. Primary and secondary prevention of periodontal and peri-implant diseases: Introduction to, and objectives of the 11th European Workshop on Periodontology consensus conference. J Clin Periodontol. 2015;42 Suppl 16:S1-4.
[12] WISDOM C, CHEN C, YUCA E, et al. Repeatedly Applied Peptide Film Kills Bacteria on Dental Implants. JOM (1989). 2019;71(4):1271-1280.
[13] PRADO A, PEREIRA J, HENRIQUES B, et al. Biofilm Affecting the Mechanical Integrity of Implant-Abutment Joints. Int J Prosthodont. 2016;29(4):381-383.
[14] GIBBS S, ROFFEL S, MEYER M, et al. Biology of soft tissue repair: gingival epithelium in wound healing and attachment to the tooth and abutment surface. Eur Cell Mater. 2019;38:63-78.
[15] ROMANOS G, DELGADO-RUIZ R, SCULEAN A. Concepts for prevention of complications in implant therapy. Periodontol 2000. 2019;81(1):7-17.
[16] CHACKARTCHI T, ROMANOS G, SCULEAN A. Soft tissue-related complications and management around dental implants. Periodontol 2000. 2019;81(1):124-138.
[17] KOUTOUZIS T. Implant-abutment connection as contributing factor to peri-implant diseases. Periodontol 2000. 2019;81(1):152-166.
[18] DAUBERT D, WEINSTEIN B. Biofilm as a risk factor in implant treatment. Periodontol 2000. 2019;81(1):29-40.
[19] RIGOLIN M, DE AVILA E, BASSO F, et al. Effect of different implant abutment surfaces on OBA-09 epithelial cell adhesion. Microsc Res Tech. 2017;80(12):1304-1309.
[20] GHEISARIFAR M, THOMPSON G, DRAGO C, et al. In vitro study of surface alterations to polyetheretherketone and titanium and their effect upon human gingival fibroblasts. J Prosthet Dent. 2021;125(1):155-164.
[21] NASCIMENTO CD, PITA MS, FERNANDES F, et al. Bacterial adhesion on the titanium and zirconia abutment surfaces. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014;25(3):337-343.
[22] CHARALAMPAKIS G, LEONHARDT Å, RABE P, et al. Clinical and microbiological characteristics of peri‐implantitis cases: a retrospective multicentre study. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2012;23(9):1045-1054.
[23] BARKARMO S, LONGHORN D, LEER K, et al. Biofilm formation on polyetheretherketone and titanium surfaces. Clin Exp Dent Res. 2019;5(4):427-437.
[24] O’TOOLE G, KAPLAN HB, KOLTER R. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2000;54(1):49-79.
[25] 高宁,肖晓蓉,柴枫,等.两种种植材料对龈下优势菌生长及生长环境的影响[J].华西医科大学学报,2002,33(1):62-64,107.
[26] ESFAHANIZADEH N, MIRMALEK S, BAHADOR A, et al. Formation of biofilm on various implant abutment materials. Gen Dent. 2018;66(5):39-44.
[27] DE AVILA E, AVILA-CAMPOS M, VERGANI C, et al. Structural and quantitative analysis of a mature anaerobic biofilm on different implant abutment surfaces. J Prosthet Dent. 2016;115(4):428-436.
[28] HAHNEL S, WIESER A, LANG R, et al. Biofilm formation on the surface of modern implant abutment materials. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2015;26(11):1297-1301.
[29] D’ERCOLE S, CELLINI L, PILATO S, et al. Material characterization and Streptococcus oralis adhesion on Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) and titanium surfaces used in implantology. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2020;31(10):84.
[30] GORTH DJ, PUCKETT S, ERCAN B, et al. Decreased bacteria activity on Si(3)N(4) surfaces compared with PEEK or titanium. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:4829-4840.
[31] BRUM R, LABES L, VOLPATO C, et al. Strategies to Reduce Biofilm Formation in PEEK Materials Applied to Implant Dentistry-A Comprehensive Review. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020;9(9):609.
[32] LORENZETTI M, DOGSA I, STOSICKI T, et al. The influence of surface modification on bacterial adhesion to titanium-based substrates. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2015;7(3):1644-1651.
[33] Quirynen M, van der Mei H, Bollen C. An in vivo study of the influence of the surface roughness of implants on the microbiology of supra- and subgingivalplaque. J Dent Res. 1993;72(9):1304-1309.
[34] 陈玉婷,李蜀光.种植体表面材料抑菌性的研究进展[J].口腔颌面外科杂志, 2007,17(4):366-368.
[35] TEGOULIA VA, COOPER SL. Staphylococcus aureus adhesion to self-assembled monolayers: effect of surface chemistry and fibrinogen presence. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2002;24(3):217-228.
[36] ZHANG X, WANG L, LEVÄNEN E. Superhydrophobic surfaces for the reduction of bacterial adhesion. RSC Adv. 2013;3(30):12003-12020.
[37] BOCK RM, JONES EN, RAY DA, et al. Bacteriostatic behavior of surface modulated silicon nitride in comparison to polyetheretherketone and titanium. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(5):1521-1534.
[38] LI B, LOGAN BE. Bacterial adhesion to glass and metal-oxide surfaces. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2004;36(2):81-90.
[39] MEI L, VAN DER MEI HC, REN Y, et al. Poisson analysis of streptococcal bond strengthening on stainless steel with and without a salivary conditioning film. Langmuir. 2009;25(11):6227-6231.
[40] WEI W, WANG S, HO F. Electrokinetic properties of colloidal zirconia powders in aqueous suspension. J Am Ceram Soc. 1999;82(12):3385-3392.
[41] WEBSTER TJ, PATEL AA, RAHAMAN MN, et al. Anti-infective and osteointegration properties of silicon nitride, poly(ether ether ketone), and titanium implants. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(12):4447-4454.
[42] VAZ J, PEZZOLI D, CHEVALLIER P, et al. Antibacterial Coatings Based on Chitosan for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications. Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(8):866-885.
[43] LI B, XIA X, GUO M, et al. Biological and antibacterial properties of the micro-nanostructured hydroxyapatite/chitosan coating on titanium. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1): 14052.
[44] IKEDA T, HIRAYAMA H, YAMAGUCHI H, et al. Polycationic biocides with pendant active groups: molecular weight dependence of antibacterial activity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986;30(1):132-136.
[45] MOONGRAKSATHUM B, CHIEN M, CHEN Y. Antiviral and Antibacterial Effects of Silver-Doped TiO₂ Prepared by the Peroxo Sol-Gel Method. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2019;19(11):7356-7362.
[46] SEDELNIKOVA M, KOMAROVA E, SHARKEEV Y, et al. Modification of titanium surface via Ag-, Sr- and Si-containing micro-arc calcium phosphate coating. Bioact Mater. 2019;4(undefined):224-235.
[47] SIVARAJ D, VIJAYALAKSHMI K. Enhanced antibacterial and corrosion resistance properties of Ag substituted hydroxyapatite/functionalized multiwall carbon nanotube nanocomposite coating on 316L stainless steel for biomedical application. Ultrason Sonochem. 2019;59:104730. |