[1] 杨晓彤,杨永进. 排龈技术在固定修复中的进展研究[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2015,16(4):253-256.
[2] 何嘉菁,钱洁蕾,王德芳. 前牙氧化锆全瓷冠粘固前排龈对牙周组织的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(2):106-108.
[3] 吴丽娜,王一霖,刘美瑜.排龈术在龈下楔状缺损修复中的临床应用[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2014,30(6):859-861.
[4] 刘继乐,苏鑫,毕良佳,等. 排龈线对牙体楔状缺损患者炎症反应及悬突的预防效果[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2016,16(11):2148-2150.
[5] 刘玉秀,周瑾. 排龈术在龈下楔状缺损修复中的应用价值分析[J].全科口腔医学杂志,2017,4(5):26-27.
[6] 高旭,刘梅,刘翠玲.种植义齿排龈后种植体周围软组织损伤预后的动物实验研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志,2018,36(3):287-290.
[7] 林曦,徐淑兰,郑相淮,等. 粘接剂残留致种植体周围炎[J].实用医学杂志, 2017,33(24):4077-4081.
[8] 程磊,于海洋,吴尧,等.牙种植体周围微生物研究[J].华西口腔医学杂志, 2019,37(1):7-12.
[9] KORSCH M, ROBRA BP, WALTHER W. Cement-associated signs of inflammation: retrospective analysis of the effect of excess cement on peri-implant tissue. Int J Prosthodont.2015;(1):11-18.
[10] 巫佩瑶,周陶,曹志炜,等.种植体周围炎与牙周炎的比较[J].医学综述, 2019,25(17):3333-3337.
[11] BENNANI V, SCHWASS D, CHANDLER N.Gingival retraction techniques for implants versus teeth.J Am Dent Assoc. 2008;139(10):1354-1363.
[12] CHANG YS, BENNANI V, TAWSE-SMITH A, et al. Effect of a cordless retraction paste material on implant surfaces:an in vitro study.Braz Oral Res. 2011;25(6):492-499.
[13] DEOGADE SC, MANTRI SS, DUBE G, et al. A new trend in recording subgingival tissue around an implant while making a direct abutment impression.Case Rep Dent. 2014;2014:847408.
[14] 张津京,刘玉华,吕培军,等. 三维模型分析法评价不同排龈时间下的龈沟宽度[J]. 北京大学学报,2011,43(1):73-76.
[15] 孙艳燕,匡斌. 双线排龈法和单线排龈法对基牙龈沟液含量和成分的影响[J]. 牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2013,23(1):41-43.
[16] 刘思言,牟雁东. 选择性双线排龈技术在前牙全瓷冠修复中的应用研究[J]. 实用医院临床杂志,2016,13(4):141-143.
[17] 陈晓峰,熊莉,汤春波. 双线排龈技术在前牙固定修复中的临床应用[J].口腔颌面修复学杂志,2017,18(5):270-272.
[18] THIMMAPPA M, BHATIA M, SOMANI P, et al. Comparative evaluation of three noninvasive gingival displacement systems:An in vivo study. J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2018;18(2):122-130.
[19] SHRIVASTAVA KJ, BHOYAR A, AGARWAL S,et al. Comparative clinical efficacy evaluation of three gingival displacement syetems.J Nat Sci Biol Med. 2015; 6(Suppl 1):S53-7.
[20] GUPTA A, PRITHVIRAJ DR, GUPTA D, et al. Clinical Evaluation of Three New Gingival Retraction Systems: A Research Report.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2013; 13(1):36-42.
[21] 王聪.排龈硅橡胶与排龈线应用效果比较[J]. 现代临床医学,2013,39(2): 121-122.
[22] 刘健,张晓明,郝鹏杰. 排龈药物对体外培养人牙龈成纤维细胞的毒性比较[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2009,27(2):202-205.
[23] 冯云枝,曾晓华. 不同排龈药物的排龈效果观察[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志,2011, 29(1):53-56.
[24] 张晓明,慧敏,刘健. 排龈时间与药物对牙龈成纤维细胞的毒性比较研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2011,27(2):248-251.
[25] 倪莹,邱振伟,孙霞,等. 3种排龈线不同时间浸堤液的细胞毒性研究[J]. 实用口腔医学杂志,2015,31(4):547-550.
[26] 倪莹,张晓明,慧敏,等. 三种排龈线对体外培养人牙龈成纤维细胞毒性的比较[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5396-5400.
[27] HUANG C, SOMAR M, LI K, et al. To cord or not to cord? That is still a question. SUMMARY REVIEW/RESTORATIVE DENTISTRY. 2017;18(1):21-22.
[28] WANG Y, FAN F, LI X, et al. Influence of gingival retraction paste versus cord on periodontal health: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Quintessence Int. 2019;50(3):234-244.
[29] HUANG C, SOMAR M, LI K, et al.Effificiency of Cordless Versus Cord Techniques of Gingival Retraction: A Systematic Review.J Prosthodont. 2017;26(3):177-185.
[30] CHANDRA S, SINGH A, GUPTA KK, et al. Effect of gingival displacement cord and cordless systems on the closure,displacement, and inflammation of the gingival crevice. J Prosthet Dent. 2016;115(2):177-182.
[31] PRASANNA GS, REDDY K, KUMAR PK,et al. Evaluation of efficacy of different gingival displacement materials on gingival sulcus width.J Contemp Dent Pract. 2013;14(2):217-221.
[32] Bennani V, Aarts JM, He LH. A comparison of pressure generated by cordless gingival displacement techniques.J Prosthet Dent. 2012;107(6):388-392.
[33] AL HAMAD KQ, AZAR WZ, ALWAELI HA, et al. A clinical study on the effects of cordless and conventional retraction techniques on the gingival and periodontal health. J Clin Periodontol. 2008;35(12):1053-1058.
[34] ABDULJABBAR TS, AL AMRI MD, AL RIFAIY MQ, et al. Effects of Gingival Retraction Paste and Subsequent Cleaning with Hydrogen Peroxide on the Polymerization of Three Elastomeric Impression Materials:An In Vitro Study.J Prosthodont. 2019; 28(6):709-714.
[35] 姜德志,屈波. ViscoStat Clear止血剂联合压线排龈法的临床疗效观察[J]. 黑龙江医药,2016,29(5):828-831.
[36] RAJAMBIGAI MA, RAJA SR, SOUNDAR SI,et al. Quick,painless,and atraumatic gingival retraction:An overview of advanced materials. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2016;8(Suppl 1):S5-S7.
[37] 欧阳罡,周欢,赵三军.不同排龈方法对排龈效果影响的对比研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2018,34(2):202-205.
[38] MAISCHBERGER C, STAWARCZYK B, VON HAJMASY A,et al. Hemostatic gingival retraction agents and their impact on prosthodontic treatment steps: A narrative review. Quintessence Int. 2018;49(9):719-732.
[39] TARIGHI P, KHOROUSHI M. A review on common chemical hemostatic agents in restorative dentistry. Dent Res J (Isfahan). 2014;11(4):423-428.
[40] KRISHNA CH V, GUPTA N, REDDY KM, et al. Laser gingival retraction: a quantitative assessment. J Clin Diagn Res.2013,7(8);1787-1788.
[41] GOUTHAM GB, JAYANTI I, JALALUDDIN M, et al. Clinical Assessment of Gingival Sulcus Width using Various Gingival Displacement Materials. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2018;19(5):502-506.
[42] 张新媛,董海涛,吴效民,等.半导体激光排龈法与排龈线排龈法的临床效果对比研究[J].现代口腔医学杂志,2018,32(1):23-24.
[43] 王婕,陈亚明. Er:YAG激光在口腔医学领域的应用及研究进展[J].激光杂志, 2015,36(9):5-9.
[44] 罗瑞,王道春. 铒激光治疗口腔疾病的应用进展[J].医学综述, 2018,24(7): 1364-1373.
[45] 杨炼,蒲高成,段少宇,等. 激光排龈法与排龈线排龈法排龈效果的临床比较研究[J].激光杂志,2015,36(5):56-60.
[46] 杨晓彤,杨永进,李超. 双线排龈法与Nd:YAG激光排龈法的临床效果比较[J].中国激光,2015,42(10):1004001-1 - 1004001-6.
[47] MELILLI D, MAUCERI R, ALBANESE A, et al. Gingival displacement using diode laser or retraction cords:A comparative clinical study.Am J Dent. 2018;31(3):131-134.
[48] 许志强,姚江武.数字化口腔修复(21)—半导体激光排龈效果的数字化分析[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2016,32(11):687-690.
[49] 刘玉凤,李玉增,沈银环,等.高频电刀结合排龈线修复老年人龈下楔状缺损的疗效观察[J].中华老年口腔医学杂志,2015,13(5):275-278.
[50] 闫改霞.临时冠在二次排龈法中的临床应用[J].求医问药下半月刊,2011, 9(12): 208-209.
[51] 许晓波,谭晓蕾,边华琴等.推龈技术在前牙美学修复中的临床应用[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2018,28(4):233-236.
[52] 游跃华. 排龈线结合推龈器排龈修复龈下楔状缺损的临床疗效[J].口腔医学, 2014,34(4):285-287.
[53] 程婧,姚江武.数字化口腔修复(34)-药物排龈线排龈对于不同牙龈生物型和牙龈形态的影响[J].临床口腔医学杂志,2017,33(6):368-371.
[54] 何光伟,张萍.三种不同排龈方法在固定义齿修复中的应用比较[J].黑龙江医药科学,2018,41(5):81-83.
[55] 冯传翠,张晓明.3种排龈方法对排龈效果影响的对比研究[J].实用口腔医学杂志,2016,32(1):127-128.
[56] 宋元英,赵强. 基于牙龈生物型探究肾上腺素对牙龈的影响[J].中国医药导报,2017,14(18):125-129.
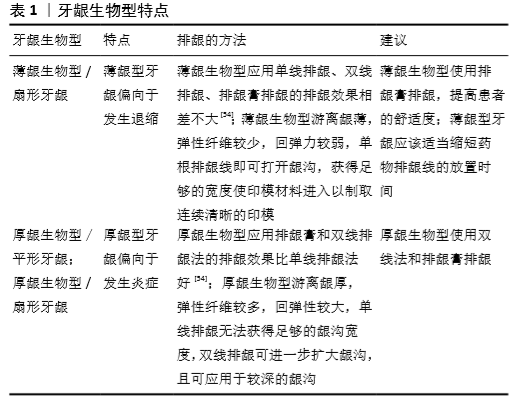
[57] 林璐,宗娟娟.牙龈生物型[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志,2015,25 (9):568-572.
[58] DALIAH SALEM, ABDULMONEM ALSHIHRI, LIRAN LEVIN, 等.排龈线残留诱发种植体周围炎[J].中国口腔医学继续教育杂志, 2014,17(6):344-346.
[59] Tabassum S, Adnan S, Khan FR.Gingival Retraction Methods:A Systematic Review.J Prosthodont. 2017;26(8):637-643.
[60] 沈银环,李雅娟,刘玉凤.不同排龈方法在老年人前牙龈下根面龋充填中的临床效果评价[J].北京口腔医学,2019,27(2):109-111. |