[1] NARITA K, NIINOMI M, NAKAI M. Effects of micro- and nano-scale wave-like structures on fatigue strength of a beta-type titanium alloy developed as a biomaterial. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2014;29: 393-402.
[2] DHIVYA S, AJITA J, SELVAMURUGAN N. Metallic Nanomaterials for Bone Tissue Engineering. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2015;11(10):1675-700.
[3] SHABALOVSKAYA S, ANDEREGG J, HUMBEECK JV. Critical overview of Nitinol surfaces and their modifications for medical applications. Acta Biomater. 2008;4(3):447-467.
[4] LIU X, CHU PK, DING C. Surface modification of titanium, titanium alloys, and related materials for biomedical applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2004; 47(3-4):49-121.
[5] 梁鹏晨,李路易,常庆,等.微弧氧化技术在骨科钛植入体生物功能改性中的应用进展[J].中国医学物理学杂志,2019,36(11): 1335-1341.
[6] BALASUNDARAM G, WEBSTER TJ. A perspective on nanophase materials for orthopedic implant applications. J Mater Chem A. 2006; 16(38):3737-3745.
[7] WEBSTER TJ, ERGUN C, DOREMUS RH, et al. Enhanced functions of osteoblasts on nanophase ceramics. Biomaterials. 2000;21(17): 1803-1810.
[8] AKIN FA, ZREIQAT H, JORDAN S, et al. Preparation and analysis of macroporous TiO2 films on Ti surfaces for bone-tissue implants. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2001;57(4):588-596.
[9] WANG Q, HU H, QIAO Y, et al. Enhanced Performance of Osteoblasts by Silicon Incorporated Porous TiO2 Coating. J Mater Sci Technol. 2012;28(2): 109-117.
[10] LIU Y, AI K, LU L. Polydopamine and its derivative materials: synthesis and promising applications in energy, environmental, and biomedical fields. Chem Rev. 2014;114(9):5057-5115.
[11] KANG SM, HWANG NS, YEOM J, et al. One-Step Multipurpose Surface Functionalization by Adhesive Catecholamine. Adv Funct Mater. 2012; 22(14):2949-2955.
[12] LEE SJ, LEE D, RIM YOON TR, et al. Surface modification of 3D-printed porous scaffolds via mussel-inspired polydopamine and effective immobilization of rhBMP-2 to promote osteogenic differentiation for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomater. 2016;40:182-191.
[13] ZHANG JK, YANG L, MENG GL, et al. Protection by Salidroside against Bone Loss via. Inhibition of Oxidative Stress and Bone-Resorbing Mediators. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57251.
[14] 梅国华,郭小芹,陈京京,等.红景天苷对成骨细胞的作用及相关分子机制研究[J].口腔医学研究,2017(9):9-12.
[15] 祁琳,王川,陈雨萌,等.红景天苷对新生大鼠颅骨成骨细胞增殖、分化及矿化的调节作用[J].武警后勤学院学报(医学版),2019, 28(3):12-17.
[16] LIU W, LI T, YANG C. Lithium-Incorporated Nanoporous Coating Formed by Micro Arc Oxidation (MAO) on Magnesium Alloy with Improved Corrosion Resistance, Angiogenesis and Osseointegration. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2019;15(6):1172.
[17] ZHOU Y, QIAN M, LIANG Y, et al. Effects of Leukemia Inhibitory Factor on Proliferation and Odontoblastic Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells. J Endod. 2011;37(6):819-824.
[18] 孙静.蛇床子素促成骨作用及代谢多态性研究[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2019.
[19] HSIN K, MATSUOKA Y, ASAI Y, et al. SystemsDock:a web server for network pharmacology based prediction and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016;44(W1):W507-W513.
[20] 梁鹏晨,周紫艳,孙苗苗,等.鄂版肺炎1号方治疗新型冠状病毒肺炎的生物信息学研究[J].上海中医药杂志,2020,54(9):1-8,19.
[21] TROTT O, OLSON AJ. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J Comput Chem. 2010;31(2):455-461.
[22] LIU H, LI W, LUO B, et al. Icariin immobilized electrospinning poly(L-lactide) fibrous membranes via polydopamine adhesive coating with enhanced cytocompatibility and osteogenic activity. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;79:399-409.
[23] YU F, CHEN S, CHEN Y, et al. Experimental and theoretical analysis of polymerization reaction process on the polydopamine membranes and its corrosion protection properties for 304 Stainless Steel. J Mol Struct. 2010;982(1-3):152-161.
[24] JIANG J, ZHU L, LI X, et al. Surface modification of PE porous membranes based on the strong adhesion of polydopamine and covalent immobilization of heparin. J Membr Sci. 2010;364(1): 194-202.
[25] CHEN S, CHEN Y, LEI Y, et al. Novel strategy in enhancing stability and corrosion resistance for hydrophobic functional films on copper surfaces. Electrochem Commun. 2009;11(8):1675-1679.
[26] LEE JJ, PARK IS, SHIN GS, et al. Effects of polydopamine coating on the bioactivity of titanium for dental implants. Int J Precis Eng Manuf. 2014; 15(8):1647-1655.
[27] SU L, YU Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Strong Antibacterial Polydopamine Coatings Prepared by a Shaking-assisted Method. Sci Rep. 2016;6(1):24420-24420.
[28] SHISHU H, NUANYI L, YANG H, et al. Polydopamine-Assisted Surface Modification for Bone Biosubstitutes. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016: 2389895.
[29] 沈佳丽,石畅,施冬健,等.多巴胺对骨修复材料表面改性的研究进展[J].材料导报,2017,31(21):54-61.
[30] ZHANG T, ZHOU W, JIA Z, et al. Polydopamine-assisted functionalization of heparin and vancomycin onto microarc-oxidized 3D printed porous Ti6Al4V for improved hemocompatibility, osteogenic and anti-infection potencies. Sci China Mater. 2018;61(4):579-592.
[31] POH CK, SHI Z, LIM TY, et al. The effect of VEGF functionalization of titanium on endothelial cells in vitro. Biomaterials. 2010;31(7): 1578-1585.
[32] LEE JS, LEE JC, HEO JS. Polydopamine-assisted BMP-2 immobilization on titanium surface enhances the osteogenic potential of periodontal ligament stem cells via integrin-mediated cell-matrix adhesion. J Cell Commun Signal. 2018;12(4):661-672.
[33] YING Y, LUO J. Salidroside promotes human periodontal ligament cell proliferation andosteocalcin secretion via ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Exp Ther Med. 2018;15(6):5041-5045.
[34] 占跃晨,张立鹏,毛根祥,等.红景天苷调节人成骨肉瘤细胞MG63成骨分化及相关信号的研究[J].中国医药生物技术,2013,8(6): 414-419.
[35] GUO XQ, QI L, YANG J, et al. Salidroside accelerates fracture healing through cell-autonomous and non-autonomous effects on osteoblasts. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;367(2):197-211.
[36] SONG J, JIN P, LI M, et al. Antibacterial properties and biocompatibility in vivo and vitro of composite coating of pure magnesium ultrasonic micro-arc oxidation phytic acid copper loaded. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2019;30(5):1-14.
[37] 申婷婷.钛植入体表面乳铁蛋白复合涂层的制备及其生物学评价[D].重庆:重庆大学,2018.
[38] CHEN JJ, ZHANG NF, MAO GX, et al. Salidroside stimulates osteoblast differentiation through BMP signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol. 2013;62:499-505.
[39] JAISWAL RK, JAISWAL N, BRUDER SP, et al. Adult human mesenchymal stem cell differentiation to the osteogenic or adipogenic lineage is regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2000; 275(13): 9645-9652.
[40] 张波,耿彬,谭小义,等.MAPK信号通路与骨质疏松关系的研究进展[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2014,22(23):2161-2164.
|
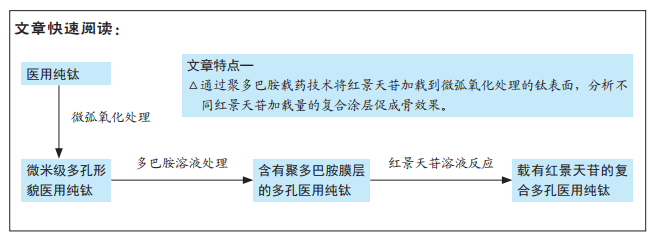 文题释义:
文题释义: