2.1 陶瓷材料的磨损机制及磨损行为的影响因素
2.1.1 陶瓷材料磨损机制 陶瓷材料的磨损机制主要分为磨粒磨损、黏着磨损和腐蚀磨损等3种。
磨粒磨损:包括二体磨粒磨损和三体磨粒磨损。磨粒磨损是牙科修复材料中最常见的磨损类型,一般发生在塑性接触下[5],主要机制是进行犁耕,通过压痕将粗糙物或硬质颗粒压入对磨物的较软表面,从而去除材料,因此它在滑动过程中会形成磨粒凹槽,这些磨损痕迹取决于锯齿状材料的性质及切削机制,从韧性表面的微切削到脆性材料的微断裂[1]。
黏着磨损:主要发生在滑动接触过程中反复的交变载荷作用下,形成塑性形变区并产生微裂纹,微裂纹在循环载荷作用下扩展[6]。由滑动引起的摩擦力在接触界面上引入剪切力,拉应力在滑动压头的后缘产生[5]。循环运动有利于裂纹的成核和扩展,最终导致裂纹达到表面。材料亚表面由于反复循环加载,部分锥裂纹形成,锥裂纹形态密度由摩擦系数和断裂韧性决定[1]。
腐蚀磨损:陶瓷体外化学腐蚀是由于陶瓷材料长期暴露在口腔酸性环境下导致的,水、人工唾液、牙齿漂白剂、酸性溶液、含乙醇的漱口水和软饮料均会产生不同程度的腐蚀损伤,化学腐蚀会显著影响其显微硬度、抗弯强度和表面粗糙度,表面粗糙度增加会降低材料抗弯强度,增加对合牙表面磨损及菌斑堆积,最终导致继发龋及牙周疾病[6]。由于腐蚀损伤的发生十分缓慢,因而进行体外模拟实验十分困难。实验研究表明,采用pH循环性测试方法比在单一pH值条件下能够更好地模拟口内腐蚀磨损行为[7]。尽管陶瓷材料相较于牙釉质对酸性溶液的敏感性低,但陶瓷材料仍会被酸性溶液降解。因此,陶瓷修复材料应用于胃食管反流症患者需要更多的考量陶瓷材料的腐蚀磨损量。
2.1.2 磨损行为影响因素 陶瓷材料属于脆性材料,其磨损机制主要为裂纹扩展机制,但对于不同类型的陶瓷材料,磨损机制会有所差异。陶瓷材料磨损机制的影响因素包括陶瓷材料的类型、微观结构、断裂韧性、表面粗糙度、摩擦系数、接触载荷、口腔环境和循环次数等[6]。总的来说,陶瓷材料磨损机制主要受接触载荷的影响。在较高接触载荷下,由于陶瓷的高弹性模量和高摩擦力导致接触面产生高拉应力,导致釉质接触表面裂纹扩展和发生分层磨损,以致磨损量呈指数级增加,称为严重磨损。而在较低的接触载荷下,由于陶瓷的晶体硬度较高,釉质主要表现为磨粒磨损,称为轻度磨损[5-6]。目前陶瓷材料磨损实验研究证明,陶瓷材料的机械性能(包括弹性模量、硬度、韧性及强度等)与陶瓷材料耐磨性相关,但高机械性能并不能直接转化为高耐磨性,特别是在较高的接触载荷下。
2.2 陶瓷材料磨损研究方法

2.2.1 对磨物 主要包括牙釉质、滑石瓷和硬质陶瓷等3种。
牙釉质:虽然可以最直观模拟口内条件,但由于选择的牙釉质尖端几何形状无法形成统一的标准,得出的磨损结果也有巨大差异;其次由于供体牙釉质年龄不同,牙釉质的弹性模量及耐磨性也有显著差异。目前实验研究中较少使用,多用于对照组参考。
滑石瓷:由于可以标准化,因而磨损结果可进行量化描述,由于与釉质相似的磨损率,其磨损行为介于釉质与本质间。滑石瓷的缺点是硬度及初始粗糙度高于釉质[2],是目前实验研究较常用的对磨物。
硬质陶瓷:多为表面高度抛光的硬质氧化锆球。Wendler等[5]选用高度抛光的硬质氧化锆球作为对磨物时,氧化锆硬度高模拟了口腔中磨损量最大时的条件,可以指导保守材料设计,同时提高材料易损性易发生断裂,可在较少循环加载中获得所需实验结果。多用于同时观察材料疲劳断裂行为实验中[8]。同时硬质氧化锆在磨损实验中自身的磨损量、化学降解量小,更有利于控制变量。此外,由于白榴石增强陶瓷IPS Empress由于其机械性能及磨损率与牙釉质相似且可以进行标准化处理,也是体外模拟实验中常用的对磨物。
2.2.2 体外试验设计 目前常用于体外磨损实验的仪器主要有立式万能摩擦磨损试验机和口腔咀嚼模拟器,见图3。

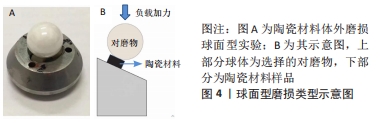
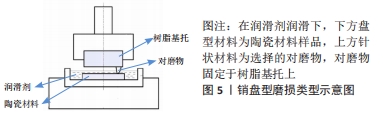
仪器的磨损类型主要有球面型(ball-on-flat test)和销盘型(pin-on-disk test),由于球面型磨损负载的疲劳应力较小,在同等条件下,销盘型磨损会多于球面型,可根据不同实验设计综合选择[9],见图4,5。
目前比较常用的磨损定性定量分析方法包括:用纳米压痕仪测量陶瓷试样的硬度及弹性模量;用白光干涉3D轮廓仪分析陶瓷试样表面粗糙度,测量表面形貌应用计算机软件计算体积损失;用精密天平测量滑石瓷体积损失;用扫描电子显微镜分析材料三维形貌及磨损下表面的微观结构;用X射线衍射仪分析材料的相变、测定应力及晶粒尺寸。
陶瓷材料磨损实验设置、测试结果与临床磨损还是存在许多差异,如何更好地模拟口腔内环境,口颌系统的运动方式是目前体外实验研究的一大挑战。虽然目前研制出许多种类的机器人模拟器,通过使用计算机平台来模拟整个下颌运动过程,可以更好地模拟体内环境,其应用的相关研究数据较少,还需要更多的实验研究。
2.2.3 体外条件模拟 体外条件模拟需要根据患者口腔生理情况选择测试参数,具体数值为口腔生理咀嚼力范围为45-125 N,在咬合初始时,咀嚼力的大小为10-20 N,在咀嚼循环结束时,磨牙的咬合力增加至100-140 N,切牙的咬合力增加至25-45 N,整个咀嚼周期持续约0.8 s,而其中上下牙接触平均持续时间为0.4-0.6 s,滑动接触距离小于1 mm,滑动速度为0.25-0.50 mm/s。排除患有磨牙症的正常成年人每日牙齿与对颌牙接触总时长为15-20 min,由于进食频率和习惯会有所差异。平均咀嚼频率约为1.6 Hz(范围为0.9-2.1 Hz)。正常成年人1年大约要进行33万次咀嚼[9]。目前实验中多选用40 N,50 N,100 N的负载,负载越高,磨损量越大。然而,负载会有一个临界点,高于临界点,增加负载也不会导致磨损增多,具体选取的负载大小,应根据不同陶瓷材料,不同实验目的综合考量。如某些实验中为了模拟紧咬牙和磨牙症情况,应用200 N的负荷能够保证裂纹的发生和扩展[10]。对于如氧化锆等耐磨性较高的陶瓷材料,如果参数较小会导致磨损量过少而无法测量[5]。
2.2.4 体外实验局限性 牙齿表面损失具有多因素性,几种磨损机制同时作用并以非常复杂的方式相互影响,如生理因素(年龄影响)和病理因素(严重牙齿磨损)。因此,要同时考虑牙齿磨损的各个方面来预测实际的磨损机制是非常困难的。体外摩擦磨损实验无法模拟咀嚼的复杂生物力学,复杂的口腔环境和相关因素如pH值、温度变化及个体进食差异[1]。当有新的陶瓷材料出现时,应用于临床试验前,均需在实验室通过可靠的磨损测试方法来评估材料的耐磨性。但目前的体外磨损实验方法缺乏统一性,不同实验中应用的测试仪器、测试方法、分析方法、参数设置、统计学分析均有较大差异,因而无法进行陶瓷材料间的横向比较。如何设置一个最佳口颌系统运动装置,建立统一的实验设计方案,是陶瓷修复材料体外实验设计的一大挑战。
2.3 口腔修复全瓷材料磨损性能
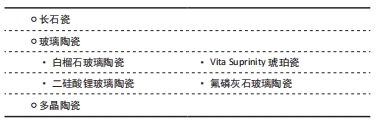
与直接修复材料相比,陶瓷和铸造合金等间接修复材料的磨损率明显较低,且陶瓷是所有间接修复材料中耐磨性最强的[10]。修复材料在磨损过程中产生的磨损颗粒如果被患者吞食或吸入可能会产生不良反应。由于陶瓷材料耐磨性高,且被认为是相对惰性的材料,相对于其他较易过敏的含铬、镍的合金和耐磨性较差的复合树脂材料,陶瓷材料修复体的安全性更高。根据全瓷材料的内部结构将全瓷材料分为3大类:主要为玻璃相的长石瓷,同时含有玻璃相和晶相的玻璃陶瓷,不含玻璃相的多晶陶瓷。
2.3.1 长石瓷 目前临床使用的长石瓷主要是Vita Mark II长石瓷块,无需进行热处理,主要用于椅旁CAD/CAM。Vita Mark II长石瓷为包含7 μm长石晶体分散于玻璃基质中的非均质结构,其硬度较牙釉质低,耐磨性高于牙釉质但不如其他CAD/CAM瓷块,磨损表面可见较大裂纹和深凹槽。由于其有限的强度及耐磨性,可用于嵌体、贴面和前牙单冠的修复[11]。
2.3.2 玻璃陶瓷
白榴石玻璃陶瓷:目前临床使用的白榴石玻璃陶瓷主要是IPS Empress CAD瓷块,主要用于椅旁CAD/CAM单颗牙齿修复。IPS Empress CAD瓷块为3-5 μm白榴石晶体分散于玻璃基质中的非均质结构,其硬度及耐磨性仅高于牙釉质及长石瓷,磨损表面可见小裂纹和粗糙面,可用于贴面、嵌体、前牙前磨牙单冠[11]。
二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷:传统的热压铸塑二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷具有较高机械性能、弹性模量、断裂韧性,本身耐磨性差但其对磨物磨损量较低。Peng等[12]研究发现未抛光的二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷表面以三体磨损为主,抛光的二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷表面以二体磨损为主。因此在临床应用中椅旁抛光对于获得耐磨损的长期稳定修复十分重要。目前临床应用的二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷还有IPS emax CAD是一种椅旁CAD/CAM材料,其磨损学行为与传统热压铸塑材料相似[13]。IPS emax CAD长期暴露于酸性溶液尤其是盐酸中会导致二硅酸锂晶体的降解,其在盐酸溶液中的质量损失约为氧化锆材料的3倍,因此二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷应尽量避免用于患有胃食管反流症的患者[14]。
Vita Suprinity琥珀瓷:是一种新型氧化锆加强型硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷,玻璃陶瓷中约含10%氧化锆成分,形成均匀精细的内部晶体结构,使其耐磨性明显高于传统二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷,长期疗效有待观察,其可预测性不如其他材料[15]。Vichi等[16]的研究比较了2种CAD/CAM二硅酸锂陶瓷的表面性能,Vita Suprinity表面粗糙度低于IPS emax CAD,光泽度高于IPS emax CAD,且具有更好的抛光性,对于抛光和上釉的敏感性均高于IPS emax CAD。用抛光膏进行约60 s的手工抛光对降低二硅酸锂玻璃陶瓷表面粗糙度效果最好,可获得最佳的光泽度。Vita Suprinity的磨损性能、美学性能更优,在临床应用中更具优势,但应用于临床时间较短,其性能还有待更多临床研究。
氟磷灰石玻璃陶瓷:Zhang等[3]发现,氟磷灰石陶瓷比二硅酸锂陶瓷更耐磨,但随着循环加载增加,其磨损机制会由磨粒磨损转化为疲劳磨损,更易破损,尤其是在潮湿环境或三体磨损机制下。在二体磨损机制下,氟磷灰石陶瓷初始表面粗糙度越大,早期摩擦系数和磨损量越大,因此抛光后的氟磷灰石陶瓷拥有更佳的摩擦磨损性能[17]。临床上常见的氟磷灰石饰面的二硅酸锂冠修复会增加材料自身及对合天然牙的磨损,因此应避免在咬合面使用这类修复。
2.3.3 多晶陶瓷 多晶陶瓷主要包括氧化铝陶瓷和氧化锆陶瓷。因氧化铝陶瓷性能较差目前不在临床应用。仅介绍目前临床常用的氧化锆陶瓷。
在正常口腔生理测试参数范围下,氧化锆由于其较小的晶粒大小及高硬度,在磨损过程中会更光滑,且由于其高弯曲强度及断裂韧性,会避免表面微裂纹及磨损颗粒产生[18],因此现在临床上全冠修复多用整体氧化锆全冠。适当的表面抛光可以显著提高氧化锆的磨损性能。氧化锆因其紧密的颗粒结构椅旁调整比较困难。实验研究表明,高度抛光的咬合面可以降低对合牙釉质磨损,抛光的氧化锆陶瓷表现出的磨损性能优于喷砂、上釉及饰瓷[19]。在临床应用中,对于氧化锆修复体大量的咬合调整会影响其表面光滑度,降低耐磨性。因此,如进行了大量咬合调整,应将修复体进行仔细抛光处理[20]。
整体氧化锆通常为钇锆陶瓷Y-TZP(含氧化钇的氧化锆陶瓷)。Stober等[21]的一项临床研究收集了20例无磨牙症的进行氧化锆全冠修复的患者随访2年中的磨损量,结果显示氧化锆对磨牙釉质的平均垂直丧失为46 μm,而对照组正常牙釉质平均垂直丧失为19-26 μm。根据定期随访的数据分析得出在经过最初的咀嚼磨合期后,第2年的氧化锆及对磨牙釉质的磨损率有轻微减少。因此目前的大多体外实验的咀嚼循环周期次数应增加至相当于口腔内超过2年的咀嚼循环。根据临床实验数据可以假设氧化锆全冠使用20年,此时对磨牙釉质平均垂直损失量仅高于对照组约0.5 mm。氧化锆全冠对于对磨牙釉质的磨损量远小于其他玻璃陶瓷。Jin等[22]研究证明,对于比牙釉质硬度低的人工树脂牙,氧化锆修复对于对磨人工树脂牙的磨损量仍小于长石瓷。
临床上多用3 mol% Y-TZP。但其美学性较低。增加氧化钇含量(4 mol%,5 mol%)可以改善材料的透明性,但会降低氧化锆陶瓷的断裂韧性和强度。实验结果表明,当表面光洁度良好时,4Y-TZP,5Y-TZP与3Y-TZP有相似的二体磨损性能,均有较高的耐磨性和较少的对磨物磨损[23]。Zhang等[23]研究证明高半透明氧化锆陶瓷在各种对磨物磨损条件下磨损性能由优于其他玻璃陶瓷,更适用于全冠修复。但考虑到氧化锆多用于高咀嚼应力承载区域,需要进一步评估这些高半透明氧化锆陶瓷在更高咀嚼负载下的磨损行为。高透明的氧化锆陶瓷由于其可以通过染色上釉达到较好美学效果,也可用于椅旁CAD/CAM。有研究表明CAD/CAM整体氧化锆比玻璃陶瓷材料耐磨性更高[24-25]。Tang等[26]为期96周的临床研究证明CAD/CAM整体氧化锆对牙周组织无不良影响,具有良好的生物相容性,且对对磨牙磨损小,后牙区全冠修复成功率高。
2.4 新型树脂陶瓷复合材料磨损性能
2.4.1 聚合物渗透陶瓷Vita Enamic El Zhawi等[27]研究发现聚合物渗透陶瓷硬度较低,为非晶体结构,表面润湿性与氧化锆相似。与玻璃陶瓷材料相比,聚合物渗透陶瓷材料具有较低的硬度和弹性模量,但具有更高的韧性,能够进行快速铣削,承受较大的咬合接触载荷[28]。目前临床使用的聚合物渗透陶瓷主要是Vita Enamic,其磨损机制主要是脆性断裂及磨粒磨损,由于其本身陶瓷颗粒及多聚物基质间缺乏黏接力,材料磨损损伤高于玻璃陶瓷材料,但其对合牙磨损损伤与氧化锆相似,均处于较低水平[29]。Vita Enamic耐磨性较差,目前临床上多用于嵌体、高嵌体修复,Spitznagel等[30]为期3年的临床研究证明其作为嵌体、高嵌体临床成功率较高。对Vita Enamic进行良好的抛光是临床上最佳的提高其磨损性能的方法。Vita Enamic为质量分数约86%的长石瓷基质及低粘度聚合物渗透。在酸性溶液中陶瓷内容物会发生降解,导致显微硬度降低,表面粗糙度升高,耐磨性降低,发生更加严重的磨粒磨损,材料下表面更易产生微裂纹。因此在胃食管反流症的患者中应避免使用Vita Enamic [31]。
2.4.2 树脂纳米陶瓷Lava Ultimate Lava Ultimate优韧瓷是一种树脂纳米陶瓷,具有良好的断裂韧性,不易折裂崩瓷。磨损实验研究表明,与玻璃陶瓷相比,Lava Ultimate陶瓷断裂韧性较高,耐磨性较差磨损量大,但对对磨物的磨损量小[32]。Yin等[33]的研究比较了目前市面上的新型树脂陶瓷复合材料的力学性能,Lava Ultimate的抗弯强度和磨损性能在目前的新型树脂陶瓷复合材料中最优,具有更适合口腔临床修复的机械性能。Lava Ultimate由质量分数80%增强团簇纳米陶瓷填料和树脂聚合体基质组成,因此具有高韧性及良好的耐磨性。Lava Ultimate的最大抗弯强度约为140 N,与人单侧天然磨牙咬合力相似,且远高于前牙最大咬合力。
根据目前实验研究Lava Ultimate适用于贴面、嵌体、高嵌体,然而在后牙区应用于年轻患者、磨牙症患者其断裂风险较高,需谨慎应用。Min等[34]研究表明Lava Ultimate与患有轻度氟斑牙釉质的磨损下表面微观结构相似,Lava Ultimate适合用于轻度氟牙症患者的修复。Sagsoz等[14]的研究表明,酸性溶液对于玻璃基陶瓷的影响高于树脂陶瓷复合材料。相对于玻璃陶瓷,树脂陶瓷复合材料的聚合物结构相对不易受到酸性溶液影响。
因此在胃食管反流症患者中应用Lava Ultimate还是一种不错的选择。目前由于Lava Ultimate应用于临床时间较短,其磨损性能还有待更多的体外体内研究。
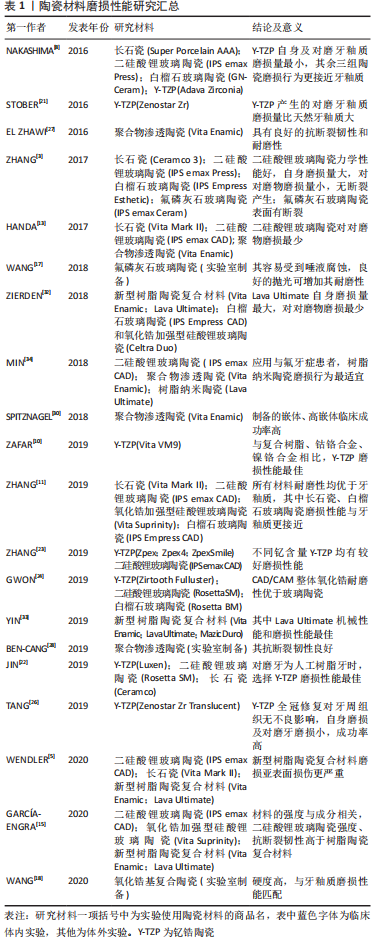
关于陶瓷材料磨损性能实验研究及结论的总结,见表1。
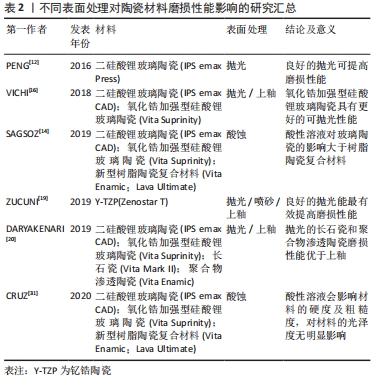
不同表面处理对陶瓷材料磨损性能的影响的总结,见表2。