中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (4): 585-590.doi: 10.12307/2022.096
• 组织工程口腔材料 tissue-engineered oral materials • 上一篇 下一篇
三维有限元分析牙种植体孔隙结构设计及生物力学性能
张建国1,陈 晨1,胡凤玲2,黄道宇1,宋 亮2
- 1上海应用技术大学机械工程学院,上海市 201418;2复旦大学附属上海市第五人民医院口腔科,上海市 200240
Design and biomechanical properties of dental implant pore structure based on three-dimensional finite element analysis
Zhang Jianguo1, Chen Chen1, Hu Fengling2, Huang Daoyu1, Song Liang2
- 1School of Mechanical Engineering, Shanghai Institute of Technology, Shanghai 201418, China; 2Department of Stomatology, Shanghai Fifth People’s Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai 200240, China
摘要:
文题释义:
应力遮蔽:是指两种或两种以上不同弹性模量(刚度)材料共同承受外载荷时,弹性模量较高的材料会承担较多载荷,弹性模量较低的材料会承担较少载荷。由于种植体材料的弹性模量与周围骨组织的弹性模量差距过大,造成种植体上的应力不能有效传递至周围骨组织上,而周围骨组织在应力刺激过小时会发生骨萎缩(骨吸收)。
表面改性:通过涂层技术、喷砂酸蚀处理技术、激光酸蚀处理技术及化学酸蚀处理技术和增加多孔结构等方式,增加种植体表面的粗糙度和减低种植体的弹性模量来提升骨结合效果的方式称为表面改性。文章通过增加多孔结构并改变孔隙结构的方式改变表面特性来提升种植体的生物力学性能。
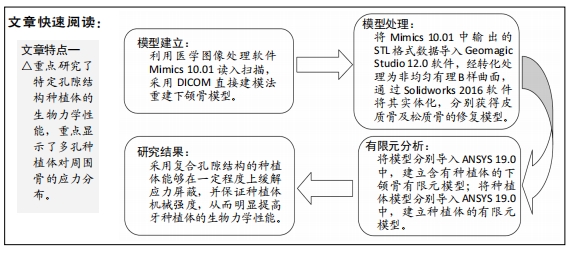
目的:通过有限元分析不同微观孔结构牙种植体生物力学性能,阐明不同微观孔结构对周围骨应力和种植体力学性能的影响。
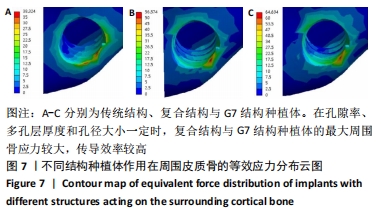
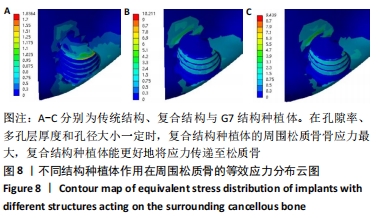
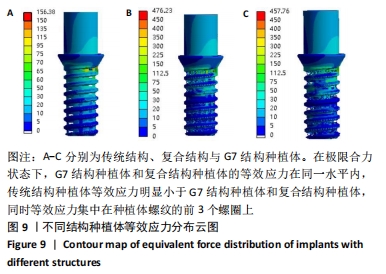
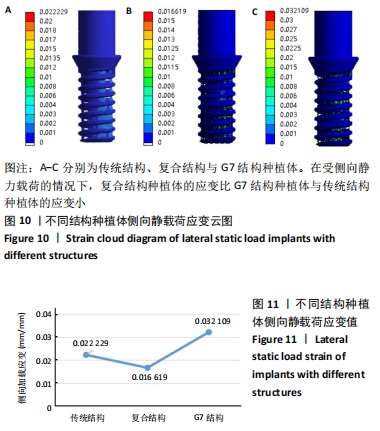
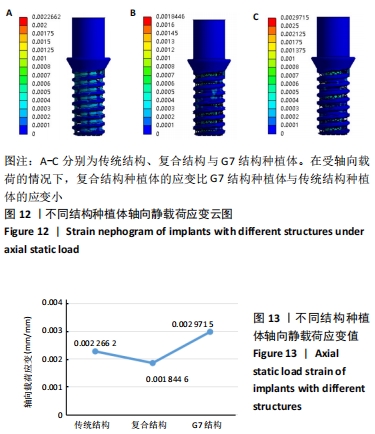
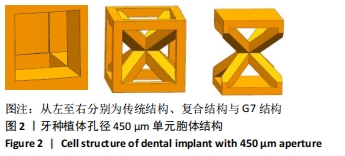
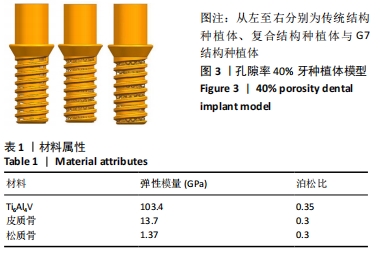
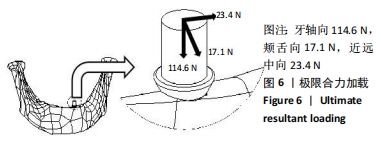
方法:通过CT扫描建立下颌骨模型和3种不同孔隙结构(传统结构孔隙、复合结构孔隙、G7结构孔隙)的牙种植体有限元模型,孔隙率为40%,多孔层厚度为1.2 mm,孔径为0.45 mm,模拟极限合力状态对每个模型施加载荷,采用ANSYS有限元软件运算并分析周围骨应力及种植体的应变。
结果与结论:①当种植体受极限合力,传统结构、复合结构与G7结构牙种植体对周围皮质骨等效应力最大值分别为38.324,56.574,64.694 MPa,对周围松质骨等效应力最大值分别为1.836,10.221,9.439 MPa,种植体等效应力最大值分别为156.38,476.23,457.76 MPa;复合结构种植体的最大周围骨应力在促进骨结合的范围内;②当种植体只受侧向力时,传统结构、复合结构与G7结构牙种植体应变最大值分别为 2.222 9×10-2,1.661 9×10-2,3.210 9×10-2 mm/mm;当种植体只受轴向力时,传统结构、复合结构与G7结构牙种植体应变最大值分别为 2.266 2×10-3,1.844 6×10-3,2.971 5×10-3 mm/mm;说明在受侧向静力载荷和轴向载荷时,复合结构种植体的应变最小,产生的微动小,有助于提高骨结合效果;③结果表明,随多孔种植体内部孔隙单元结构的变化,周围骨应力发生明显变化,种植体力学性能也发生明显变化,种植体表面多孔结构的单元胞体结构形状的改变显著影响弹性模量和种植体的力学性能,复合孔隙结构的牙种植体与传统结构和G7结构相比具有更好的生物力学性能。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4651-4803 (张建国)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:生物材料;骨生物材料; 口腔生物材料; 纳米材料; 缓释材料; 材料相容性;组织工程
中图分类号: