中国组织工程研究 ›› 2022, Vol. 26 ›› Issue (7): 1107-1112.doi: 10.12307/2022.152
• 干细胞综述 stem cell review • 上一篇 下一篇
传递特定miRNA的外泌体可调控成骨并促进成血管
周洪琴,吴丹丹,杨 琨,刘 琪
- 遵义医科大学附属医院牙周科,贵州省遵义市 563003
-
收稿日期:2021-02-09修回日期:2021-02-20接受日期:2021-03-31出版日期:2022-03-08发布日期:2021-10-29 -
通讯作者:刘琪,博士,教授,遵义医科大学附属口腔医院牙周科,贵州省遵义市 563003 -
作者简介:周洪琴,女,1992年生,贵州省遵义市人,汉族,遵义医科大学在读硕士,主要从事干细胞方面的研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(81860196),项目负责人:刘琪;国家自然科学基金(81760199),项目负责人:杨琨
Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis
Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi
- Department of Periodontology, Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China
-
Received:2021-02-09Revised:2021-02-20Accepted:2021-03-31Online:2022-03-08Published:2021-10-29 -
Contact:Liu Qi, MD, Professor, Department of Periodontology, Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
About author:Zhou Hongqin, Master candidate, Department of Periodontology, Stomatological Hospital Affiliated to Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi 563003, Guizhou Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81860196 (to LQ); and National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81760199 (to YK)
摘要:
文题释义:
外泌体:是一种细胞旁分泌产生的纳米尺度的细胞外脂质双层囊泡,直径40-150 nm,由细胞经过“内吞-融合-外排”等系列调控过程产生并分泌外泌体,其内含功能性蛋白质、mRNA、microRNA等物质,作为细胞间通讯的载体,通过转运、内吞的方式进入靶细胞,调节细胞基因表达,改变细胞命运。
MiRNAs:是长度为18-25个核苷酸的一种小的非编码RNA,可通过结合mRNA的3’端非翻译区抑制mRNA转录或降解mRNA来沉默靶基因,在多种生物过程中起重要作用。
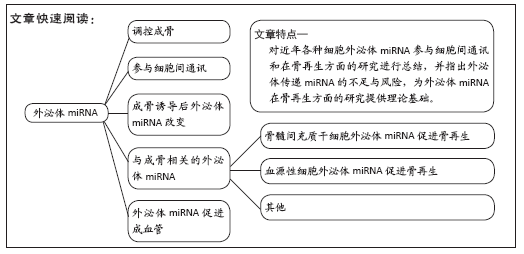
背景:外泌体是细胞旁分泌的纳米级囊泡,含有多种生物活性因子,外泌体miRNA在细胞间通讯中起重要作用。近年来,越来越多的研究着眼于外泌体内miRNA是否促进骨再生。
目的:就近年来外泌体miRNA促进骨再生的研究现状进行综述,为其在骨再生领域进一步研究和应用提供理论依据。
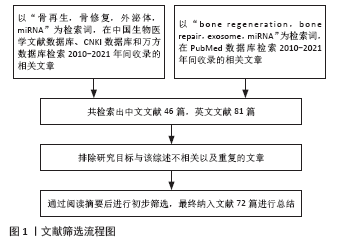
方法:以“骨再生,骨修复,外泌体,miRNA”“bone repair,bone regeneration,exosome,miRNA”为检索词,在中国生物医学文献数据库、CNKI数据库、PubMed数据库中检索2010-2021年间收录的与外泌体miRNA和骨再生相关的文章。
结果与结论:不同来源细胞外泌体通过传递特定miRNA可有效调控成骨,并促进成血管,在骨组织工程中有广泛前景。
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-5620-5246(周洪琴)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
引用本文
周洪琴, 吴丹丹, 杨 琨, 刘 琪. 传递特定miRNA的外泌体可调控成骨并促进成血管[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112.
Zhou Hongqin, Wu Dandan, Yang Kun, Liu Qi. Exosomes that deliver specific miRNAs can regulate osteogenesis and promote angiogenesis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(7): 1107-1112.
2.2 外泌体miRNA参与细胞间通讯 2007年,VALADI等[18]发现外泌体可在细胞间转移miRNA实现细胞间通讯,外泌体介导的miRNA转移可对受体细胞产生影响,如调节蛋白表达。外泌体相关miRNA可以在囊泡结构的保护下稳定在血液循环中而不被降解,然后转移到靶细胞中抑制某些基因的表
达[19-20]。外泌体一旦被邻近或远端细胞吸收,外泌体miRNA在基因表达的转录后调控中起着重要作用。外泌体miRNA进入靶细胞,通过部分序列互补与靶基因mRNA结合。外泌体miRNA参与不同生理过程和病理发生发展,包括伤口愈合、炎症、骨折愈合和阿尔茨海默病[21-24]。miRNA的5’端有7个核苷酸组成种子区,这是mRNA识别的关键。miRNA与靶mRNA结合,通过形成miRISC调控蛋白质合成[25]。许多研究证明了细胞来源外泌体miRNA在细胞间通讯起重要作用,改变外泌体中miRNA可影响多种疾病进程,如癌症、阿尔茨海默症和心肌梗死等[26-28]。例如,氧化应激下心肌祖细胞分泌的外泌体miR-21通过靶向PDCD4抑制H9C2心肌细胞的凋亡[29]。
2.3 成骨诱导后外泌体miRNA改变 在成骨诱导过程中,细胞内会发生一系列改变,外泌体内miRNA也会发生相应变化。不同细胞在成骨诱导分化过程中分泌的外泌体miRNA也会有所不同。
间充质干细胞来源外泌体的应用为组织工程和再生医学提供一种新的策略。WANG等[30]发现来自不同成骨分化阶段的间充质干细胞外泌体可使同型细胞向成骨谱系分化,但只有来自成骨分化晚期的外泌体可诱导细胞外基质矿化。MiRNA谱分析发现一组与成骨分化后期差异表达的外泌体miRNA与成骨形成相关。靶标预测表明,这些miRNA富集通路参与了成骨分化的调控和外泌体发挥其功能的一般机制,如Wnt信号通路和内吞作用。最近,ZHAI等[4]提取成骨诱导10 d和15 d间充质干细胞的外泌体(EXO-D10、EXO-D15),发现能促进间充质干细胞成骨分化,并将此外泌体加载到3D打印纯钛支架,然后植入大鼠骨缺损处,发现有哈弗斯管结构的新骨和血管形成;用下一代测序技术检测外泌体差异表达的miRNA,相对未成骨诱导间充质干细胞分泌的外泌体(EXO-D0),EXO-D10、EXO-D15中分别有166和193种miRNA上调,139和150种miRNA下调;在EXO-D10、EXO-D15中,与成骨相关的miRNA如Hsa-miR-146a-5p、Hsa-miR-503-5p、Hsa-miR-483-3p、Hsa-miR-129-5上调,这些miRNA在EXO-D10、EXO-D15中的丰度高于其他外泌体,根据下一代测序技术测序结果分析,PI3K/Akt信号通路和MAPK信号通路可能在间充质干细胞成骨过程中起主导作用,miRNA可能与生长因子或受体如TARF6、FGF2、BMPR、BMP1和RUNX2相互作用,激活PI3K/Akt和MAPK信号通路,促进间充质干细胞的成骨。
XU等[31]使用安捷伦定制miRNA v3.5阵列绘制了人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中外泌体内差异表达的miRNA,检测到79个miRNA。研究发现,在培养骨髓间充质干细胞0,0.5,1,1.5,2,2.5,3,3.5,4,4.5,7 d时,骨髓间充质干细胞培养上清中有14个外泌体miRNA的差异表达,其中0.5-7 d,5个miRNA (miR-199b,miR-218,miR-148a,miR-135b和miR-221)变化超过0 d变化最大值的2倍以上。通过DIANA-mirPath的生物信息分析表明,RNA降解、mRNA监视通路、Wnt信号通路、RNA转运是最显著的富集于与成骨分化相关的不同外泌体miRNA模式分位的通路。
YANG等[32]通过微阵列分析来自未分化和成骨分化脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体miRNA的表达谱,相对于未分化的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体,成骨诱导分化的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体有201个miRNA上调,33个miRNA下调。选取差异表达最明显的6个miRNA (miR-130a-3p、miR-513b-5p、miR-30b-5p、miR-34a-5p、miR-324-5p、miR-378f),用qPCR验证微阵列分析,结果与微阵列获得的初步结论一致,与未分化脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体相比,成骨分化脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体中5个miRNA (miR-130a-3p、miR-30b-5p、miR-34a-5p、miR-324-5p和miR-378f)的表达显著增加。外泌体miRNA可以通过一系列生物学过程影响成骨分化,在这些过程中,它们首先靶向相关基因,从而调控MAPK信号通路和Wnt信号转导并修饰基因表达、细胞代谢等生物学功能促进成骨。MiRNA-mRNA网络分析显示一个miRNA可以同时识别多个靶标mRNA,一个基因也可能受多个miRNA的调控。更重要的是,大量miRNA被预测参与多种促进成骨分化的途径。例如,miR-130a-3p是差异表达最高的miRNA,预测其与SIRT7结合的可能性很高。既往研究发现,敲低SIRT7可增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[33]。
牙周膜干细胞是牙周膜来源的间充质干细胞,牙周膜干细胞较其他牙干细胞如牙髓干细胞和牙滤泡祖细胞具有更佳的再生能力和多能性[34]。牙周膜干细胞是一种比较容易获得的间充质干细胞,并已用于骨再生[35]。LIU等[36]发现成骨诱导可增强牙周膜干细胞来源外泌体的成骨能力,促进大鼠骨髓干细胞的成骨分化。通过RNA测序分析未分化和成骨分化牙周膜干细胞外泌体miRNA表达谱,结果显示,成骨诱导后72个miRNA表达上调(其中4个miRNA显著上调:miR-122-5p,miR-142-5p,miR-25-3p,miR-192-5p),35个miRNA表达下调(其中3个miRNA显著下调:miR-125b-5p,let-7b-5p,miR-100-5p)。基因本体论分析和路径分析结果表明,外泌体miRNA差异表达的靶基因参与多种生物学过程,如催化活性、蛋白质绑定、代谢过程、细胞的发育和分化,并富含成骨分化相关途径,如MAPK信号传导、AMPK信号和胰岛素信号通路。
诱导干细胞成骨分化后,干细胞分泌的外泌体miRNA表达与未分化的干细胞有所不同,许多变化的miRNA与成骨分化有关,但还未经过进一步的实验验证。
2.4 与成骨相关的外泌体miRNA
2.4.1 骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体miRNA促进骨再生
(1)miR-29a:miR-29a可调节血管生成[37],LU等[38]发现骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体可被人脐静脉内皮细胞吸收,并促进人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖、迁移和管的形成。MiR-29a在骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中表达较高,可通过VASH1依赖的方式转运到人脐静脉内皮细胞中调控血管生成。更重要的是,携带miR-29a的骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体具有促进小鼠血管生成和成骨的强大能力。
(2)miR-122-5p:LIAO等[39]用生物信息学方法推测
miR-122-5p可能通过调控SPRY2基因来影响股骨头坏死。用过表达miR-122-5p的骨髓间充质干细胞与成骨细胞共培养,发现骨髓间充质干细胞分泌外泌体能被成骨细胞摄取,并且使成骨细胞成骨、增殖能力增强和SPRY2表达下降。研究发现miR-122-5p通过RTK/Ras/MAPK信号通路抑制SPRY2的表达,激活RTK的活性来实现这一功能。体内实验证明miR-122-5p修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体促进兔股骨头坏死血管生成、骨修复和愈合,从而抑制股骨头坏死的发展。
(3)miR-31a-5p:GE等[40]发现骨髓间充质干细胞的miR-31a-5p在牙萌出过程中通过SATB2 信号通路调节成骨,而SATB2能够提高老龄人骨髓间充质干细胞的干性能力和成骨分化能力[41]。XU等[42]发现老年大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力降低,伴随miR-31a-5p表达增加。将年轻大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞过表达miR-31a-5p后,骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力降低;抑制老年大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞miR-31a-5p表达,则促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。研究显示,SATB2为miR-31a-5p靶基因。老年大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体中miR-31a-5p的表达明显高于年轻大鼠,抑制外泌体中的miR-31a-5p可以在翻译水平上提高RhoA的表达来减少破骨形成和骨吸收,体内实验显示抗agomiR-31a-5p处理的骨组织可防止老年大鼠的骨丢失和破骨细胞分化,说明外泌体包装的骨髓间充质干细胞来源miR-31a-5p不仅影响成骨分化,而且通过外泌体在细胞之间的穿梭影响破骨分化。
(4)miR-146a:锶(Sr)是人体内一种重要的微量元素,在元素周期表中与钙同族,具有相似的化学性质。既往研究表明锶元素可促进成骨[43-44]。锶代硅酸钙提取物促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨和血管生成相关基因表达,锶代硅酸钙刺激后的骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体(BMSCs-derived exosomes after Sr-CS stimulation,Sr-CS-Exo)中miR-146a表达增加,并可促进脐静脉内皮细胞体外血管生成,外泌体转移的miR-146a参与了Sr-CS-Exo介导的血管生成,Sr-CS-Exo通过抑制Smad4和NF2上调miR-146a,促进脐静脉内皮细胞血管生成;Sr-CS-Exo促进斑马鱼发育血管生成,另外,Sr-CS-Exo促进体内SD大鼠血管生成和骨再生[45]。
(5)miR-375:CHEN等[46]研究发现miR-375在间充质干细胞成骨分化中具有正向调节作用,miR-375过表达显著增强了脂肪间充质干细胞的碱性磷酸酶活性和钙沉积,miR-375通过YAP1/DEPTOR/AKT调控网络促进脂肪间充质干细胞的成骨分化。CHEN等[47]继续研究发现miR-375可以通过在人脂肪间充质干细胞中过表达而在外泌体中富集,50 mg/L外泌体(miR-375)可促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。miR-375被骨髓间充质干细胞吸收后,胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白3通过与其3’非编码端结合而被抑制,重组胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白3降低了外泌体(miR-375)触发的成骨作用。与水凝胶结合后,外泌体(miR-375)表现出缓慢和可控的释放,进一步的体内分析表明,外泌体(miR-375)增强了大鼠颅骨缺损模型的骨再生能力。另外,有学者发现携带miR-375的神经母细胞瘤分泌外泌体可促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化[48]。
(6)miR-128-3p:间充质细胞的修复能力随着年龄的增长而下降。老年大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体的修复能力亦相对减弱。XU等[49]发现年轻大鼠间充质干细胞来源外泌体比老年大鼠间充质干细胞外泌体能更显著促进大鼠骨折愈合,通过miRNA微阵列分析,发现与年轻大鼠间充质干细胞来源外泌体相比,老年大鼠间充质干细胞外泌体中
miR-128-3p是表达上调最多的miRNA;并证实了miR-128-3p和Smad5之间的直接相互作用,体内实验表明miR-128-3p在体内具有靶向Smad5的抗成骨功能。外泌体miR-128-3p拮抗剂可能是一种很有前途的针对老年人骨折愈合的治疗策略。
(7)miR-186:绝经后骨质疏松症是老年妇女最常见的原发性骨质疏松症,行卵巢切除术SD大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨能力均下降,人骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体可改善卵巢切除术大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨能力。LI等[50]通过miRNA-seq研究人骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体成骨作用的分子机制,结果显示,在外泌体+卵巢切除术组中有9个miRNA表达上调,5个miRNA表达下调,其中miR-186在外泌体+卵巢切除术组中的表达明显高于卵巢切除术组。体外实验也证实miR-186在外泌体+卵巢切除术大鼠的骨组织中上调。分子机制研究显示外泌体miR-186通过hippo信号通路调控卵巢切除大鼠成骨。
(8)miR-25:有研究发现miR-25通过上调Rac1的表达促进成骨细胞增殖、分化和迁移[51]。后来,JIANG等[52]发现外泌体miR-25介导的骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体促进MC3T3-E1C细胞的成骨分化、增殖和迁移,并且骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体可促进小鼠骨折愈合,但是抑制骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体内miR-25则无此种促进作用,进一步研究发现,SMURF1是miR-25下游基因,miR-25通过SMURF1促进MC3T3-E1C细胞的成骨分化、增殖和迁移。SMURF1通过促进Runx2泛素化降解抑制Runx2蛋白的表达。值得注意的是,骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体分泌的miR-25可通过SMURF1/Runx2轴加速成骨细胞的成骨分化、增殖和迁移,体外实验表明,骨髓间充质干细胞外泌体中的miR-25通过SMURF1调控Runx2的泛素降解,促进小鼠骨折愈合。
2.4.2 血源性干细胞外泌体miRNA促进骨再生
(1)miR-5106:巨噬细胞对骨折愈合的所有阶段都是至关重要的,是最早迁移到骨折部位的细胞。对于愈合过程尤为重要的是巨噬细胞表型从促炎性的M1亚型转变为抗炎性的M2亚型,而不愈合往往与延长的促炎性巨噬细胞反应相
关[53]。XIONG等[54]发现M2亚型来源的外泌体(M2
macrophage-derived exosomes,M2D-Exos)能促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨,而M1亚型来源的外泌体(M1 macrophage-derived exosomes,M1D-Exos)抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨;体内实验显示M2D-Exos加速小鼠股骨骨折愈合。微阵列鉴定M1D-Exos和M2D-Exos中差异表达的miRNA,发现M2D-Exos
中miR-709、miR-3112-3p、miR-3069-3p、miR-6406、miR-6389、miR-5106、miR-8103、miR-1934-3p、miR-22-3p、miR-505-5p上调,其中miR-5106上调最为显著并可从M2D-Exos传递至骨髓间充质干细胞。此外,用miR-5106抑制剂处理M2巨噬细胞并提取外泌体(ExosantagomiR- 5106),发现ExosantagomiR-5106抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨并抑制大鼠骨折愈合,分子机制研究显示miR-5106直接靶向SIK2和SIK3参与骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。
(2)miR-26a:CD34+干细胞是一组血管祖细胞,具有非凡的血管生成特性[55]。CD34+干细胞来源外泌体(CD34+-Exos)移植可通过促进新生血管形成治疗缺血性疾病[56],miR-26a是重要的成骨正向调节因子[57-58]。ZUO等[59]在CD34+-Exos中过表达miR-26a(miR-26a-CD34+-Exos),然后通过体外迁移和管形成能力评估miR-26a-CD34+-Exos的血管生成能力,发现miR-26a-CD34+-Exos增强了人脐静脉内皮细胞的迁移和成管能力。此外,为了观察miR-26a-CD34+-Exos对骨髓基质细胞的成骨作用,采用茜素红染色、碱性磷酸酶活性测定和qPCR检测,发现miR-26a-CD34+-Exos可在体外糖皮质激素作用下增强骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。最后,将miR-26a-CD34+-Exos注射到糖皮质激素诱导的股骨头坏死大鼠模型中,发现miR-26a-CD34+-Exos增加了股骨头坏死大鼠股骨头血管密度和骨小梁完整性,从而抑制了股骨头坏死的进展。
2.4.3 其他
(1)miR-27a-3p:越来越多的证据表明,骨骼和肌肉组织作为内分泌器官都能影响葡萄糖、能量和其他代谢。最近有研究表明,骨和肌肉也可以通过内分泌的方式相互调节[60-61]。C2C12成肌细胞源性外泌体可进入前成骨细胞MC3T3-E1,促进其成骨分化。具有成骨功能的miR-27a-3p在C2C12成肌细胞源性外泌体中富集,此外泌体miR-27a-3p可能通过靶向APC调控成骨细胞分化,从而激活对成骨有重要作用的β-catenin通路以促进成骨[62]。
(2)miR-181b-5p:机械张力可促进大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化[63]。在炎症环境中,机械张力下MLO-Y4细胞分泌的外泌体不仅能促进牙周膜干细胞的增殖,还能促进成骨分化;GO富集分析表明,机械张力下MLO-Y4细胞来源外泌体miRNA在代谢过程中起关键作用。在差异表达的miRNA中,选择miR-181b-5p进行进一步研究,发现外泌体miR-181b-5p通过PTEN/AKT信号通路调控牙周膜干细胞增殖[64]。
(3)miR-130a-3p:通过成骨诱导可使细胞外泌体miRNA表达谱发生改变,部分增强细胞成骨分化。诱导成骨分化14 d
的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体(Exos-D14)较未诱导成骨分化的脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体(Exos-D0)miR-130a-3p显著增加。过表达miR-130a-3p可增强脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体成骨分化,同时降低miR-130a-3p靶点SIRT7的蛋白和mRNA水平。进一步发现,过表达miR-130a-3p可导致SIRT7表达下调,Wnt信号通路相关蛋白上调。研究结果表明,外泌体miR-130a-3p可部分通过介导SIRT7/Wnt/β-catenin轴促进脂肪间充质干细胞外泌体的成骨分化,从而促进外泌体miRNA在骨再生领域的应用[65]。
2.5 外泌体miRNA促进成血管 骨再生成功的关键在于是否有血管化发生,以便输送足够的营养物质、生长因子、矿物质和氧气用于组织修复[66]。多项研究发现携带特定miRNA的外泌体有成骨及成血管的双重作用。携带miR-29a、
miR-122-5p、miR-146a、miR-26a的外泌体都有这种成骨和成血管的双重作用,除此之外,外泌体miR-126也有此作用,与骨折愈合密切相关。有学者发现外泌体miR-126能同时促进成骨及成血管,JIA等[67]对SD大鼠行截骨术后进行牵张成骨,在骨缝隙内注射SD大鼠内皮祖细胞来源外泌体,与对照组比较,内皮祖细胞来源外泌体组能显著促进成骨和血管生成。后来,LIU等[9]发现低氧通过低氧诱导因子1α促进人脐带间充质干细胞外泌体释放并使其中miR-126上调,体内实验发现此种外泌体通过成血管促进小鼠骨折愈合,体外实验发现此种外泌体通过SPRED1/Ras/Erk途径促进人脐静脉内皮细胞增殖、血管生成和迁移,敲除外泌体miR-126可抑制人脐静脉内皮细胞的增殖、血管生成和迁移能力,体内注射敲除miR-126的外泌体可显著减少新生血管并抑制内皮细胞增殖,可见外泌体miR-126在成血管方面有重要作用,并可能因此促进骨折愈合。外泌体miR-126在成骨和成血管生成中有重要作用,未来有可能用于骨折的治疗。

| [1] DIMITRIOU R, JONES E, MCGONAGLE D, et al. Bone regeneration: current concepts and future directions. BMC Med. 2011;9:66. [2] BENIC GI, HÄMMERLE CH. Horizontal bone augmentation by means of guided bone regeneration. Periodontol 2000. 2014;66(1):13-40. [3] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346. [4] ZHAI M, ZHU Y, YANG M, et al. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Exosomes Enhance Cell-Free Bone Regeneration by Altering Their miRNAs Profiles. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020;7(19):2001334. [5] BAGLIO SR, ROOIJERS K, KOPPERS-LALIC D, et al. Human bone marrow- and adipose-mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2015;6(1):127. [6] ZHANG X, SAI B, WANG F, et al. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):40. [7] FRANK AC, EBERSBERGER S, FINK AF, et al. Apoptotic tumor cell-derived microRNA-375 uses CD36 to alter the tumor-associated macrophage phenotype. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):1135. [8] CHENG M, YANG J, ZHAO X, et al. Circulating myocardial microRNAs from infarcted hearts are carried in exosomes and mobilise bone marrow progenitor cells. Nat Commun. 2019;10(1):959. [9] LIU W, LI L, RONG Y, et al. Hypoxic mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promote bone fracture healing by the transfer of miR-126. Acta Biomater. 2020;103:196-212. [10] TREIBER T, TREIBER N, MEISTER G. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20(1):5-20. [11] FANG S, DENG Y, GU P, et al. MicroRNAs regulate bone development and regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(4):8227-8253. [12] HILTON C, NEVILLE MJ, KARPE F. MicroRNAs in adipose tissue: their role in adipogenesis and obesity. Int J Obes (Lond). 2013;37(3):325-332. [13] FAN C, JIA L, ZHENG Y, et al. MiR-34a Promotes Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells via the RBP2/NOTCH1/CYCLIN D1 Coregulatory Network. Stem Cell Reports. 2016; 7(2):236-248. [14] YANG C, LIU X, ZHAO K, et al. miRNA-21 promotes osteogenesis via the PTEN/PI3K/Akt/HIF-1α pathway and enhances bone regeneration in critical size defects. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):65. [15] GENG Z, YU Y, LI Z, et al. miR-21 promotes osseointegration and mineralization through enhancing both osteogenic and osteoclastic expression. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;111:110785. [16] WAN S, WU Q, JI Y, et al. Promotion of the immunomodulatory properties and osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in vitro by lentivirus-mediated mir-146a sponge expression. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2020;14(11):1581-1591. [17] DENG Y, WU S, ZHOU H, et al. Effects of a miR-31, Runx2, and Satb2 regulatory loop on the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22(16):2278-2286. [18] VALADI H, EKSTRÖM K, BOSSIOS A, et al. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(6):654-659. [19] ZHANG Y, LIU D, CHEN X, et al. Secreted monocytic miR-150 enhances targeted endothelial cell migration. Mol Cell. 2010;39(1):133-144. [20] DE JONG OG, VERHAAR MC, CHEN Y, et al. Cellular stress conditions are reflected in the protein and RNA content of endothelial cell-derived exosomes. J Extracell Vesicles. 2012;1:18396. [21] TI D, HAO H, FU X, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNAs contribute to wound inflammation. Sci China Life Sci. 2016; 59(12):1305-1312. [22] FANG S, XU C, ZHANG Y, et al. Umbilical Cord-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Suppress Myofibroblast Differentiation by Inhibiting the Transforming Growth Factor-β/SMAD2 Pathway During Wound Healing. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2016; 5(10):1425-1439. [23] ZHANG Y, HAO Z, WANG P, et al. Exosomes from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells enhance fracture healing through HIF-1α-mediated promotion of angiogenesis in a rat model of stabilized fracture. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(2):e12570. [24] SONG Y, DOU H, LI X, et al. Exosomal miR-146a Contributes to the Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy of Interleukin-1β-Primed Mesenchymal Stem Cells Against Sepsis. Stem Cells. 2017;35(5):1208-1221. [25] ZHENG D, HUO M, LI B, et al. The Role of Exosomes and Exosomal MicroRNA in Cardiovascular Disease. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021;8: 616161. [26] ASGARPOUR K, SHOJAEI Z, AMIRI F, et al. Exosomal microRNAs derived from mesenchymal stem cells: cell-to-cell messages. Cell Commun Signal. 2020;18(1):149. [27] ZHOU Y, REN H, DAI B, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma-derived exosomal miRNA-21 contributes to tumor progression by converting hepatocyte stellate cells to cancer-associated fibroblasts. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018;37(1):324. [28] CHEN Z, WANG H, XIA Y, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol. 2018;201(8):2472-2482. [29] XIAO J, PAN Y, LI XH, et al. Cardiac progenitor cell-derived exosomes prevent cardiomyocytes apoptosis through exosomal miR-21 by targeting PDCD4. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(6):e2277. [30] WANG X, OMAR O, VAZIRISANI F, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes have altered microRNA profiles and induce osteogenic differentiation depending on the stage of differentiation. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0193059. [31] XU JF, YANG GH, PAN XH, et al. Altered microRNA expression profile in exosomes during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(12):e114627. [32] YANG S, GUO S, TONG S, et al. Promoting Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells by Altering the Expression of Exosomal miRNA. Stem Cells Int. 2019;2019:1351860. [33] CHEN EEM, ZHANG W, YE CCY, et al. Knockdown of SIRT7 enhances the osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells partly via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8(9):e3042. [34] PARK JY, JEON SH, CHOUNG PH. Efficacy of periodontal stem cell transplantation in the treatment of advanced periodontitis. Cell Transplant. 2011;20(2):271-285. [35] LI J, ZHANG F, ZHANG N, et al. Osteogenic capacity and cytotherapeutic potential of periodontal ligament cells for periodontal regeneration in vitro and in vivo. PeerJ. 2019;7:e6589. [36] LIU T, HU W, ZOU X, et al. Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Bone Regeneration by Altering MicroRNA Profiles. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:8852307. [37] LI Z, JIANG R, YUE Q, et al. MicroRNA-29 regulates myocardial microvascular endothelial cells proliferation and migration in association with IGF1 in type 2 diabetes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017;487(1):15-21. [38] LU GD, CHENG P, LIU T, et al. BMSC-Derived Exosomal miR-29a Promotes Angiogenesis and Osteogenesis. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8: 608521. [39] LIAO W, NING Y, XU HJ, et al. BMSC-derived exosomes carrying microRNA-122-5p promote proliferation of osteoblasts in osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Clin Sci (Lond). 2019;133(18):1955-1975. [40] GE J, GUO S, FU Y, et al. Dental Follicle Cells Participate in Tooth Eruption via the RUNX2-MiR-31-SATB2 Loop. J Dent Res. 2015;94(7): 936-944. [41] ZHOU P, WU G, ZHANG P, et al. SATB2-Nanog axis links age-related intrinsic changes of mesenchymal stem cells from craniofacial bone. Aging (Albany NY). 2016;8(9):2006-2011. [42] XU R, SHEN X, SI Y, et al. MicroRNA-31a-5p from aging BMSCs links bone formation and resorption in the aged bone marrow microenvironment. Aging Cell. 2018;17(4):e12794. [43] YE H, ZHU J, DENG D, et al. Enhanced osteogenesis and angiogenesis by PCL/chitosan/Sr-doped calcium phosphate electrospun nanocomposite membrane for guided bone regeneration. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2019;30(16):1505-1522. [44] WU Q, WANG X, JIANG F, et al. Study of Sr-Ca-Si-based scaffolds for bone regeneration in osteoporotic models. Int J Oral Sci. 2020;12(1):25. [45] LIU L, YU F, LI L, et al. Bone marrow stromal cells stimulated by strontium-substituted calcium silicate ceramics: release of exosomal miR-146a regulates osteogenesis and angiogenesis. Acta Biomater. 2021;119:444-457. [46] CHEN S, ZHENG Y, ZHANG S, et al. Promotion Effects of miR-375 on the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;8(3):773-786. [47] CHEN S, TANG Y, LIU Y, et al. Exosomes derived from miR-375-overexpressing human adipose mesenchymal stem cells promote bone regeneration. Cell Prolif. 2019;52(5):e12669. [48] COLLETTI M, TOMAO L, GALARDI A, et al. Neuroblastoma-secreted exosomes carrying miR-375 promote osteogenic differentiation of bone-marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. J Extracell Vesicles. 2020; 9(1):1774144. [49] XU T, LUO Y, WANG J, et al. Exosomal miRNA-128-3p from mesenchymal stem cells of aged rats regulates osteogenesis and bone fracture healing by targeting Smad5. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):47. [50] LI L, ZHOU X, ZHANG JT, et al. Exosomal miR-186 derived from BMSCs promote osteogenesis through hippo signaling pathway in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021;16(1):23. [51] LI X, JI J, WEI W, Et al. MiR-25 promotes proliferation, differentiation and migration of osteoblasts by up-regulating Rac1 expression. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;99:622-628. [52] JIANG Y, ZHANG J, LI Z, et al. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal miR-25 Regulates the Ubiquitination and Degradation of Runx2 by SMURF1 to Promote Fracture Healing in Mice. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:577578. [53] PAJARINEN J, LIN T, GIBON E, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials. 2019;196:80-89. [54] XIONG Y, CHEN L, YAN C, et al. M2 Macrophagy-derived exosomal miRNA-5106 induces bone mesenchymal stem cells towards osteoblastic fate by targeting salt-inducible kinase 2 and 3. J Nanobiotechnology. 2020;18(1):66. [55] LOSORDO DW, KIBBE MR, MENDELSOHN F, et al. A randomized, controlled pilot study of autologous CD34+ cell therapy for critical limb ischemia. Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;5(6):821-830. [56] MATHIYALAGAN P, LIANG Y, KIM D, et al. Angiogenic Mechanisms of Human CD34+ Stem Cell Exosomes in the Repair of Ischemic Hindlimb. Circ Res. 2017;120(9):1466-1476. [57] LIU Z, CHANG H, HOU Y, et al. Lentivirus‑mediated microRNA‑26a overexpression in bone mesenchymal stem cells facilitates bone regeneration in bone defects of calvaria in mice. Mol Med Rep. 2018; 18(6):5317-5326. [58] LI Y, FAN L, HU J, et al. MiR-26a Rescues Bone Regeneration Deficiency of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived From Osteoporotic Mice. Mol Ther. 2015;23(8):1349-1357. [59] ZUO R, KONG L, WANG M, et al. Exosomes derived from human CD34+ stem cells transfected with miR-26a prevent glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head by promoting angiogenesis and osteogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):321. [60] BROTTO M, BONEWALD L. Bone and muscle: Interactions beyond mechanical. Bone. 2015;80:109-114. [61] GIRGIS CM. Integrated therapies for osteoporosis and sarcopenia: from signaling pathways to clinical trials. Calcif Tissue Int. 2015;96(3):243-255. [62] XU Q, CUI Y, LUAN J, et al. Exosomes from C2C12 myoblasts enhance osteogenic differentiation of MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts by delivering miR-27a-3p. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;498(1):32-37. [63] LIU Y, YANG G, JI H, et al. Synergetic effect of topological cue and periodic mechanical tension-stress on osteogenic differentiation of rat bone mesenchymal stem cells. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2017;154:1-9. [64] LV PY, GAO PF, TIAN GJ, et al. Osteocyte-derived exosomes induced by mechanical strain promote human periodontal ligament stem cell proliferation and osteogenic differentiation via the miR-181b-5p/PTEN/AKT signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):295. [65] YANG S, GUO S, TONG S, et al. Exosomal miR-130a-3p regulates osteogenic differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived stem cells through mediating SIRT7/Wnt/β-catenin axis. Cell Prolif. 2020;53(10): e12890. [66] DIOMEDE F, MARCONI GD, FONTICOLI L, et al. Functional Relationship between Osteogenesis and Angiogenesis in Tissue Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(9):3242. [67] JIA Y, ZHU Y, QIU S, et al. Exosomes secreted by endothelial progenitor cells accelerate bone regeneration during distraction osteogenesis by stimulating angiogenesis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):12. [68] WEI F, LI M, CRAWFORD R, et al. Exosome-integrated titanium oxide nanotubes for targeted bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2019;86: 480-492. [69] ZHANG J, LIU X, LI H, et al. Exosomes/tricalcium phosphate combination scaffolds can enhance bone regeneration by activating the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7(1):136. [70] WU Z, PU P, SU Z, et al. Schwann Cell-derived exosomes promote bone regeneration and repair by enhancing the biological activity of porous Ti6Al4V scaffolds. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;531(4):559-565. [71] LI SP, LIN ZX, JIANG XY, et al. Exosomal cargo-loading and synthetic exosome-mimics as potential therapeutic tools. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(4):542-551. [72] ZHANG D, LEE H, ZHU Z, et al. Enrichment of selective miRNAs in exosomes and delivery of exosomal miRNAs in vitro and in vivo. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017;312(1):L110-L121. |
| [1] | 孔亚敏, 严隽陶, 马丙祥, 李华伟. 推拿振法干预坐骨神经损伤模型大鼠MyoD表达及肌卫星细胞的增殖与分化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1216-1222. |
| [2] | 吴 聪, 贾全忠, 刘 伦. 成年关节软骨碎块化后转化生长因子β1表达与软骨细胞迁移的关系[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1223-1228. |
| [3] | 王宝娟, 郑曙光, 张 琪, 李田洋. 苗药熏蒸治疗膝骨关节炎模型兔可延缓细胞外基质的破坏[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1236-1242. |
| [4] | 李 琴, 毛双法, 李 敏, 程基焱. 石斛多糖保护中波紫外线损伤成纤维细胞的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1284-1289. |
| [5] | 王 景, 熊 山, 曹 金, 冯林伟, 王 信. 白细胞介素3在骨代谢中的作用及机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1316-1322. |
| [6] | 肖 豪, 刘 静 , 周 君. 脉冲电磁场治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的研究进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1323-1329. |
| [7] | 朱 婵, 韩栩珂, 姚承佼, 张 强, 刘 静, 邵 明. 针刺治疗帕金森病:动物实验显示的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(8): 1330-1335. |
| [8] | 安维政, 何 萧, 任 帅, 刘建宇. 肌源干细胞在周围神经再生中的潜力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1130-1136. |
| [9] | 范一鸣, 刘方煜, 张洪宇, 李 帅, 王岩松. 脊髓损伤后室管膜区内源性神经干细胞反应的系列问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1137-1142. |
| [10] | 轩娟娟, 白鸿太, 张继翔, 王耀权, 陈国勇, 魏思东. 调节性T细胞亚群在肝移植中的作用及临床应用进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1143-1148. |
| [11] | 田 川, 朱向情, 杨再玲, 鄢东海, 李 晔, 王严影, 杨育坤, 何 洁, 吕冠柯, 蔡学敏, 舒丽萍, 何志旭, 潘兴华. 骨髓间充质干细胞调控猕猴卵巢的衰老[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 985-991. |
| [12] | 胡 伟, 谢兴奇, 屠冠军. 骨髓间充质干细胞来源外泌体改善脊髓损伤后血脊髓屏障的完整性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 992-998. |
| [13] | 高俞锦, 彭双麟, 马治超, 陆 诗, 曹花月, 王 浪, 肖金刚. 糖尿病骨质疏松症模型小鼠脂肪干细胞的成骨能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 999-1004. |
| [14] | 侯婧瑛, 郭天柱, 于萌蕾, 龙会宝, 吴 浩. 缺氧预处理通过激活MALAT1靶向抑制miR-195促进骨髓间充质干细胞的生存和血管形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1005-1011. |
| [15] | 周 颖, 张 幻, 廖 松, 胡凡琦, 易 静, 刘玉斌, 靳继德. 去铁胺联合干扰素γ预处理对人牙髓干细胞的免疫调节作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2022, 26(7): 1012-1019. |
1.2 纳入与排除标准 纳入标准:归纳与骨再生相关的综述、实验性文章。排除标准:与此次研究无关及重复性研究;低质量、证据等级不够的文章。
1.3 数据提取 共检索到相关文献127篇,其中中文文献46篇,英文文献81篇,排除与研究目的不符、指标不清、信度不足或重复的文献55篇,纳入符合此次研究内容的72篇文献进行综述,见图1。
外泌体miRNA研究仍处于起步阶段,细胞分泌的外泌体数量也有限,这严重阻碍了使用外泌体miRNA进行基础研究和临床试验。通过细胞挤压或细胞膜包裹的纳米粒子合成外泌体模拟物,这种外泌体模拟物可大规模制造,为药物传递提供了新的平台[71]。外泌体如何有效装载miRNA也是值得深入研究的问题,ZHANG等[72]用一种改良的氯化钙介导的转染方法,成功地在外泌体中直接增强指定的miRNA模拟物或抑制剂,而不是转染它们的母细胞,并且并成功地将外泌体miRNA分子运送到受体细胞。使外泌体携带特定的miRNA会提高其成骨能力,同时也可能会导致外泌体的不良改变,上文提到脂肪干细胞分泌的富含miR-375的外泌体可促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨,有骨髓转移的神经母细胞瘤患者血液中外泌体miR-375较高,可能与神经母细胞瘤转移进展有关,因此装载特定miRNA的外泌体效果和安全性应该独立评估。

文题释义:#br# 外泌体:是一种细胞旁分泌产生的纳米尺度的细胞外脂质双层囊泡,直径40-150 nm,由细胞经过“内吞-融合-外排”等系列调控过程产生并分泌外泌体,其内含功能性蛋白质、mRNA、microRNA等物质,作为细胞间通讯的载体,通过转运、内吞的方式进入靶细胞,调节细胞基因表达,改变细胞命运。#br# MiRNAs:是长度为18-25个核苷酸的一种小的非编码RNA,可通过结合mRNA的3’端非翻译区抑制mRNA转录或降解mRNA来沉默靶基因,在多种生物过程中起重要作用。#br# 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
#br#
间充质干细胞在骨组织工程研究中有举足轻重的作用,其分泌的外泌体可以囊括间充质干细胞的生物活性,并可替代整个细胞治疗。MiRNA是外泌体内重要的内含物,携带特定miRNA的外泌体可有效调控骨形成。在体内,良好的血管生成可促进骨缺损区骨形成,能促进血管形成的外泌体可能对骨形成也有促进作用。因此,将携带miRNA、能促进成骨和成血管的外泌体附着在支架材料上有更加优异的成骨效果,将外泌体加载于静电纺丝或者纳米材料等新型材料可能是未来骨组织工程的一个研究方向。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:干细胞;骨髓干细胞;造血干细胞;脂肪干细胞;肿瘤干细胞;胚胎干细胞;脐带脐血干细胞;干细胞诱导;干细胞分化;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||