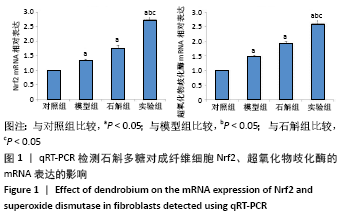
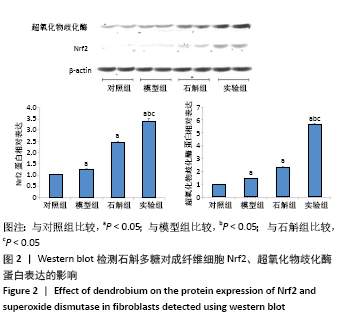
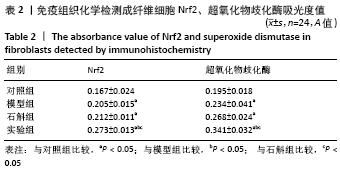
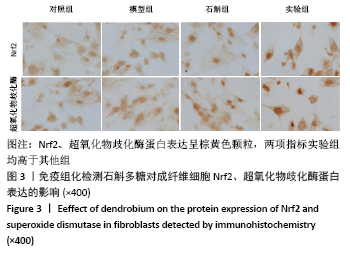
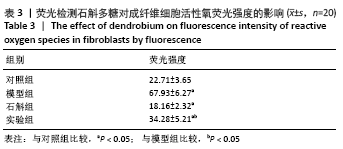
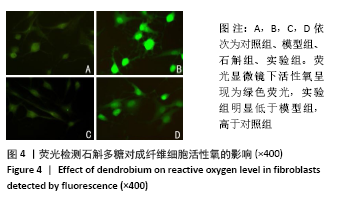
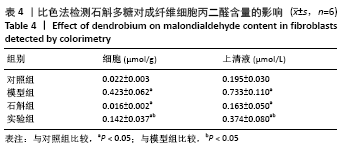
[1] 闫建华,许晓玲,李荷莲,等.铁皮石斛总黄酮对D-半乳糖所致小鼠衰老模型的影响[J].中医学报,2021,36(2):366-370.
[2] 陈斌.金钗石斛植物提取液在化妆品中的应用研究[J].中国野生植物资源,2020,39(6):35-39.
[3] 赵倩,戴天浥,洪文龙,等.铁皮石斛糖蛋白对皮肤炎症期的调控作用及机制[J].食品工业科技,2020,41(21):304- 310,316.
[4] 李贺,钱柳青,陈雪,等.铁皮石斛超微粉对光老化模型小鼠的预防作用及机制研究[J].中国中药杂志,2019(21):4677-4684.
[5] SUBEDI L, LEE TH, WAHEDI HM, et al. Resveratrol-Enriched Rice Attenuates UVB-ROS-Induced Skin Aging via Downregulation of Inflammatory Cascades. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017;2017:8379539.
[6] SHIN D, MOON HW, OH Y, et al. Defensive Properties of Ginsenoside Re against UV-B-Induced Oxidative Stress through Up-Regulating Glutathione and Superoxide Dismutase in HaCaT Keratinocytes. Iran J Pharm Res. Winter 2018;17(1):249-260.
[7] WANG YS, CHO JG, HWANG ES, et al.Enhancement of Protective Effects of Radix Scutellariae on UVB-induced Photo Damage in Human HaCaT Keratinocytes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2018;184(4):1073-1093.
[8] 潘长伟,赵峰,郎宏鑫,等.过氧化氢诱导人皮肤成纤维细胞衰老模型的建立[J].解剖科学进展,2019,25(2):193-195,199.
[9] ZOUBOULIS CC, GANCEVICIENE R, LIAKOU AI, et al.Aesthetic aspects of skin aging, prevention, and local treatment.Clin Dermatol. 2019; 37(4):365-372.
[10] CHE DN, XIE GH, CHO BO, et al. Protective effects of grape stem extract against UVB-induced damage in C57BL mice skin.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2017;173:551-559.
[11] 李凌霞,赵晶,党文军,等.归素膏对衰老小鼠皮肤SOD活性及MDA含量影响的实验研究[J].中国中医药科技,2014,21(6):637-638.
[12] NOH D, CHOI JG, HUH E, et al. Tectorigenin, a Flavonoid-Based Compound of Leopard Lily Rhizome, Attenuates UV-B-Induced Apoptosis and Collagen Degradation by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress in Human Keratinocytes.Nutrients. 2018;10(12):1998.
[13] 王彩霞.针刺对8-MOP∕UVA诱导光老化模型小鼠皮肤SOD、MDA、T-AOC、LF、ATP酶的影响[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2020,26(1):49-50.
[14] DODSON M, REDMANN M, RAJASEKARAN NS, et al. KEAP1-NRF2 signalling and autophagy in protection against oxidative and reductive proteotoxicity. Biochem J. 2015;469(3):347-355.
[15] 江娜. Nrf2信号通路在姜黄素防御UVB致无毛鼠皮肤急性光损伤的机制[D]. 广州:广州医科大学,2016.
[16] VAISERMAN AM, LUSHCHAK OV, KOLIADA AK.Anti-aging pharmacology: Promises and pitfalls. Ageing Res Rev. 2016;31:9-35.
[17] CHO HY, KLEEBERGER SR. Association of Nrf2 with airway pathogenesis: lessons learned from genetic mouse models. Arch Toxicol. 2015;89(11): 1931-1957.
[18] 杨成华,巫岳龙,李敏,等. 大黄酚与转化生长因子-β1对体外培养人成纤维细胞胶原及盘状结构域受体2的调控作用及机制[J].中国老年学杂志,2020,40(18):3947-3950.
[19] 陈高敏,王璐,杜沛,等. 麦冬多糖对中波紫外线损伤人皮肤成纤维细胞的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(32):5183-5188.
[20] 陈振辉,王明光,等. 雷帕霉素对人皮肤成纤维细胞光老化模型自噬及氧化应激的影响[J].中国皮肤性病学杂志,2019,33(3):253-257.
[21] 杨凯业,汪丽萍,王冰心,等.复合多糖抑制紫外线诱导皮肤细胞的光老化[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(29):4707- 4713.
[22] YANG D, LIU Y, ZHANG L.Tremella polysaccharide: The molecular mechanisms of its drug action. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2019;163:383-421.
[23] CHARTOUMPEKIS DV, WAKABAYASHI N, KENSLER TW.Keap1/Nrf2 pathway in the frontiers of cancer and non-cancer cell metabolism.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015;43(4):639-644.
[24] LARA J, SHERRATT MJ, REES M. Aging and anti-aging. Maturitas. 2016;93:1-3.
[25] LU MC, JI JA, JIANG ZY, et al. The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE Pathway As a Potential Preventive and Therapeutic Target: An Update. Med Res Rev. 2016;36(5):924-963.
[26] DAVID JA, RIFKIN WJ, RABBANI PS,et al.The Nrf2/Keap1/ARE Pathway and Oxidative Stress as a Therapeutic Target in Type II Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Res. 2017;2017:4826724.
[27] 田黎明,彭圆,胡荣毅, 等.衰老标记蛋白30对过氧化氢所致人皮肤成纤维细胞衰老表型的影响[J].新乡医学院学报,2016,33(6): 452-456.
[28] DUAN X, WU T, LIU T, et al. Vicenin-2 ameliorates oxidative damage and photoaging via modulation of MAPKs and MMPs signaling in UVB radiation exposed human skin cells. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2019;190:76-85.
[29] TANG R, LI QQ, WANG D, et al. The protective effect of Dendrobium officinale polysaccharides on photoaging fibroblasts by scavenging reactive oxygen species and promoting the expression of TGF-β1. TMR. 2018;3(3):131-139.
[30] 张沛,张国庆,曹建平,等.铁皮石斛对人正常皮肤成纤维细胞GM0639辐照后微核的影响研究[J].中国血液流变学杂志,2011, 21(2):227-230.
[31] 刘婵,刘娟,商黔惠.石斛碱抑制高钠盐诱导的心脏成纤维细胞增殖[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2017,25(7):649-654. |