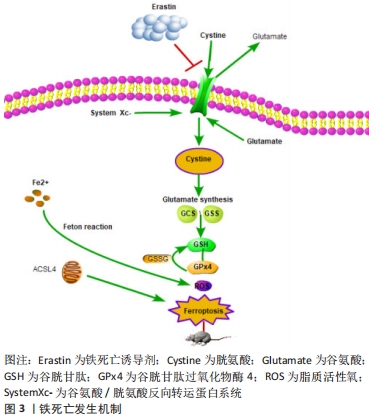
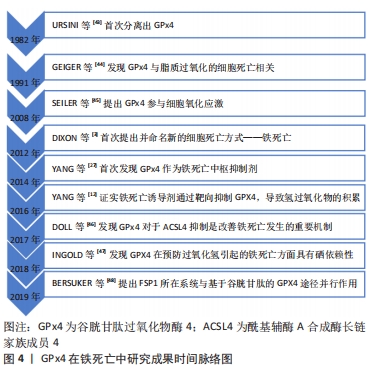
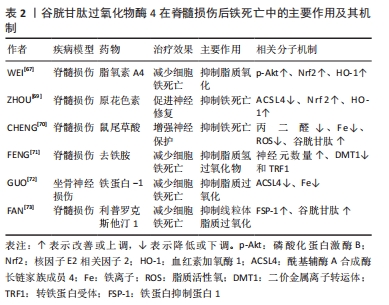
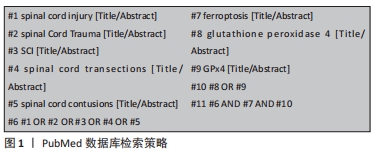
[1] HUTSON TH, DI GIOVANNI S. The translational landscape in spinal cord injury: focus on neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 2019;15(12):732-745.
[2] AHUJA CS, WILSON JR, NORI S, et al. Traumatic spinal cord injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17018.
[3] DIXON SJ, LEMBERG KM, LAMPRECHT MR, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149(5):1060-1072.
[4] DO VB, GOUEL F, JONNEAUX A, et al. Ferroptosis, a newly characterized form of cell death in Parkinson’s disease that is regulated by PKC. Neurobiol Dis. 2016;94:169-178.
[5] XIE BS, WANG YQ, LIN Y, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis attenuates tissue damage and improves long-term outcomes after traumatic brain injury in mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2019;25(4):465-475.
[6] ASHRAF A, JEANDRIENS J, PARKES HG, et al. Iron dyshomeostasis, lipid peroxidation and perturbed expression of cystine/glutamate antiporter in Alzheimer’s disease: Evidence of ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2020;32:101494.
[7] YAN N, ZHANG JJ. The Emerging Roles of Ferroptosis in Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Front Neurosci. 2019;13:811.
[8] YAO X, ZHANG Y, HAO J, et al. Deferoxamine promotes recovery of traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(3):532-541.
[9] YUAN H, LI X, ZHANG X, et al. CISD1 inhibits ferroptosis by protection against mitochondrial lipid peroxidation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;478(2):838-844.
[10] CONRAD M, ANGELI JP, VANDENABEELE P, et al. Regulated necrosis: disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15(5):348-366.
[11] HASSANNIA B, VANDENABEELE P, VANDEN BT. Targeting Ferroptosis to Iron Out Cancer. Cancer Cell. 2019;35(6):830-849.
[12] YANG WS, KIM KJ, GASCHLER MM, et al. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(34):E4966-E4975.
[13] CONRAD M, PRONETH B. Selenium: Tracing Another Essential Element of Ferroptotic Cell Death. Cell Chem Biol. 2020;27(4):409-419.
[14] DI DOMENICO F, TRAMUTOLA A, BUTTERFIELD DA. Role of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal (HNE) in the pathogenesis of alzheimer disease and other selected age-related neurodegenerative disorders. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;111:253-261.
[15] GALEIRAS VR, FERREIRO VM, MOURELO FM, et al. Update on traumatic acute spinal cord injury. Part 1. Med Intensiva. 2017;41(4):237-247.
[16] XIAO W, YU A, LIU D, et al. Ligustilide treatment promotes functional recovery in a rat model of spinal cord injury via preventing ROS production. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(10):12005-12013.
[17] HAO J, LI B, DUAN HQ, et al. Mechanisms underlying the promotion of functional recovery by deferoxamine after spinal cord injury in rats. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(6):959-968.
[18] MENG FX, HOU JM, SUN TS. Effect of oxidative stress induced by intracranial iron overload on central pain after spinal cord injury. J Orthop Surg Res. 2017;12(1):24.
[19] ZHANG Y, SUN C, ZHAO C, et al. Ferroptosis inhibitor SRS 16-86 attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 2019;1706:48-57.
[20] ZILKA O, SHAH R, LI B, et al. On the Mechanism of Cytoprotection by Ferrostatin-1 and Liproxstatin-1 and the Role of Lipid Peroxidation in Ferroptotic Cell Death. ACS Cent Sci. 2017;3(3):232-243.
[21] WANG H, HUO X, HAN C, et al. Ferroptosis is involved in the development of neuropathic pain and allodynia. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021;476(8):3149-3161.
[22] SKOUTA R, DIXON SJ, WANG J, et al. Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136(12):4551-4556.
[23] COTTICELLI MG, XIA S, LIN D, et al. Ferroptosis as a Novel Therapeutic Target for Friedreich’s Ataxia. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2019;369(1):47-54.
[24] LINKERMANN A, SKOUTA R, HIMMERKUS N, et al. Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014; 111(47):16836-16841.
[25] MAO C, LIU X, ZHANG Y, et al. DHODH-mediated ferroptosis defence is a targetable vulnerability in cancer. Nature. 2021;593(7860):586-590.
[26] ANANDHAN A, DODSON M, SCHMIDLIN CJ, et al. Breakdown of an Ironclad Defense System: The Critical Role of NRF2 in Mediating Ferroptosis. Cell Chem Biol. 2020;27(4):436-447.
[27] YANG WS, SRIRAMARATNAM R, WELSCH ME, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156(1-2):317-331.
[28] CHEN L, NA R, DANAE MK, et al. Overexpression of ferroptosis defense enzyme Gpx4 retards motor neuron disease of SOD1G93A mice. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):12890.
[29] FLOHE L, TOPPO S, COZZA G, et al. A comparison of thiol peroxidase mechanisms. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2011;15(3):763-780.
[30] TANG D, CHEN X, KANG R, et al. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31(2):107-125.
[31] RECZEK CR, CHANDEL NS. ROS-dependent signal transduction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2015;33:8-13.
[32] CONRAD M, SCHNEIDER M, SEILER A, et al. Physiological role of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase in mammals. Biol Chem. 2007;388(10):1019-1025.
[33] KOEBERLE SC, GOLLOWITZER A, LAOUKILI J, et al. Distinct and overlapping functions of glutathione peroxidases 1 and 2 in limiting NF-kappaB-driven inflammation through redox-active mechanisms. Redox Biol. 2020;28:101388.
[34] WOOD I, TROSTCHANSKY A, RUBBO H. Structural considerations on lipoxygenase function, inhibition and crosstalk with nitric oxide pathways. Biochimie. 2020;178:170-180.
[35] GRIESSER M, SHAH R, VAN KESSEl AT, et al. The Catalytic Reaction of Nitroxides with Peroxyl Radicals and Its Relevance to Their Cytoprotective Properties. J Am Chem Soc. 2018;140(10):3798-3808.
[36] CHEN L, HAMBRIGHT WS, NA R, et al. Ablation of the Ferroptosis Inhibitor Glutathione Peroxidase 4 in Neurons Results in Rapid Motor Neuron Degeneration and Paralysis. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(47): 28097-28106.
[37] DRECOURT A, BABDOR J, DUSSIOT M, et al. Impaired Transferrin Receptor Palmitoylation and Recycling in Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Accumulation. Am J Hum Genet. 2018;102(2):266-277.
[38] CAO S, HUA Y, KEEP RF, et al. Minocycline Effects on Intracerebral Hemorrhage-Induced Iron Overload in Aged Rats: Brain Iron Quantification With Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Stroke. 2018;49(4): 995-1002.
[39] DAGLAS M, ADLARD PA. The Involvement of Iron in Traumatic Brain Injury and Neurodegenerative Disease. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:981.
[40] SAINT-GERMAIN E, MIGNACCA L, VERNIER M, et al. SOCS1 regulates senescence and ferroptosis by modulating the expression of p53 target genes. Aging (Albany NY). 2017;9(10):2137-2162.
[41] GIOVANNI CF, SCOTT JD. GPX4 at the Crossroads of Lipid Homeostasis and Ferroptosis. Proteomics. 2019;19(18):e1800311.
[42] IMAI H, NAKAGAWA Y. Biological significance of phospholipid hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (PHGPx, GPx4) in mammalian cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 2003;34(2):145-169.
[43] URSINI F, MAIORINO M, VALENTE M, et al. Purification from pig liver of a protein which protects liposomes and biomembranes from peroxidative degradation and exhibits glutathione peroxidase activity on phosphatidylcholine hydroperoxides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982; 710(2):197-211.
[44] GEIGER PG, THOMAS JP, GIROTTI AW. Lethal damage to murine L1210 cells by exogenous lipid hydroperoxides: protective role of glutathione-dependent selenoperoxidases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1991;288(2):671-680.
[45] SEILER A, SCHNEIDER M, FORSTER H, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4 senses and translates oxidative stress into 12/15-lipoxygenase dependent- and AIF-mediated cell death. Cell Metab. 2008;8(3):237-248.
[46] DOLL S, PRONETH B, TYURINA YY, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017; 13(1):91-98.
[47] INGOLD I, BERNDT C, SCHMITT S, et al. Selenium Utilization by GPX4 Is Required to Prevent Hydroperoxide-Induced Ferroptosis. Cell. 2018; 172(3):409-422.
[48] BERSUKER K, HENDRICKS JM, LI Z, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575(7784): 688-692.
[49] ADENIRAN SO, ZHENG P, FENG R, et al. The Antioxidant Role of Selenium via GPx1 and GPx4 in LPS-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Endometrial Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2021. doi: 10.1007/s12011-021-02731-0.
[50] WANG Y, HUANG J, SUN Y, et al. SARS-CoV-2 suppresses mRNA expression of selenoproteins associated with ferroptosis, endoplasmic reticulum stress and DNA synthesis. Food Chem Toxicol. 2021;153: 112286.
[51] MIN Z, GUO Y, SUN M, et al. Selenium-sensitive miRNA-181a-5p targeting SBP2 regulates selenoproteins expression in cartilage. J Cell Mol Med. 2018;22(12):5888-5898.
[52] INGOLD I, AICHLER M, YEFREMOVA E, et al. Expression of a Catalytically Inactive Mutant Form of Glutathione Peroxidase 4 (Gpx4) Confers a Dominant-negative Effect in Male Fertility. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(23): 14668-14678.
[53] INGOLD I, CONRAD M. Selenium and iron, two elemental rivals in the ferroptotic death process. Oncotarget. 2018;9(32):22241-22242.
[54] ALIM I, CAULFIELD JT, CHEN Y, et al. Selenium Drives a Transcriptional Adaptive Program to Block Ferroptosis and Treat Stroke. Cell. 2019; 177(5):1262-1279.
[55] WANG S, LIU W, WANG J, et al. Curculigoside inhibits ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis through the induction of GPX4. Life Sci. 2020;259: 118356.
[56] CARDOSO BR, HARE DJ, BUSH AI, et al. Glutathione peroxidase 4: a new player in neurodegeneration? Mol Psychiatry. 2017;22(3):328-335.
[57] SHAW P, CHATTOPADHYAY A. Nrf2-ARE signaling in cellular protection: Mechanism of action and the regulatory mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 2020;235(4):3119-3130.
[58] YAN N, XU Z, QU C, et al. Dimethyl fumarate improves cognitive deficits in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rats by alleviating inflammation, oxidative stress, and ferroptosis via NRF2/ARE/NF-kappaB signal pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;98:107844.
[59] GE MH, TIAN H, MAO L, et al. Zinc attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury by activating Nrf2/GPX4 defense pathway. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2021;27(9):1023-1040
[60] WANG Q, BIN C, XUE Q, et al. GSTZ1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib-induced ferroptosis via inhibition of NRF2/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12(5):426.
[61] JOSÉ PFA, DMITRI VK, MARCUS C. Ferroptosis at the crossroads of cancer-acquired drug resistance and immune evasion. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2019;19(7):97-111.
[62] WU X, WANG J, SONG L, et al. Catalpol weakens depressive-like behavior in mice with streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia via PI3K/AKT/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. Neuroscience. 2021; S0306-4522(21)00383-3.
[63] JIANG B, ZHAO Y, SHI M, et al. DNAJB6 Promotes Ferroptosis in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2020;65(7):1999-2008.
[64] LI X, ZOU Y, XING J, et al. Pretreatment with Roxadustat (FG-4592) Attenuates Folic Acid-Induced Kidney Injury through Antiferroptosis via Akt/GSK-3beta/Nrf2 Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020;2020: 6286984.
[65] FUJIKI K, INAMURA H, SUGAYA T, et al. Blockade of ALK4/5 signaling suppresses cadmium- and erastin-induced cell death in renal proximal tubular epithelial cells via distinct signaling mechanisms. Cell Death Differ. 2019;26(11):2371-2385.
[66] LU T, WU X, WEI N, et al. Lipoxin A4 protects against spinal cord injury via regulating Akt/nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;97:905-910.
[67] WEI N, LU T, YANG L, et al. Lipoxin A4 protects primary spinal cord neurons from Erastin-induced ferroptosis by activating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio. 2021;11(8):2118-2126
[68] XIAO X, JIANG Y, LIANG W, et al. miR-212-5p attenuates ferroptotic neuronal death after traumatic brain injury by targeting Ptgs2. Mol Brain. 2019;12(1):78.
[69] ZHOU H, YIN C, ZHANG Z, et al. Proanthocyanidin promotes functional recovery of spinal cord injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. J Chem Neuroanat. 2020;107:101807.
[70] CHENG J, XU T, XUN C, et al. Carnosic acid protects against ferroptosis in PC12 cells exposed to erastin through activation of Nrf2 pathway. Life Sci. 2021;266:118905.
[71] FENG Z, MIN L, CHEN H, et al. Iron overload in the motor cortex induces neuronal ferroptosis following spinal cord injury. Redox Biol. 2021;43:101984.
[72] GUO Y, DU J, XIAO C, et al. Inhibition of ferroptosis-like cell death attenuates neuropathic pain reactions induced by peripheral nerve injury in rats. Eur J Pain. 2021;25(6):1227-1240.
[73] FAN BY, PANG YL, LI WX, et al. Liproxstatin-1 is an effective inhibitor of oligodendrocyte ferroptosis induced by inhibition of glutathione peroxidase 4. Neural Regen Res. 2021;16(3):561-566.
[74] CLEMENTE LP, RABENAU M, TANG S, et al. Dynasore Blocks Ferroptosis through Combined Modulation of Iron Uptake and Inhibition of Mitochondrial Respiration. Cells. 2020;9(10):2259.
|