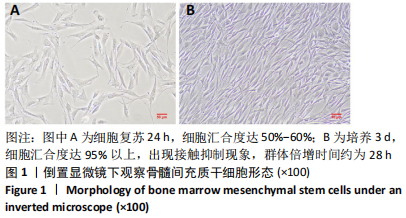
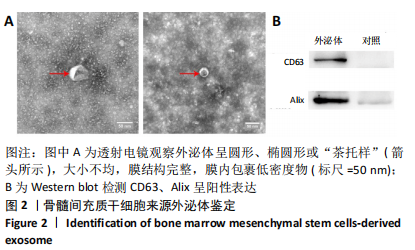
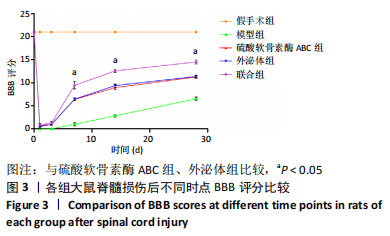
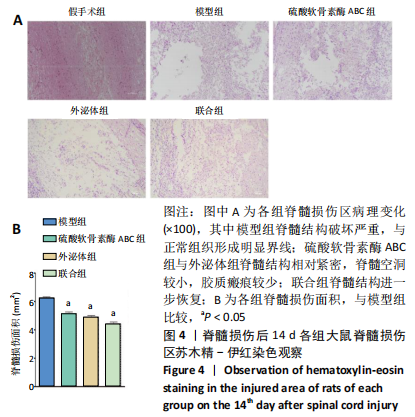
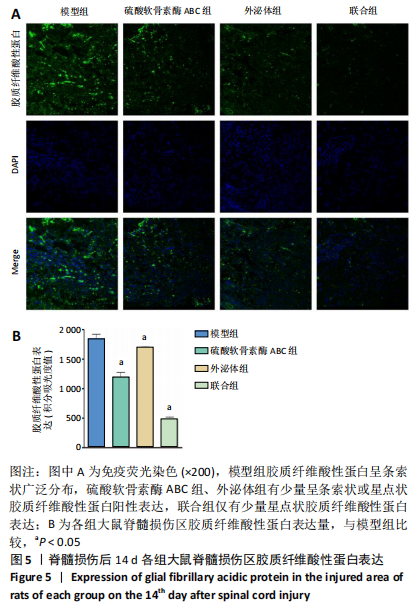
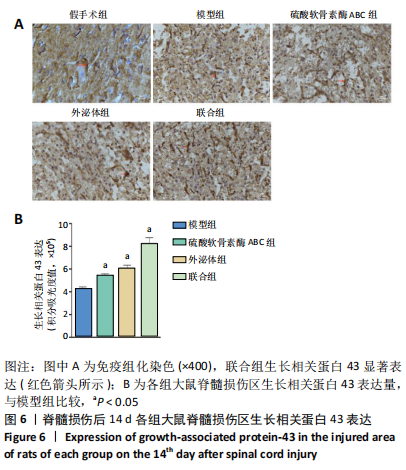
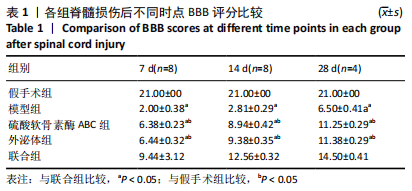
[1] ECKERT MJ, MARTIN MJ. Trauma: Spinal Cord Injury. Surg Clin North Am. 2017;97(5):1031-1045.
[2] 吴周睿,朱元贵,程黎明,等.SCI与修复的关键科学问题——第81期“双清论坛”综述[J].中国科学基金,2013,27(3):147-153.
[3] LEE H, MCKEON RJ, BELLAMKONDA RV. Sustained delivery of thermostabilized chABC enhances axonal sprouting and functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(8): 3340-3345.
[4] BRADBURY EJ, CARTER LM. Manipulating the glial scar: chondroitinase ABC as a therapy for spinal cord injury. Brain Res Bull. 2011;84(4-5):306-316.
[5] TESTER NJ, PLAAS AH, HOWLAND DR. Effect of body temperature on chondroitinase ABC’s ability to cleave chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycans. J Neurosci Res. 2007;85(5):1110-1118.
[6] MORTAZAVI MM, HARMON OA, ADEEB N, et al. Treatment of spinal cord injury: a review of engineering using neural and mesenchymal stem cells. Clin Anat. 2015;28(1):37-44.
[7] FILIPPI M, BOIDO M, PASQUINO C, et al. Successful in vivo MRI tracking of MSCs labeled with Gadoteridol in a Spinal Cord Injury experimental model. Exp Neurol. 2016;282:66-77.
[8] BOIDO M, RUPA R, GARBOSSA D, et al. Embryonic and adult stem cells promote raphespinal axon outgrowth and improve functional outcome following spinal hemisection in mice. Eur J Neurosci. 2009;30(5):833-846.
[9] ZACHAR L, BAČENKOVÁ D, ROSOCHA J. Activation, homing, and role of the mesenchymal stem cells in the inflammatory environment. J Inflamm Res. 2016;9:231-240.
[10] COFANO F, BOIDO M, MONTICELLI M, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Spinal Cord Injury: Current Options, Limitations, and Future of Cell Therapy. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(11):2698.
[11] CHEN X, LI Y, WANG L, et al. Ischemic rat brain extracts induce human marrow stromal cell growth factor production. Neuropathology. 2002; 22(4):275-279.
[12] THÉRY C, ZITVOGEL L, AMIGORENA S. Exosomes: composition, biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2002;2(8):569-579.
[13] 万然,史旭,刘京松,等.间充质干细胞分泌组治疗SCI的研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究,2021,25(7):1088-1095.
[14] REN Z, QI Y, SUN S, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes: Hope for Spinal Cord Injury Repair. Stem Cells Dev. 2020;29(23):1467-1478.
[15] ALLEN AR. Surgery of experimental lesion of spinal cord equivalent to crush injury of fracture dislocaion of spinal colum. JAMA. 1911;57(4): 878-880.
[16] 王琳,裴双,郭斌,等.骨髓间充质干细胞来源的外泌体用于大鼠SCI修复的初步探索[J].中国病理生理杂志,2018,34(5):862-869.
[17] GOLDSTEIN M, WATKINS S. Immunohistochemistry. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2008;Chapter 14:Unit 14.6.
[18] GAZDIC M, VOLAREVIC V, HARRELL CR, et al. Stem Cells Therapy for Spinal Cord Injury. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(4):1039.
[19] LIU AM, CHEN BL, YU LT, et al. Human adipose tissue- and umbilical cord-derived stem cells: which is a better alternative to treat spinal cord injury? Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(12):2306-2317.
[20] JIN MC, MEDRESS ZA, AZAD TD, et al. Stem cell therapies for acute spinal cord injury in humans: a review. Neurosurg Focus. 2019;46(3):E10.
[21] CSOBONYEIOVA M, POLAK S, ZAMBORSKY R, et al. Recent Progress in the Regeneration of Spinal Cord Injuries by Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3838.
[22] CURTIS E, MARTIN JR, GABEL B, et al. A First-in-Human, Phase I Study of Neural Stem Cell Transplantation for Chronic Spinal Cord Injury. Cell Stem Cell. 2018;22(6):941-950.e6.
[23] LIAU LL, LOOI QH, CHIA WC, et al. Treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Biosci. 2020;10:112.
[24] SHENDE P, SUBEDI M. Pathophysiology, mechanisms and applications of mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;91:693-706.
[25] ZURITA M, VAQUERO J. Functional recovery in chronic paraplegia after bone marrow stromal cells transplantation. Neuroreport. 2004; 15(7):1105-1108.
[26] PAUL C, SAMDANI AF, BETZ RR, et al. Grafting of human bone marrow stromal cells into spinal cord injury: a comparison of delivery methods. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(4):328-334.
[27] VAQUERO J, ZURITA M, OYA S, et al. Cell therapy using bone marrow stromal cells in chronic paraplegic rats: systemic or local administration? Neurosci Lett. 2006;398(1-2):129-134.
[28] HELDRING N, MÄGER I, WOOD MJ, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Extracellular Vesicles. Hum Gene Ther. 2015;26(8):506-517.
[29] BAGNO L, HATZISTERGOS KE, BALKAN W, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Based Therapy for Cardiovascular Disease: Progress and Challenges. Mol Ther. 2018;26(7):1610-1623.
[30] LOU G, CHEN Z, ZHENG M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes as a new therapeutic strategy for liver diseases. Exp Mol Med. 2017;49(6):e346.
[31] FORSBERG MH, KINK JA, HEMATTI P, et al. Mesenchymal stromal cells and exo: progress and challenges. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020;8:665.
[32] ZHANG Y, WANG WT, GONG CR, et al. Combination of olfactory ensheathing cells and human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes promotes sciatic nerve regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2020;15(10):1903-1911.
[33] LIEW LC, KATSUDA T, GAILHOUSTE L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles: a glimmer of hope in treating Alzheimer’s disease. Int Immunol. 2017;29(1):11-19.
[34] LIU W, WANG Y, GONG F, et al. Exosomes derived from bone mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by suppressing the activation of A1 neurotoxic reactive astrocytes. J Neurotrauma. 2019;36(3):469-484.
[35] ZHAO C, ZHOU X, QIU J, et al. Exosomes derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit complement activation in rats with spinal cord injury. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019;13:3693-3704.
[36] LANKFORD KL, ARROYO EJ, NAZIMEK K, et al. Intravenously delivered mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes target M2-type macrophages in the injured spinal cord. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0190358.
[37] LI C, JIAO G, WU W, et al. Exosomes from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells inhibit neuronal apoptosis and promote motor function recovery via the wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Transplant. 2019;28(11):1373-1383.
[38] PEKNY M, PEKNA M. Astrocyte intermediate filaments in CNS pathologies and regeneration. J Pathol. 2004;204(4):428-437.
[39] 熊薇,袁娅金,张桂仙,等.中枢神经系统损伤后胶质瘢痕形成的机制及其对神经修复的影响[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2020,42(10): 1876-1883.
[40] AZIZI M, FARAHMANDGHAVI F, JOGHATAEI MT, et al. ChABC-loaded PLGA nanoparticles: A comprehensive study on biocompatibility, functional recovery, and axonal regeneration in animal model of spinal cord injury. Int J Pharm. 2020;577:119037.
[41] XIA T, HUANG B, NI S, et al. The combination of db-cAMP and ChABC with poly(propylene carbonate) microfibers promote axonal regenerative sprouting and functional recovery after spinal cord hemisection injury. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;86:354-362.
[42] LIU X, WANG J, LI G, et al. Effect of combined chondroitinase ABC and hyperbaric oxygen therapy in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Mol Med Rep. 2018;18(1):25-30.
[43] FÜHRMANN T, ANANDAKUMARAN PN, PAYNE SL, et al. Combined delivery of chondroitinase ABC and human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuroepithelial cells promote tissue repair in an animal model of spinal cord injury. Biomed Mater. 2018;13(2):024103.
[44] JANZADEH A, SARVEAZAD A, YOUSEFIFARD M, et al. Combine effect of chondroitinase ABC and low level laser (660nm) on spinal cord injury model in adult male rats. Neuropeptides. 2017;65:90-99.
[45] SARVEAZAD A, BABAHAJIAN A, BAKHTIARI M, et al. The combined application of human adipose derived stem cells and chondroitinase ABC in treatment of a spinal cord injury model. Neuropeptides. 2017;61:39-47.
[46] NOVOTNA I, SLOVINSKA L, VANICKY I, et al. IT delivery of ChABC modulates NG2 and promotes GAP-43 axonal regrowth after spinal cord injury. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2011;31(8):1129-1139.
(责任编辑:MZH,ZN,JY)
|