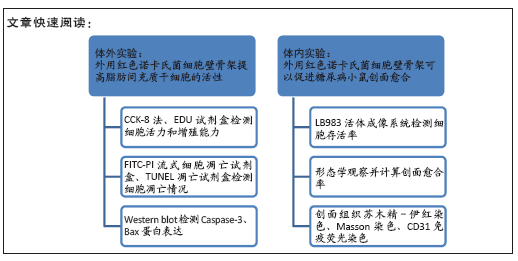
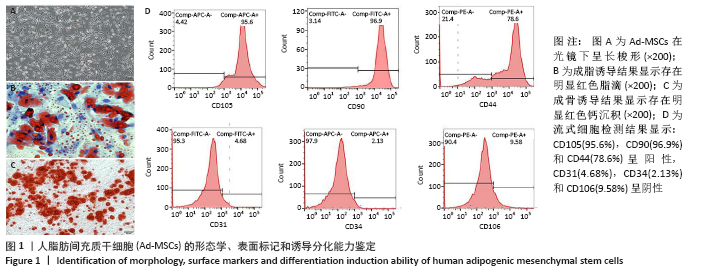
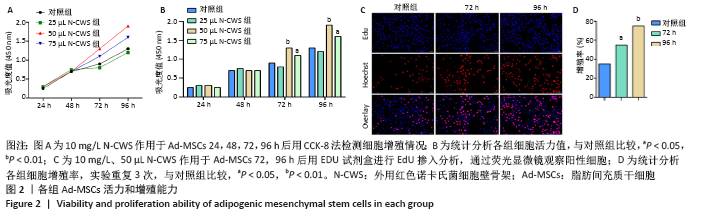
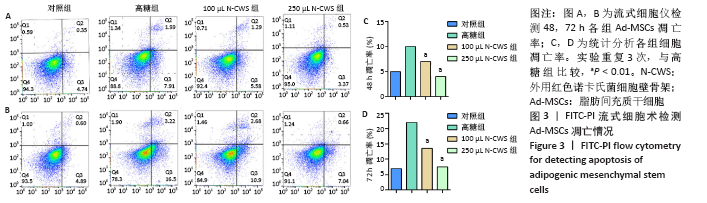
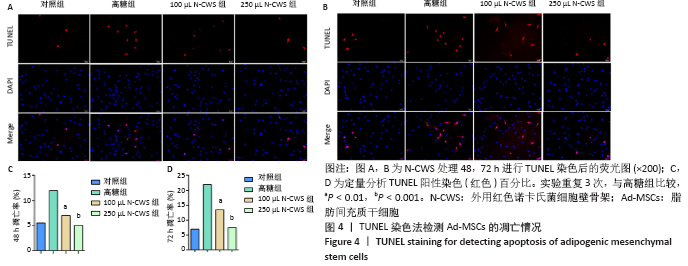
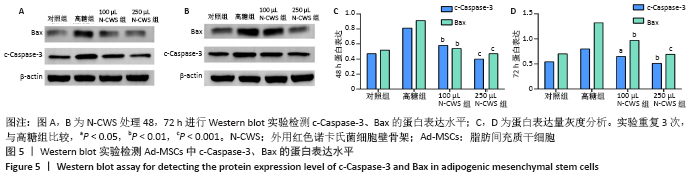
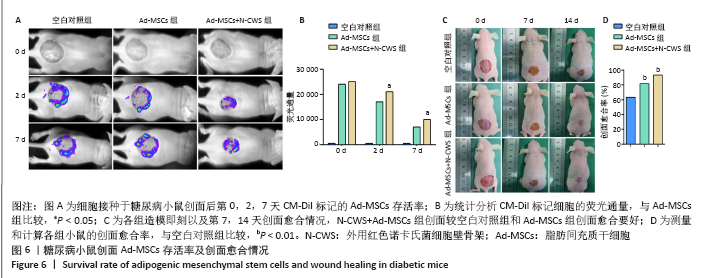
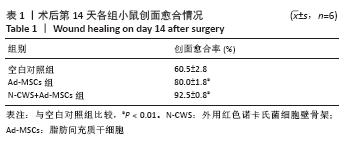
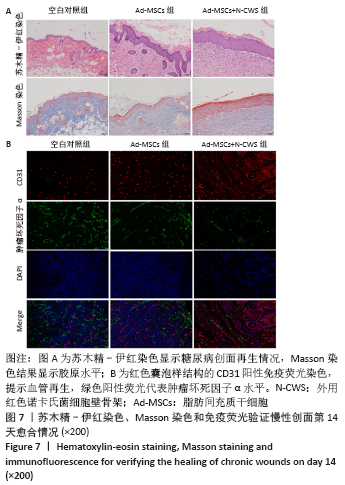
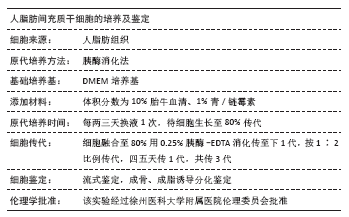
[1] 张宏亮,刘景焕,郑炜,等.脂肪干细胞局部注射治疗糖尿病慢性创面的临床疗效[J].临床与病理杂志,2019,39(9):1940-1945.
[2] 郑炜,刘景焕,马琳,等.自体脂肪源性干细胞联合无菌生物护创膜对慢性创面愈合的影响分析[J].饮食保健,2019,6(15):49-50.
[3] NUSCHKE A. Activity of mesenchymal stem cells in therapies for chronic skin wound healing. Organogenesis. 2014;10(1):29-37.
[4] DAS R, JAHR H, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. The role of hypoxia in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: considerations for regenerative medicine approaches. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2010;16(2):159-168.
[5] IZUMI S, OGAWA T, MIYAUCHI M, et al. Antitumor effect of Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton on syngeneically transplanted P388 tumors. Cancer Res. 1991;51(15):4038-4044.
[6] ZHAO J, ZHAN SB, LI XQ, et al. Effect of Nocardia rubra cell wall skeleton (Nr-CWS) on oncogenicity of TC-1 cells and anti-human papillomavirus effect of Nr-CWS in lower genital tract of women. Zhonghua Shi Yan He Lin Chuang Bing Du Xue Za Zhi. 2007;21(4):340-342.
[7] 邹华,单锦露,李梦侠,等.438例肺癌恶性胸腔积液的诊治及预后因素分析[J].重庆医学,2015,44(27):3794-3797,3802.
[8] 于顺利,顾朝辉,罗彬杰,等.红色诺卡菌细胞壁骨架膀胱灌注预防非肌层浸润性膀胱癌术后复发的疗效和安全性[J].中华泌尿外科杂志,2019,40(7):521-525.
[9] 霍泳贤.宫颈局部外用红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架制剂治疗宫颈人乳头瘤病毒亚临床感染的疗效观察[J].现代诊断与治疗,2019,30(16): 2865-2866.
[10] 齐利,陈岩.红色诺卡氏菌细胞壁骨架胸腔内注射治疗恶性胸腔积液的临床效果[J].中国实用医刊,2019,46(20):104-106.
[11] RATHUR HM, BOULTON AJ. The diabetic foot. Clin Dermatol. 2007; 25(1):109-120.
[12] GUO WY, WANG GJ, WANG P, et al. Acceleration of diabetic wound healing by low-dose radiation is associated with peripheral mobilization of bone marrow stem cells. Radiat Res. 2010;174(4):467-479.
[13] FIORINA P, PIETRAMAGGIORI G, SCHERER SS, et al. The mobilization and effect of endogenous bone marrow progenitor cells in diabetic wound healing. Cell Transplant. 2010;19(11):1369-1381.
[14] 谢平,柳志原,董剑秋,等.宫颈上皮内瘤变组织中HPV检测及分型结果分析[J].现代诊断与治疗,2016,27(13):2381-2382.
[15] KAISANG L, SIYU W, LIJUN F, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells seeded in Pluronic F-127 hydrogel promotes diabetic wound healing. J Surg Res. 2017;217:63-74.
[16] GONG JH, DONG JY, XIE T, et al. The Influence of AGEs Environment on Proliferation, Apoptosis, Homeostasis, and Endothelial Cell Differentiation of Human Adipose Stem Cells. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 2017;16(2):94-103.
[17] KATO Y, IWATA T, WASHIO K, et al. Creation and Transplantation of an Adipose-derived Stem Cell (ASC) Sheet in a Diabetic Wound-healing Model. J Vis Exp. 2017;(126):54539.
[18] REHMAN J, TRAKTUEV D, LI J, et al. Secretion of angiogenic and antiapoptotic factors by human adipose stromal cells. Circulation. 2004;109(10):1292-1298.
[19] EBRAHIMIAN TG, POUZOULET F, SQUIBAN C, et al. Cell therapy based on adipose tissue-derived stromal cells promotes physiological and pathological wound healing. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2009; 29(4):503-510.
[20] KIM WS, PARK BS, SUNG JH, et al. Wound healing effect of adipose-derived stem cells: a critical role of secretory factors on human dermal fibroblasts. J Dermatol Sci. 2007;48(1):15-24.
[21] SIVAN U, JAYAKUMAR K, KRISHNAN LK. Constitution of fibrin-based niche for in vitro differentiation of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to keratinocytes. Biores Open Access. 2014;3(6):339-347.
[22] LI Q, XIA S, YIN Y, et al. miR-5591-5p regulates the effect of ADSCs in repairing diabetic wound via targeting AGEs/AGER/JNK signaling axis. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(5):566.
[23] LI Q, GUO Y, CHEN F, et al. Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes human adipose tissue-derived stem cell survival and chronic wound healing. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(1):45-50. |