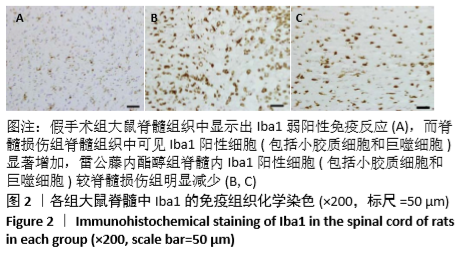
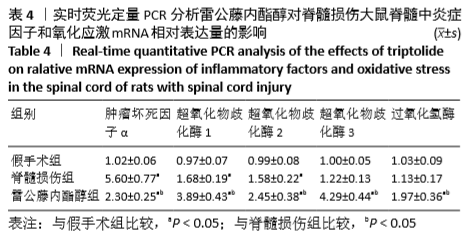
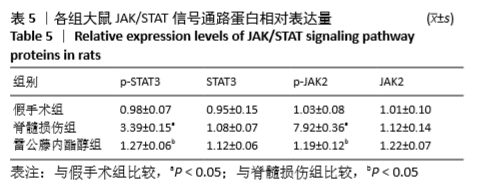
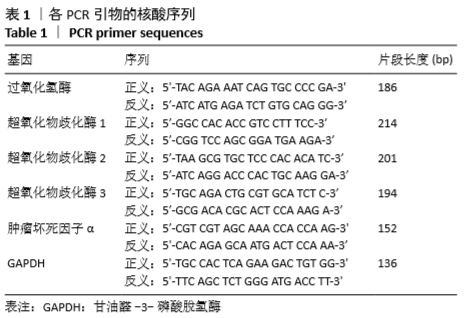
[1] HUBER E, DAVID G, THOMPSON AJ, et al. Dorsal and ventral horn atrophy is associated with clinical outcome after spinal cord injury. Neurology. 2018;90(17):1510-1522.
[2] 杜俊龙,陈显兵,王凤杰,等.延龄草苷对脊髓损伤大鼠核因子E2相关因子2/抗氧化反应元件信号通路的影响[J].中国康复理论与实践,2019,11(10):1140-1145.
[3] 黄腾立,郑宪友.脊髓损伤后自我修复的细胞与分子机制[J].国际骨科学杂志,2019,40(6):348-352.
[4] FATIMA G, SHARMA VP, DAS SK, et al. Oxidative stress and antioxidative parameters in patients with spinal cord injury: Implications in the pathogenesis of disease. Spinal Cord. 2015;53(1):3-6.
[5] LIN Y, CHEN Z, TANG J, et al. Acrolein Contributes to the Neuropathic Pain and Neuron Damage after Ischemic–Reperfusion Spinal Cord Injury. Neuroscience. 2018;384(1):120-130.
[6] 羊丽丽,王晓燕,郑丽云,等.FOXO3a-Bim信号通路在雷公藤内酯醇诱导膀胱癌T24细胞凋亡中的作用[J].中华医学杂志,2017, 97(15):1187-1190.
[7] 丁帅,高延征,张广泉,等.Six1基因siRNA联合雷公藤内酯醇对骨肉瘤细胞增殖、凋亡、侵袭的影响及机制[J].中国地方病防治杂志, 2018,33(3):262-275.
[8] 刘扬,卢斌,赵红卫.半乳糖凝集素-1联合雷公藤内酯醇对急性脊髓损伤的保护作用及机制[J].山东医药, 2017, 57(45):44-47.
[9] 王亮,钟武,陈睦虎.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对急性脊髓损伤的保护作用及其机制[J].免疫学杂志,2018, 34(7): 568-574.
[10] WANG B, CHEN C, ZHANG JT, et al. Retraction Note to: Triptolide (TPL) improves locomotor function recovery in rats and reduces inflammation after spinal cord injury. Neurol Sci. 2017;38(4):707-717.
[11] 曾欢欢,黄英如,李子健,等.大黄素对大鼠急性脊髓损伤后氧化应激和炎症反应的影响研究[J].中国中药杂志,2018,43(9): 1886-1893.
[12] JENS M, MARIA RJ, KATHARINA M, et al. Quantitative Tissue Factor Gene Expression Analysis in Whole Blood: Development and Evaluation of a Real-Time PCR Platform. Clin Chem. 2004;50(1):245-247.
[13] 杨晓燕,张平安,牛志立,等.慢性乙型肝炎患者外周血单个核细胞中STING基因表达与HBV DNA载量的关系[J].中国感染控制杂志,2018,17(3):196-201.
[14] 杨晓慧,张钦,庾红林,等.过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体γ激动剂对脊髓损伤后大鼠自噬相关蛋白表达的抑制作用[J].中华危重症医学杂志(电子版),2019,12(4):223-228.
[15] VAIKUNTAM BP, MIDDLETON JW, MCELDUFF P, et al. Identifying predictors of higher acute care costs for patients with traumatic spinal cord injury and modeling acute care pathway redesign: a record linkage study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2019;44(16):e974-e983.
[16] TIBBETT JA , EDELLE C. THOMAS CK, et al. Spasticity and pain after spinal cord injury: Impact on daily life and the influence of psychological factors. PM R. 2020;12(2):119-129.
[17] 卢斌,魏世坤,赵红卫,等.雷公藤内酯醇治疗急性脊髓损伤的保护作用及机制研究[J]. 海南医学,2018,29(2):152-155.
[18] GOMES ED, SILVA NA, SALGADO AJ. Combinatorial therapies for spinal cord injury: strategies to induce regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(1):69-71.
[19] ZHENG Y, ZHANG WJ, WANG XM. Triptolide with potential medicinal value for diseases of the central nervous system. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2013;19(2):76-82.
[20] 王力文,王齐敏,吴喆,等.雷公藤内酯醇通过抑制一氧化氮合成酶2表达减缓大鼠移植物血管病的作用[J].中华器官移植杂志, 2017,38(12):741-743.
[21] LI XG, DU JH, LU Y, et al. Neuroprotective effects of rapamycin on spinal cord injury in rats by increasing autophagy and Akt signaling. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(4):721-727.
[22] HUANG Y, ZHU N, CHEN T, et al. Triptolide Suppressed the Microglia Activation to Improve Spinal Cord Injury Through miR-96/IKKβ/NF-κB Pathway. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2019;44(12):707-714.
[23] JIAO J, BING X, LEI Z, et al. Triptolide inhibits amyloid-β1-42-induced TNF-α and IL-1β production in cultured rat microglia. J Neuroimmunol. 2008;205(1-2):32-36.
[24] 彭桉平,黄宪章,刘瑞萍,等.雷公藤内酯醇调控miR-155抑制类风湿性关节炎患者单核细胞促炎反应[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2014,30(6):635-638.
[25] 张海峰,张彬,周国雄,等.雷公藤内酯醇抑制TNF-α表达对小鼠溃疡性结肠炎的影响[J]. 中国现代医学杂志,2018,28(20):12-19.
[26] CHEN M, LV Z, JIANG S. The effects of triptolide on airway remodelling and transforming growth factor-β1/Smad signalling pathway in ovalbumin-sensitized mice. Immunology. 2011;132(3):376-384.
[27] 杨永祥,叶玉勤,苏鑫洪,等.创伤性脑损伤后大鼠海马区神经干细胞增殖及其与Janus激酶2/信号传导与转录激活因子3信号通路活性的关系[J].中华创伤杂志,2019,35(5):416-422.
[28] YONG Y, DONG Q, MA C, et al. Efficacy of Zhonglun’a-decoction-containing serum on fibroblastlike synoviocyte apoptosis in rats with collagen-induced arthritis via inhibiting Janus kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription signaling pathway. J Tradit Chin Med. 2019;39(2):181-190.
[29] ZHAO H, FENG Y, WEI C, et al. Colivelin Rescues Ischemic Neuron and Axons Involving JAK/STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Neuroscience. 2019;416:198-206.
[30] CHEN S, DONG Z, ZHAO Y, et al. Homocysteine induces mitochondrial dysfunction involving the crosstalk between oxidative stress and mitochondrial pSTAT3 in rat ischemic brain. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):6932.
[31] ZHOU L, OUYANG L, LIN S, et al. Protective role of β-carotene against oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in a rat model of spinal cord injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2018;61:92-99.
[32] SHANG AJ, YANG Y, WANG HY, et al. Spinal cord injury effectively ameliorated by neuroprotective effects of rosmarinic acid. Nutr Neurosci. 2017;20(3):172-179.
[33] WANG Y, LI W, WANG M, et al. Quercetin reduces neural tissue damage and promotes astrocyte activation after spinal cord injury in rats. J Cell Biochem. 2017;119(2):2298-2306. |