[1] SOARES ROS, LOSADA DM, JORDANI MC, et al. Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Revisited: An Overview of the Latest Pharmacological Strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(20):5034.
[2] CHOUCHANI ET, PELL VR, JAMES AM, et al. A Unifying Mechanism for Mitochondrial Superoxide Production during Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Cell Metab. 2016;23(2):254-263.
[3] MARIN W, MARIN D, AO X, et al. Mitochondria as a therapeutic target for cardiac ischemia‑reperfusion injury (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2021; 47(2):485-499.
[4] SUN MS, JIN H, SUN X, et al. Free Radical Damage in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury: An Obstacle in Acute Ischemic Stroke after Revascularization Therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2018;2018:3804979.
[5] GONZÁLEZ-MONTERO J, BRITO R, GAJARDO AI, et al. Myocardial reperfusion injury and oxidative stress: Therapeutic opportunities. World J Cardiol. 2018;10(9):74-86.
[6] ELTZSCHIG HK, ECKLE T. Ischemia and reperfusion--from mechanism to translation. Nat Med. 2011;17(11):1391-1401.
[7] BERNARDI P, RASOLA A, FORTE M, et al. The Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore: Channel Formation by F-ATP Synthase, Integration in Signal Transduction, and Role in Pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2015; 95(4):1111-1155.
[8] DARE AJ, LOGAN A, PRIME TA, et al. The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant MitoQ decreases ischemia-reperfusion injury in a murine syngeneic heart transplant model. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2015; 34(11):1471-1480.
[9] BASILI S, TANZILLI G, MANGIERI E, et al. Intravenous ascorbic acid infusion improves myocardial perfusion grade during elective percutaneous coronary intervention: relationship with oxidative stress markers. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2010;3(2):221-229.
[10] PANISELLO-ROSELLÓ A, LOPEZ A, FOLCH-PUY E, et al. Role of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in ischemia reperfusion injury: An update. World J Gastroenterol. 2018;24(27):2984-2994.
[11] SOLIMAN S, ISHRAT T, FOUDA AY, et al. Sequential Therapy with Minocycline and Candesartan Improves Long-Term Recovery After Experimental Stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 2015;6(4):309-322.
[12] YU L, GONG B, DUAN W, et al. Melatonin ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 1 diabetic rats by preserving mitochondrial function: role of AMPK-PGC-1α-SIRT3 signaling. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41337.
[13] CHEN C, LU W, WU G, et al. Cardioprotective effects of combined therapy with diltiazem and superoxide dismutase on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Life Sci. 2017;183:50-59.
[14] Kalimeris K, Briassoulis P, Ntzouvani A, et al. N-acetylcysteine ameliorates liver injury in a rat model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion. J Surg Res. 2016;206(2):263-272.
[15] TSUJITA K, SHIMOMURA H, KAIKITA K, et al. Long-term efficacy of edaravone in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ J. 2006; 70(7):832-837.
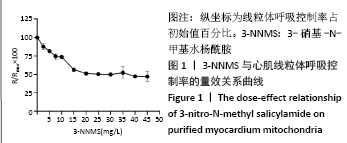
[16] 徐建兴,钟永利,肖燕,等. 3-硝基-N-甲基水杨酰胺对琥珀酸-细胞色素C还原酶的抑制作用[J]. 生物化学杂志,1987,3(2):139-145.
[17] 沈明,徐建兴,陈清棠. 3-硝基-N-甲基-水杨酰胺对大鼠局灶脑缺血再灌注损伤的保护作用[J]. 中风与神经疾病,2002,19(1):17-19.
[18] WÖLKART G, SCHRAMMEL A, KOYANI CN, et al. Cardioprotective effects of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural mediated by inhibition of L-type Ca2+ currents. Br J Pharmacol. 2017;174(20):3640-3653.
[19] KWAN JC, GAO L, MACDONALD PS, et al. Cardio-protective signalling by glyceryl trinitrate and cariporide in a model of donor heart preservation. Heart Lung Circ. 2015;24(3):306-318.
[20] CHAMBERS DC, YUSEN RD, CHERIKH WS, et al. The Registry of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation: Thirty-fourth Adult Lung And Heart-Lung Transplantation Report-2017;Focus Theme: Allograft ischemic time. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2017;36(10): 1047-1059.
[21] CADENAS S. ROS and redox signaling in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection. Free Radic Biol Med. 2018; 117:76-89.
[22] VENKAT P, SHEN Y, CHOPP M, et al. Cell-based and pharmacological neurorestorative therapies for ischemic stroke. Neuropharmacology. 2018;134(Pt B):310-322.
[23] ZHOU H, MA Q, ZHU P, et al. Protective role of melatonin in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury: From pathogenesis to targeted therapy. J Pineal Res. 2018;64(3):10.1111/jpi.12471.
[24] ZHOU H, ZHANG Y, HU S, et al. Melatonin protects cardiac microvasculature against ischemia/reperfusion injury via suppression of mitochondrial fission-VDAC1-HK2mPTP-mitophagy axis. J Pineal Res. 2017;63(1): e12413.
[25] KALIMERIS K, BRIASSOULIS P, NTZOUVANI A, et al. N-acetylcysteine ameliorates liver injury in a rat model of intestinal ischemia reperfusion. J Surg Res. 2016;206(2):263-272.
[26] VALLS-LACALLE L, BARBA I, MIRÓ-CASAS E, et al. Succinate dehydrogenase inhibition with malonate during reperfusion reduces infarct size by preventing mitochondrial permeability transition. Cardiovasc Res. 2016;109(3):374-384.
[27] GUO L, SHESTOV AA, WORTH AJ, et al. Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex II by the Anticancer Agent Lonidamine. J Biol Chem. 2016; 291(1):42-57.
[28] VANDEN HOEK TL, BECKER LB, SHAO Z, et al. Reactive oxygen species released from mitochondria during brief hypoxia induce preconditioning in cardiomyocytes. J Biol Chem. 1998;273(29): 18092-18098.
[29] SUZUKI C, HATAYAMA N, OGAWA T, et al. Cardioprotection via metabolism for rat heart preservation using the high-pressure gaseous mixture of carbon monoxide and oxygen. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(22):8858.
[30] ELGEBALY SA, POSTON R, TODD R, et al. Cyclocreatine protects against ischemic injury and enhances cardiac recovery during early reperfusion. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. 2019;17(9):683-697.
[31] YANG C, XU H, CAI L, et al. Donor pretreatment with adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase activator protects cardiac grafts from cold ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2016;49(5):1354-1360.
[32] WU MY, YIANG GT, LIAO WT, et al. Current mechanistic concepts in ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;46(4):1650-1667.
[33] ZOROVA LD, POPKOV VA, PLOTNIKOV EY, et al. Mitochondrial membrane potential. Anal Biochem. 2018; 552:50-59.
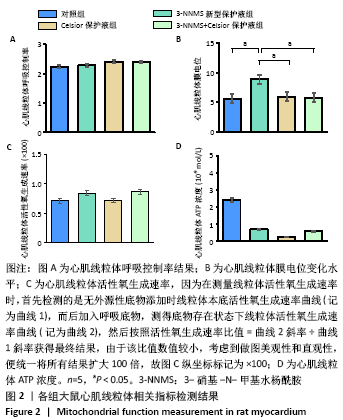
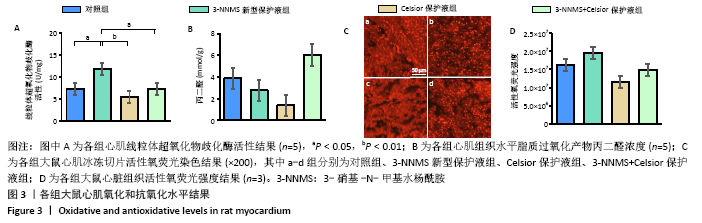
[34] ZHOU HY, ZHANG LN, ZHENG MZ, et al. Improved myocardial function with supplement of levosimendan to Celsior solution. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;64(3):256-265. |