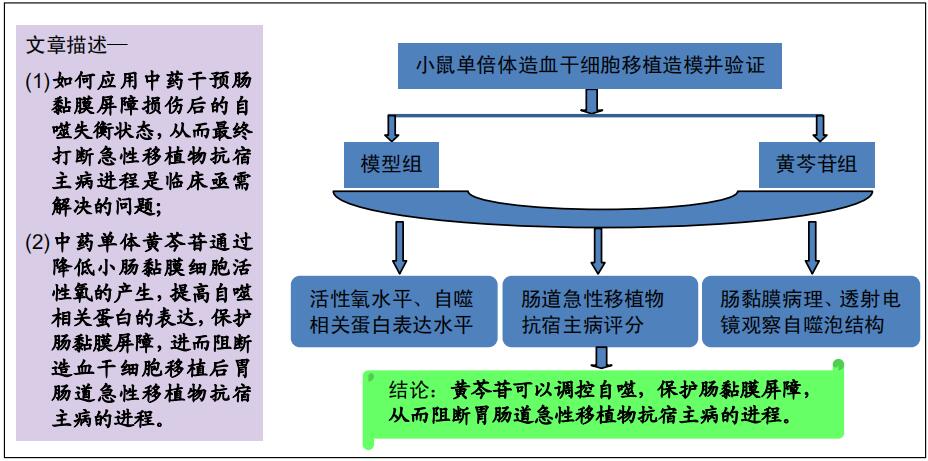
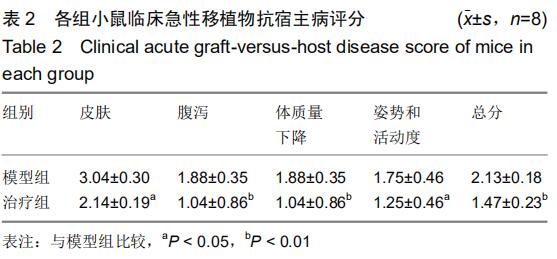
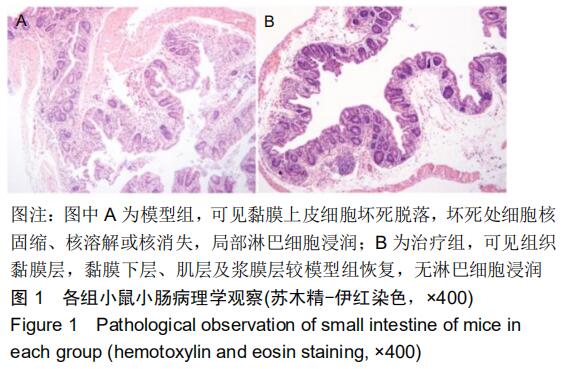
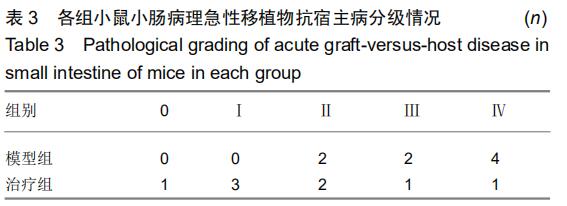
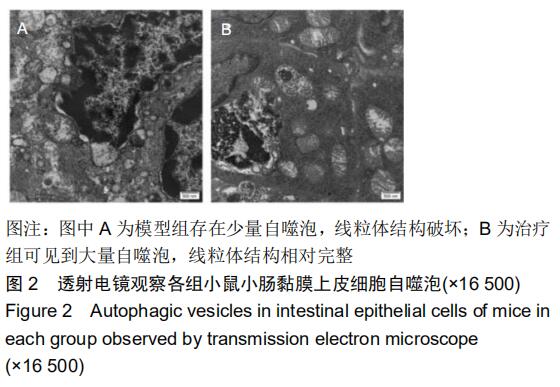
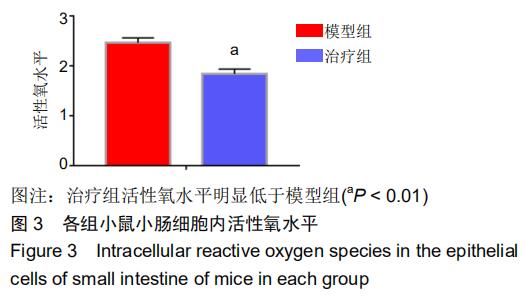
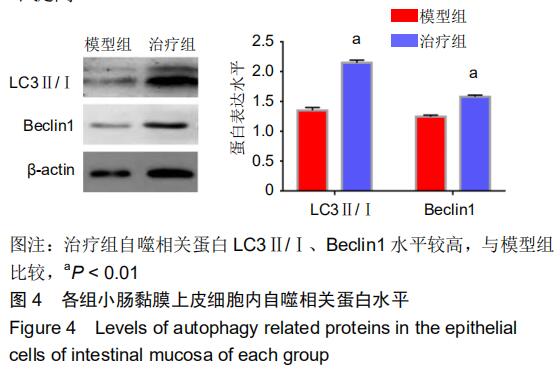
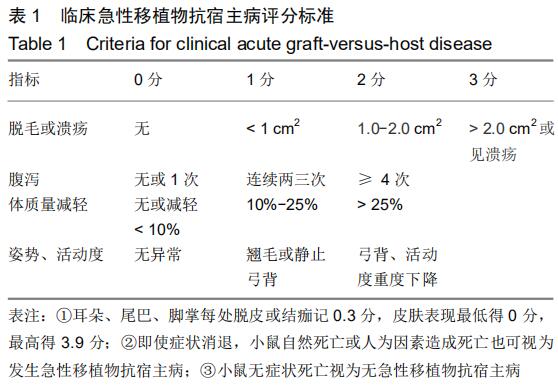
|
[1] 黄晓军,吴德沛,刘代红,等.实用造血干细胞移植[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2014:246-247.
[2] ASLAN M, NAZLIGUL Y, BOLUKBAS C, et al. Peripheral lymphocyte DNA damage and oxidative stress in patients with ulcerative colitis. Pol Arch Med Wewn. 2011;121(7-8):223-229.
[3] PARADIES G, PETROSILLO G, PARADIES V, et al. Role of cardiolipin peroxidation and Ca2+ in mitochondrial dysfunction and disease. Cell Calcium. 2009;45(6):643-650.
[4] 龚晴丽,李雪,鲁严.氧化应激相关性疾病中线粒体机制的研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2013,35(10):1540-1545.
[5] 邹颖,戴世学,迟宏罡,等.Th17/Treg平衡在湿热型结肠炎大鼠中的变化及黄芩汤的调节作用[J].中药药理与临床,2012,28(2):2-5.
[6] CHOU TC, CHANG LP, LI CY, et al. The antiinflammatory and analgesic effects of baicalin in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. Anesth Analg. 2003;97(6):1724-1729.
[7] 陈慧瑶,张伟,方芳,等.肠三叶因子通过自噬在急性移植物抗宿主病中发挥保护作用[J].温州医科大学学报,2017,47(7):480-484.
[8] 杨志刚,曾耀英,王青,等.小鼠异基因骨髓移植急性移植物抗宿主病模型的建立[J].中国病理生理杂志,2004, 20(10):1947-1949.
[9] EVANS GS, FLINT N, SOMERS AS, et al. The development of a method for the preparation of rat intestinal epithelial cell primary cultures. J Cell Sci. 1992;101 ( Pt 1):219-231.
[10] GHIMIRE S, WEBER D, MAVIN E, et al. Pathophysiology of GvHD and Other HSCT-Related Major Complications. Front Immunol. 2017;8:79.
[11] HAYASE E, TESHIMA T. Disruption of gut immune system caused by damage of intestinal stem cells and their niche in graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Clin Calcium. 2017;27(6):829-833.
[12] KONYA V, MJÖSBERG J. Innate lymphoid cells in graft-versus- host disease. Am J Transplant. 2015;15(11):2795-2801.
[13] TOUBAI T, ROSSI C, ORAVECZ-WILSON K, et al. IAPs protect host target tissues from graft-versus-host disease in mice. Blood Adv. 2017;1(19):1517-1532.
[14] LE TEXIER L, LINEBURG KE, MACDONALD KP. Harnessing bone marrow resident regulatory T cells to improve allogeneic stem cell transplant outcomes. Int J Hematol. 2017;105(2): 153-161.
[15] LE TEXIER L, LINEBURG KE, CAO B, et al. Autophagy- dependent regulatory T cells are critical for the control of graft-versus-host disease. JCI Insight. 2016;1(15):e86850.
[16] HUBBARD-LUCEY VM, SHONO Y, MAURER K, et al. Autophagy gene Atg16L1 prevents lethal T cell alloreactivity mediated by dendritic cells. Immunity. 2014;41(4):579-591.
[17] LU Y, GAO J, ZHANG S, et al. miR-142-3p regulates autophagy by targeting ATG16L1 in thymic-derived regulatory T cell (tTreg). Cell Death Dis. 2018;9(3):290.
[18] NGUYEN H, KURIL S, BASTIAN D, et al. Complement C3a and C5a receptors promote GVHD by suppressing mitophagy in recipient dendritic cells. JCI Insight. 2018;3(24):121697.
[19] ZHANG F, DENG Z, LI W, et al. Activation of autophagy in rats with plateau stress-induced intestinal failure. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015;8(2):1816-1821.
[20] WEN Z, LIU W, LI X, et al. A Protective Role of the NRF2-Keap1 Pathway in Maintaining Intestinal Barrier Function. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019;2019:1759149.
[21] LAM W, BUSSOM S, GUAN F, et al. The four-herb Chinese medicine PHY906 reduces chemotherapy-induced gastrointestinal toxicity. Sci Transl Med. 2010;2(45):45ra59.
[22] ENG C. Are herbal medicines ripe for the cancer clinic? Sci Transl Med. 2010;2(45):45ps41.
[23] 王声勇,朱燕莉,张海.黄芩汤颗粒剂对克罗恩病的免疫调节作用研究以及临床疗效分析[J].中国中西医结合消化杂志, 2016,24(4): 314-316.
[24] JUNG SH, KANG KD, JI D, et al. The flavonoid baicalin counteracts ischemic and oxidative insults to retinal cells and lipid peroxidation to brain membranes. Neurochem Int. 2008;53(6-8): 325-337.
[25] 朱磊,沈洪,顾培青,等.黄芩苷对溃疡性结肠炎模型大鼠炎性反应、凋亡的影响及与PI3K/AKT通路的关系[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,32(9): 4001-4004.
[26] 于丰彦,黄绍刚,张海燕,等.黄芩苷对溃疡性结肠炎患者信号转导和转录激活因子表达的影响[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2015,35(4):419-424.
[27] 朱磊,沈洪,顾培青,等.黄芩苷对溃疡性结肠炎模型大鼠NF-κB表达的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报,2016,32(5):447-450.
[28] 邹颖,迟宏罡,欧阳霖芮,等.黄芩苷对实验性结肠炎小鼠TLRs/MyD88通路的作用研究[J].天然产物研究与开发,2014,26(6):952-956.
[29] 洪湘隆,陈岳峰,马萍璇.黄芩苷对大鼠脑缺血损伤自噬的发生及Beclin-1因子表达的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2016,22(14): 1473-1475.
|